|
List Of Variational Topics
{{Short description, none This is a list of variational topics in from mathematics and physics. See calculus of variations for a general introduction. * Action (physics) * Averaged Lagrangian * Brachistochrone curve * Calculus of variations * Catenoid * Cycloid * Dirichlet principle * Euler–Lagrange equation cf. Action (physics) * Fermat's principle * Functional (mathematics) * Functional derivative * Functional integral * Geodesic * Isoperimetry * Lagrangian (field theory), Lagrangian * Lagrangian mechanics * Legendre transformation * Luke's variational principle * Minimal surface * Morse theory * Noether's theorem * Path integral formulation * Plateau's problem * Prime geodesic * Principle of least action * Soap bubble * Soap film * Tautochrone curve Mathematics-related lists, Variations Calculus of variations, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mathematics
Mathematics is an area of knowledge that includes the topics of numbers, formulas and related structures, shapes and the spaces in which they are contained, and quantities and their changes. These topics are represented in modern mathematics with the major subdisciplines of number theory, algebra, geometry, and analysis, respectively. There is no general consensus among mathematicians about a common definition for their academic discipline. Most mathematical activity involves the discovery of properties of abstract objects and the use of pure reason to prove them. These objects consist of either abstractions from nature orin modern mathematicsentities that are stipulated to have certain properties, called axioms. A ''proof'' consists of a succession of applications of deductive rules to already established results. These results include previously proved theorems, axioms, andin case of abstraction from naturesome basic properties that are considered true starting points of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lagrangian (field Theory)
Lagrangian may refer to: Mathematics * Lagrangian function, used to solve constrained minimization problems in optimization theory; see Lagrange multiplier ** Lagrangian relaxation, the method of approximating a difficult constrained problem with an easier problem having an enlarged feasible set ** Lagrangian dual problem, the problem of maximizing the value of the Lagrangian function, in terms of the Lagrange-multiplier variable; See Dual problem * Lagrangian, a functional whose extrema are to be determined in the calculus of variations * Lagrangian submanifold, a class of submanifolds in symplectic geometry * Lagrangian system, a pair consisting of a smooth fiber bundle and a Lagrangian density Physics * Lagrangian mechanics, a reformulation of classical mechanics * Lagrangian (field theory), a formalism in classical field theory * Lagrangian point, a position in an orbital configuration of two large bodies * Lagrangian coordinates, a way of describing the motions of particles o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
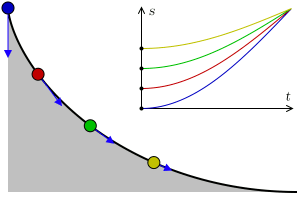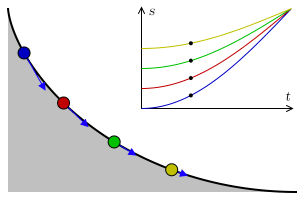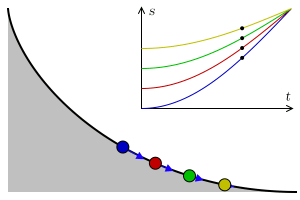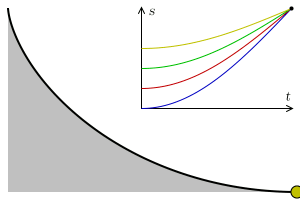
Tautochrone Curve
A tautochrone or isochrone curve (from Greek prefixes tauto- meaning ''same'' or iso- ''equal'', and chrono ''time'') is the curve for which the time taken by an object sliding without friction in uniform gravity to its lowest point is independent of its starting point on the curve. The curve is a cycloid, and the time is equal to π times the square root of the radius (of the circle which generates the cycloid) over the acceleration of gravity. The tautochrone curve is related to the brachistochrone curve, which is also a cycloid. The tautochrone problem The tautochrone problem, the attempt to identify this curve, was solved by Christiaan Huygens in 1659. He proved geometrically in his ''Horologium Oscillatorium'', originally published in 1673, that the curve is a cycloid. The cycloid is given by a point on a circle of radius r tracing a curve as the circle rolls along the x axis, as: \begin x &= r(\theta - \sin \theta) \\ y &= r(1 - \cos \theta), \end Huygens al ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Soap Film
Soap films are thin layers of liquid (usually water-based) surrounded by air. For example, if two soap bubbles come into contact, they merge and a thin film is created in between. Thus, foams are composed of a network of films connected by Plateau borders. Soap films can be used as model systems for minimal surfaces, which are widely used in mathematics. Stability Daily experience shows that soap bubble formation is not feasible with water or with any pure liquid. Actually, the presence of soap, which is composed at a molecular scale of surfactants, is necessary to stabilize the film. Most of the time, surfactants are amphiphilic, which means they are molecules with both a hydrophobic and a hydrophilic part. Thus, they are arranged preferentially at the air/water interface (see figure 1). Surfactants stabilize films because they create a repulsion between both surfaces of the film, preventing it from thinning and consequentially bursting. This can be shown quantitatively thr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
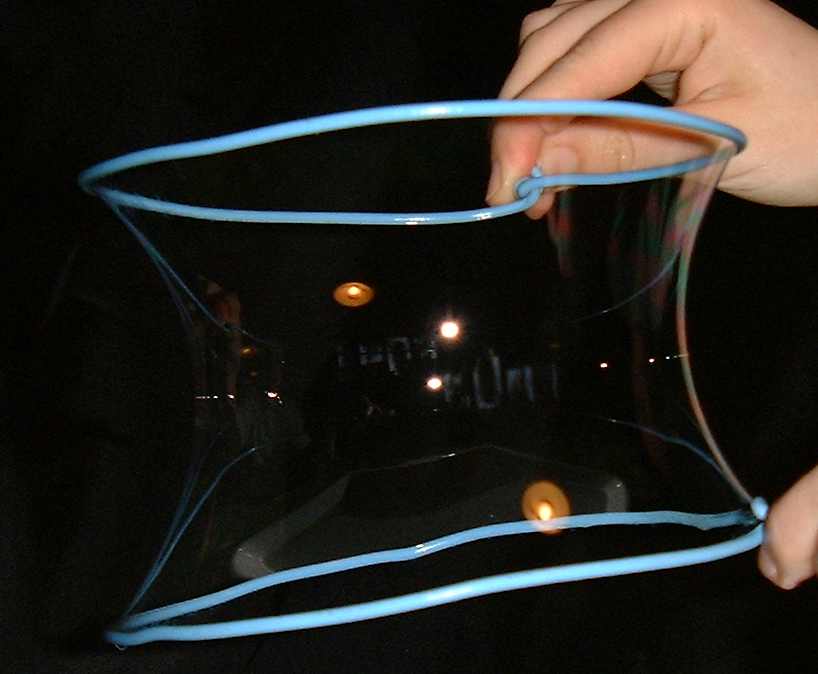
Soap Bubble
A soap bubble is an extremely thin film of soap or detergent and water enclosing air that forms a hollow sphere with an iridescent surface. Soap bubbles usually last for only a few seconds before bursting, either on their own or on contact with another object. They are often used for children's enjoyment, but they are also used in artistic performances. Assembling many bubbles results in foam. When light shines onto a bubble it appears to change colour. Unlike those seen in a rainbow, which arise from differential refraction, the colours seen in a soap bubble arise from light wave interference, reflecting off the front and back surfaces of the thin soap film. Depending on the thickness of the film, different colours interfere constructively and destructively. Mathematics Soap bubbles are physical examples of the complex mathematical problem of minimal surface. They will assume the shape of least surface area possible containing a given volume. A true minimal surface is more ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Principle Of Least Action
The stationary-action principle – also known as the principle of least action – is a variational principle that, when applied to the '' action'' of a mechanical system, yields the equations of motion for that system. The principle states that the trajectories (i.e. the solutions of the equations of motion) are ''stationary points'' of the system's ''action functional''. The term "least action" is a historical misnomer since the principle has no minimality requirement: the value of the action functional need not be minimal (even locally) on the trajectories. The principle can be used to derive Newtonian, Lagrangian and Hamiltonian equations of motion, and even general relativity (see Einstein–Hilbert action). In relativity, a different action must be minimized or maximized. The classical mechanics and electromagnetic expressions are a consequence of quantum mechanics. The stationary action method helped in the development of quantum mechanics. In 1933, the physicist Paul ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Prime Geodesic
In mathematics, a prime geodesic on a hyperbolic geometry, hyperbolic Surface (topology), surface is a primitive closed geodesic, i.e. a geodesic which is a curve, closed curve that traces out its image exactly once. Such geodesics are called prime geodesics because, among other things, they obey an asymptotic analysis, asymptotic distribution law similar to the prime number theorem. Technical background We briefly present some facts from hyperbolic geometry which are helpful in understanding prime geodesics. Hyperbolic isometries Consider the Poincaré half-plane model ''H'' of 2-dimensional hyperbolic geometry. Given a Fuchsian group, that is, a discrete subgroup Γ of projective linear group, PSL(2, R), Γ Group action (mathematics), acts on ''H'' via linear fractional transformation. Each element of PSL(2, R) in fact defines an isometry of ''H'', so Γ is a group of isometries of ''H''. There are then 3 types of transformation: hyperbolic, elliptic, and parabolic. (The loxodro ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Plateau's Problem
In mathematics, Plateau's problem is to show the existence of a minimal surface with a given boundary, a problem raised by Joseph-Louis Lagrange in 1760. However, it is named after Joseph Plateau who experimented with soap films. The problem is considered part of the calculus of variations. The existence and regularity problems are part of geometric measure theory. History Various specialized forms of the problem were solved, but it was only in 1930 that general solutions were found in the context of mappings (immersions) independently by Jesse Douglas and Tibor Radó. Their methods were quite different; Radó's work built on the previous work of René Garnier and held only for rectifiable simple closed curves, whereas Douglas used completely new ideas with his result holding for an arbitrary simple closed curve. Both relied on setting up minimization problems; Douglas minimized the now-named Douglas integral while Radó minimized the "energy". Douglas went on to be awarded ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Path Integral Formulation
The path integral formulation is a description in quantum mechanics that generalizes the action principle of classical mechanics. It replaces the classical notion of a single, unique classical trajectory for a system with a sum, or functional integral, over an infinity of quantum-mechanically possible trajectories to compute a quantum amplitude. This formulation has proven crucial to the subsequent development of theoretical physics, because manifest Lorentz covariance (time and space components of quantities enter equations in the same way) is easier to achieve than in the operator formalism of canonical quantization. Unlike previous methods, the path integral allows one to easily change coordinates between very different canonical descriptions of the same quantum system. Another advantage is that it is in practice easier to guess the correct form of the Lagrangian of a theory, which naturally enters the path integrals (for interactions of a certain type, these are ''coordinat ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Noether's Theorem
Noether's theorem or Noether's first theorem states that every differentiable symmetry of the action of a physical system with conservative forces has a corresponding conservation law. The theorem was proven by mathematician Emmy Noether in 1915 and published in 1918. The action of a physical system is the integral over time of a Lagrangian function, from which the system's behavior can be determined by the principle of least action. This theorem only applies to continuous and smooth symmetries over physical space. Noether's theorem is used in theoretical physics and the calculus of variations. It reveals the fundamental relation between the symmetries of a physical system and the conservation laws. It also made modern theoretical physicists much more focused on symmetries of physical systems. A generalization of the formulations on constants of motion in Lagrangian and Hamiltonian mechanics (developed in 1788 and 1833, respectively), it does not apply to systems that cann ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Morse Theory
In mathematics, specifically in differential topology, Morse theory enables one to analyze the topology of a manifold by studying differentiable functions on that manifold. According to the basic insights of Marston Morse, a typical differentiable function on a manifold will reflect the topology quite directly. Morse theory allows one to find CW structures and handle decompositions on manifolds and to obtain substantial information about their homology. Before Morse, Arthur Cayley and James Clerk Maxwell had developed some of the ideas of Morse theory in the context of topography. Morse originally applied his theory to geodesics ( critical points of the energy functional on the space of paths). These techniques were used in Raoul Bott's proof of his periodicity theorem. The analogue of Morse theory for complex manifolds is Picard–Lefschetz theory. Basic concepts To illustrate, consider a mountainous landscape surface M (more generally, a manifold). If f is the function M ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Minimal Surface
In mathematics, a minimal surface is a surface that locally minimizes its area. This is equivalent to having zero mean curvature (see definitions below). The term "minimal surface" is used because these surfaces originally arose as surfaces that minimized total surface area subject to some constraint. Physical models of area-minimizing minimal surfaces can be made by dipping a wire frame into a soap solution, forming a soap film, which is a minimal surface whose boundary is the wire frame. However, the term is used for more general surfaces that may self-intersect or do not have constraints. For a given constraint there may also exist several minimal surfaces with different areas (for example, see minimal surface of revolution): the standard definitions only relate to a local optimum, not a global optimum. Definitions Minimal surfaces can be defined in several equivalent ways in R3. The fact that they are equivalent serves to demonstrate how minimal surface theory lies at the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |