|
Lituya Glacier
Lituya Glacier is a tidewater glacier in the U.S. state of Alaska. Located at inside Glacier Bay National Park and Preserve, its source is in the Fairweather Range and it feeds into Lituya Bay on the gulf coast of Southeast Alaska. It is partially responsible for creating the 1958 Lituya Bay megatsunami. The glacier, which has receded over the years, carved Lituya Bay into a unique topographic phenomenon with steep walls, a very deep submerged bottom, and a very narrow entrance to the ocean which created the opportunity for a megatsunami to occur. The glacier is also the namesake of the Alaska Marine Highway ferry M/V ''Lituya''. See also * List of glaciers A glacier ( ) or () is a persistent body of dense ice that is constantly moving under its own weight; it forms where the accumulation of snow exceeds its ablation (melting and sublimation) over many years, often centuries. Glaciers slowly deform ... External links * * World's Biggest Tsunami: The largest recorded tsunami ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
United States
The United States of America (U.S.A. or USA), commonly known as the United States (U.S. or US) or America, is a country primarily located in North America. It consists of 50 states, a federal district, five major unincorporated territories, nine Minor Outlying Islands, and 326 Indian reservations. The United States is also in free association with three Pacific Island sovereign states: the Federated States of Micronesia, the Marshall Islands, and the Republic of Palau. It is the world's third-largest country by both land and total area. It shares land borders with Canada to its north and with Mexico to its south and has maritime borders with the Bahamas, Cuba, Russia, and other nations. With a population of over 333 million, it is the most populous country in the Americas and the third most populous in the world. The national capital of the United States is Washington, D.C. and its most populous city and principal financial center is New York City. Paleo-Americ ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
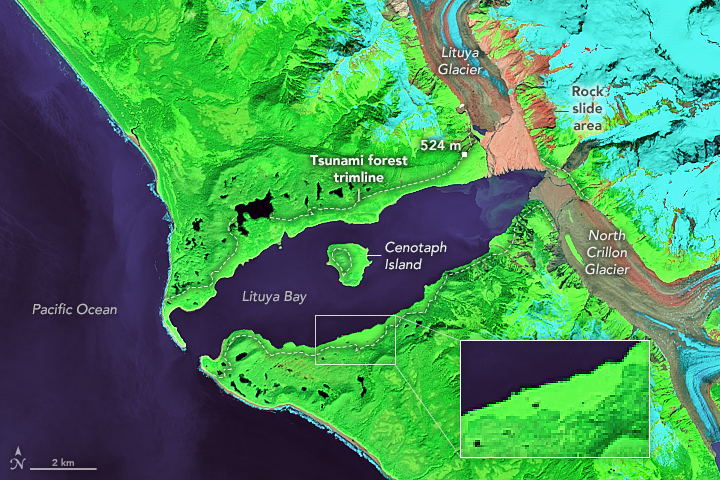
Lituya Bay
Lituya Bay (; Tlingit: ''Ltu.aa'',. Spelled L'tua in translation of Tebenkov's log. meaning 'lake within the point') is a fjord located on the coast of the south-east part of the U.S. state of Alaska. It is long and wide at its widest point. The bay was noted in 1786 by Jean-François de Lapérouse, who named it Port des Français. Twenty-one of his men perished in the tidal current in the bay. Description The smaller Cascade and Crillon glaciers and the larger Lituya Glacier all spill into Lituya Bay, which is a part of Glacier Bay National Park and Preserve. Cenotaph Island is located roughly in the middle of the bay. The entrance of the bay is approximately wide, with a narrow navigable channel. The bay is known for its tremendous size tides, which have a range of approximately . Tidal currents in the entrance reach . The entrance is considered dangerous to navigation, especially when the tidal currents are running, but the interior of the bay provides good protection ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Glacier
A glacier (; ) is a persistent body of dense ice that is constantly moving under its own weight. A glacier forms where the accumulation of snow exceeds its Ablation#Glaciology, ablation over many years, often Century, centuries. It acquires distinguishing features, such as Crevasse, crevasses and Serac, seracs, as it slowly flows and deforms under stresses induced by its weight. As it moves, it abrades rock and debris from its substrate to create landforms such as cirques, moraines, or fjords. Although a glacier may flow into a body of water, it forms only on land and is distinct from the much thinner sea ice and lake ice that form on the surface of bodies of water. On Earth, 99% of glacial ice is contained within vast ice sheets (also known as "continental glaciers") in the polar regions, but glaciers may be found in mountain ranges on every continent other than the Australian mainland, including Oceania's high-latitude oceanic island countries such as New Zealand. Between lati ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Alaska
Alaska ( ; russian: Аляска, Alyaska; ale, Alax̂sxax̂; ; ems, Alas'kaaq; Yup'ik: ''Alaskaq''; tli, Anáaski) is a state located in the Western United States on the northwest extremity of North America. A semi-exclave of the U.S., it borders the Canadian province of British Columbia and the Yukon territory to the east; it also shares a maritime border with the Russian Federation's Chukotka Autonomous Okrug to the west, just across the Bering Strait. To the north are the Chukchi and Beaufort Seas of the Arctic Ocean, while the Pacific Ocean lies to the south and southwest. Alaska is by far the largest U.S. state by area, comprising more total area than the next three largest states (Texas, California, and Montana) combined. It represents the seventh-largest subnational division in the world. It is the third-least populous and the most sparsely populated state, but by far the continent's most populous territory located mostly north of the 60th parallel, with ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Glacier Bay National Park And Preserve
Glacier Bay National Park and Preserve is an American national park located in Southeast Alaska west of Juneau. President Calvin Coolidge proclaimed the area around Glacier Bay a national monument under the Antiquities Act on February 26, 1925. Chapter 8 Subsequent to an expansion of the monument by President Jimmy Carter in 1978, the Alaska National Interest Lands Conservation Act (ANILCA) enlarged the national monument by on December 2, 1980, and created Glacier Bay National Park and Preserve. Title 2, section 202(1). The national preserve encompasses of public land to the immediate northwest of the park, protecting a portion of the Alsek River with its fish and wildlife habitats, while allowing sport hunting. Glacier Bay became part of a binational UNESCO World Heritage Site in 1979, and was inscribed as a Biosphere Reserve in 1986. The National Park Service undertook an obligation to work with Hoonah and Yakutat Tlingit Native American organizations in the management of the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fairweather Range
The Fairweather Range is the unofficial name for a mountain range located in the U.S. state of Alaska and the Canadian province of British Columbia. It is the southernmost range of the Saint Elias Mountains. The northernmost section of the range is situated in Tatshenshini-Alsek Provincial Park while the southernmost section resides in Glacier Bay National Park, in the Hoonah-Angoon Census Area. In between it goes through the southeastern corner of Yakutat Borough. Peaks of this range include Mount Fairweather (the highest point in British Columbia) and Mount Quincy Adams . The range is home to the Fairweather Fault, an active geologic transform fault of the larger Queen Charlotte Fault along the boundary between the Pacific and North American plates. Mountains *Mount Crillon *Mount Fairweather *Mount La Perouse *Mount Orville * Mount Quincy Adams * Mount Wilbur Panorama See also *Alsek Ranges - mountain range to the east *Centennial Range The Centennial Range is a sub-rang ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gulf Of Alaska
The Gulf of Alaska (Tlingit: ''Yéil T'ooch’'') is an arm of the Pacific Ocean defined by the curve of the southern coast of Alaska, stretching from the Alaska Peninsula and Kodiak Island in the west to the Alexander Archipelago in the east, where Glacier Bay and the Inside Passage are found. The Gulf shoreline is a combination of forest, mountain and a number of tidewater glaciers. Alaska's largest glaciers, the Malaspina Glacier and Bering Glacier, spill out onto the coastal line along the Gulf of Alaska. The coast is heavily indented with Cook Inlet and Prince William Sound, the two largest connected bodies of water. It includes Yakutat Bay and Cross Sound. Lituya Bay (a fjord north of Cross Sound, and south of Mount Fairweather) is the site of the largest recorded tsunami in history. It serves as a sheltered anchorage for fishing boats. Ecology The Gulf of Alaska is considered a Class I, productive ecosystem with more than 300 grams of carbon per square meter per year ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Alaska Panhandle
Southeast Alaska, colloquially referred to as the Alaska(n) Panhandle, is the southeastern portion of the U.S. state of Alaska, bordered to the east and north by the northern half of the Canadian province of British Columbia (and a small part the Yukon Territories). The majority of Southeast Alaska's area is part of the Tongass National Forest, the United States' largest national forest. In many places, the international border runs along the crest of the Boundary Ranges of the Coast Mountains (see Alaska boundary dispute). The region is noted for its scenery and mild, rainy climate. The largest cities in the region are Juneau, Sitka, and Ketchikan. This region is also home to Hyder, the easternmost town in Alaska. Geography Southeast Alaska has a land area of , comprising much of the Alexander Archipelago. The largest islands are, from North to South, Chichagof Island, Admiralty Island, Baranof Island, Kupreanof Island, Revillagigedo Island and Prince of Wales Island. Maj ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
1958 Lituya Bay Megatsunami
The 1958 Lituya Bay earthquake occurred on PST with a moment magnitude of 7.8 to 8.3 and a maximum Mercalli intensity of XI (''Extreme''). The strike-slip earthquake took place on the Fairweather Fault and triggered a rockslide of 30 million cubic meters (40 million cubic yards) and about 90 million tons into the narrow inlet of Lituya Bay, Alaska. The impact was heard away, and the sudden displacement of water resulted in a megatsunami that washed out trees to a maximum elevation of at the entrance of Gilbert Inlet. This is the largest and most significant megatsunami in modern times; it forced a re-evaluation of large-wave events and the recognition of impact events, rockfalls, and landslides as causes of very large waves. Event outline Lituya Bay is a fjord located on the Fairweather Fault in the northeastern part of the Gulf of Alaska. It is a T-shaped bay with a width of and a length of . Lituya Bay is an ice-scoured tidal inlet with a maximum depth of . The narro ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Alaska Marine Highway
The Alaska Marine Highway (AMH) or the Alaska Marine Highway System (AMHS) is a ferry service operated by the U.S. state of Alaska. It has its headquarters in Ketchikan, Alaska. The Alaska Marine Highway System operates along the south-central coast of the state, the eastern Aleutian Islands and the Inside Passage of Alaska and British Columbia, Canada. Ferries serve communities in Southeast Alaska that have no road access, and the vessels can transport people, freight, and vehicles. AMHS's of routes go as far south as Bellingham, Washington, in the contiguous United States and as far west as Unalaska/Dutch Harbor, with a total of 32 terminals throughout Alaska, British Columbia, and Washington. It is part of the National Highway System and receives federal highway funding. It is also the only method of transportation of vehicles between the state and the contiguous United States, not requiring international customs and immigration. The Alaska Marine Highway System is a rare ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
M/V Lituya
MV ''Lituya'' is a shuttle ferry operated by the Alaska Marine Highway System. Her route connects Metlakatla on Annette Island to Ketchikan. Construction and characteristics The state of Alaska issued contracts for a ferry dock at Metlakatla in 1973. The town was originally served by Alaska Marine Highway System ferry M/V ''Chilkat''. The terminal was later modified for use by M/V ''LeConte'' and M/V ''Aurora'' instead. During the summer there were several stops a week, but in the winter, the town had one ferry visit per week. Metlakatla residents argued for daily service, so that people could commute to work in Ketchikan. The state of Alaska issued a request for proposals for the design of a Metlakatla ferry on May 30, 2000. The Alaska Legislature appropriated $3 million for a new ferry and $880,000 for a new ferry terminal for it to dock at as part of the state's 2001 budget. ''Lituya'' was designed by Coastwise Engineering of Juneau, Alaska in 2001. She was built ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |