|
List Of Power Stations In The Northwest Territories
This is a list of electrical generating stations in the Northwest Territories, Canada. Although the territory is not connected to the North American power grid, there are two electric networks operating in the province, the first one in the Yellowknife area and the other in Fort Smith. In most communities, loads are served by local diesel generators. The government-owned Northwest Territories Power Corporation is in charge of power generation. Hydroelectric List of all hydroelectric generating stations in the Northwest Territories. Fossil fuel List of all fossil fuel electrical generating stations in the Northwest Territories. References See also * Energy in Canada * List of electrical generating stations in Canada Canada is home to a wide variety of power stations (or generating stations). The lists below outline power stations of significance by type, or by the province/territory in which they reside. By type The following pages lists the power stations ... ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Northwest Territories
The Northwest Territories (abbreviated ''NT'' or ''NWT''; french: Territoires du Nord-Ouest, formerly ''North-Western Territory'' and ''North-West Territories'' and namely shortened as ''Northwest Territory'') is a federal territory of Canada. At a land area of approximately and a 2016 census population of 41,790, it is the second-largest and the most populous of the three territories in Northern Canada. Its estimated population as of 2022 is 45,605. Yellowknife is the capital, most populous community, and only city in the territory; its population was 19,569 as of the 2016 census. It became the territorial capital in 1967, following recommendations by the Carrothers Commission. The Northwest Territories, a portion of the old North-Western Territory, entered the Canadian Confederation on July 15, 1870. Since then, the territory has been divided four times to create new provinces and territories or enlarge existing ones. Its current borders date from April 1, 1999, when the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Canada
Canada is a country in North America. Its ten provinces and three territories extend from the Atlantic Ocean to the Pacific Ocean and northward into the Arctic Ocean, covering over , making it the world's second-largest country by total area. Its southern and western border with the United States, stretching , is the world's longest binational land border. Canada's capital is Ottawa, and its three largest metropolitan areas are Toronto, Montreal, and Vancouver. Indigenous peoples have continuously inhabited what is now Canada for thousands of years. Beginning in the 16th century, British and French expeditions explored and later settled along the Atlantic coast. As a consequence of various armed conflicts, France ceded nearly all of its colonies in North America in 1763. In 1867, with the union of three British North American colonies through Confederation, Canada was formed as a federal dominion of four provinces. This began an accretion of provinces an ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
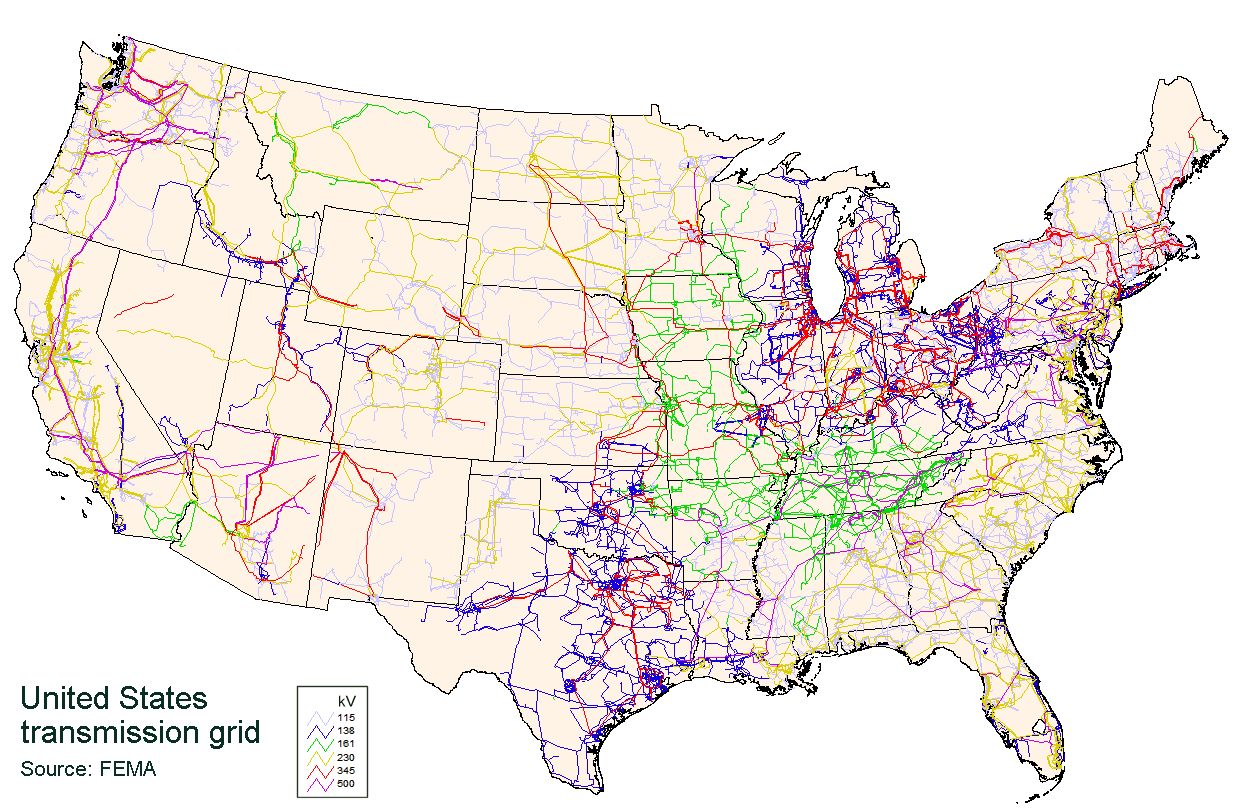
North American Electric Reliability Corporation
The North American Electric Reliability Corporation (NERC) is a nonprofit corporation based in Atlanta, Georgia, and formed on March 28, 2006, as the successor to the North American Electric Reliability Council (also known as NERC). The original NERC was formed on June 1, 1968, by the electric utility industry to promote the reliability and adequacy of bulk power transmission in the electric utility systems of North America. NERC's mission states that it is to "ensure the reliability of the North American bulk power system." NERC oversees six regional reliability entities and encompasses all of the interconnected power systems of Canada and the contiguous United States, as well as a portion of the Mexican state of Baja California. NERC's major responsibilities include working with all stakeholders to develop standards for power system operation, monitoring and enforcing compliance with those standards, assessing resource adequacy, and providing educational and training resour ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Yellowknife
Yellowknife (; Dogrib: ) is the capital, largest community, and only city in the Northwest Territories, Canada. It is on the northern shore of Great Slave Lake, about south of the Arctic Circle, on the west side of Yellowknife Bay near the outlet of the Yellowknife River. Yellowknife and its surrounding water bodies were named after a local Dene tribe, who were known as the "Copper Indians" or "Yellowknife Indians", today incorporated as the Yellowknives Dene First Nation. They traded tools made from copper deposits near the Arctic Coast. Its population, which is ethnically mixed, was 19,569 per the 2016 Canadian Census. Of the eleven official languages of the Northwest Territories, five are spoken in significant numbers in Yellowknife: Dene Suline, Dogrib, South and North Slavey, English, and French. In the Dogrib language, the city is known as ''Sǫǫ̀mbak’è'' (, "where the money is"). Modern Yellowknives members can be found in the adjoining, primarily Indigenous c ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fort Smith, Northwest Territories
Fort Smith ( chp, Thebacha "beside the rapids") is a town in the South Slave Region of the Northwest Territories (NWT), Canada. It is located in the southeastern portion of the Northwest Territories, on the Slave River and adjacent to the Alberta border along the 60th parallel north. History Fort Smith was founded around the Slave River. It served a vital link for water transportation between southern Canada and the western Arctic. Early fur traders found an established portage route from what is now Fort Fitzgerald on the western bank of the Slave River to Fort Smith. This route allowed its users to navigate the four sets of impassable rapids (Cassette Rapids, Pelican Rapids, Mountain Rapids, and Rapids of the Drowned). The portage trail had been traditionally used by local Indigenous people for centuries. The Indigenous population of the region shifted as the fortunes of the tribes changed. By 1870, Cree had occupied the Slave River Valley. The Slavey had moved north by t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Diesel Generator
A diesel generator (DG) (also known as a diesel Genset) is the combination of a diesel engine with an electric generator (often an alternator) to generate electrical energy. This is a specific case of engine generator. A diesel compression-ignition engine is usually designed to run on diesel fuel, but some types are adapted for other liquid fuels or natural gas. Diesel generating sets are used in places without connection to a power grid, or as an emergency power supply if the grid fails, as well as for more complex applications such as peak-lopping, grid support, and export to the power grid. Diesel generator size is crucial to minimize low load or power shortages. Sizing is complicated by the characteristics of modern electronics, specifically non-linear loads. In size ranges around 50 MW and above, an open cycle gas turbine is more efficient at full load than an array of diesel engines, and far more compact, with comparable capital costs; but for regular part-loading, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Government-owned Corporation
A state-owned enterprise (SOE) is a government entity which is established or nationalised by the ''national government'' or ''provincial government'' by an executive order or an act of legislation in order to earn profit for the government, control monopoly of the private sector entities, provide products and services to citizens at a lower price and for the achievement of overall financial goals & developmental objectives in a particular country. The national government or provincial government has majority ownership over these ''state owned enterprises''. These ''state owned enterprises'' are also known as public sector undertakings in some countries. Defining characteristics of SOEs are their distinct legal form and possession of financial goals & developmental objectives (e.g., a state railway company may aim to make transportation more accessible and earn profit for the government), SOEs are government entities established to pursue financial objectives and devel ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Northwest Territories Power Corporation
The Northwest Territories Power Corporation (NTPC) is an electric utility in the Northwest Territories of Canada. NTPC was formed in 1988 to acquire and operate the former assets of the Northern Canada Power Commission in the Northwest Territories, including what is now Nunavut. Since 2007, NTPC is organised as a subsidiary of the Northwest Territories Hydro Corporation. 76% of NTPC's electrical generation is in the form of Hydro electricity. Hydro production has increased approximately 15% since 1990/91, reducing demand on diesel production and lower GHG emissions by 58% of 1990/91 levels. This has led NTPC to be recognized as a Gold Champion Level Reporter by the Canadian voluntary Challenge and Registry for seven consecutive years, including a leadership award and an honourable mention. NTPC sells electricity wholesale to Northland Utilities, a private company majority-owned by ATCO, which provides electricity in Yellowknife and Hay River. Liquid natural gas and diesel are us ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hydroelectricity
Hydroelectricity, or hydroelectric power, is Electricity generation, electricity generated from hydropower (water power). Hydropower supplies one sixth of the world's electricity, almost 4500 TWh in 2020, which is more than all other Renewable energy, renewable sources combined and also more than nuclear power. Hydropower can provide large amounts of Low-carbon power, low-carbon electricity on demand, making it a key element for creating secure and clean electricity supply systems. A hydroelectric power station that has a dam and reservoir is a flexible source, since the amount of electricity produced can be increased or decreased in seconds or minutes in response to varying electricity demand. Once a hydroelectric complex is constructed, it produces no direct waste, and almost always emits considerably less greenhouse gas than fossil fuel-powered energy plants. [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Megawatt
The watt (symbol: W) is the unit of Power (physics), power or radiant flux in the International System of Units, International System of Units (SI), equal to 1 joule per second or 1 kg⋅m2⋅s−3. It is used to quantification (science), quantify the rate of Energy transformation, energy transfer. The watt is named after James Watt (1736–1819), an 18th-century Scottish people, Scottish invention, inventor, mechanical engineer, and chemist who improved the Newcomen steam engine, Newcomen engine with his own Watt steam engine, steam engine in 1776. Watt's invention was fundamental for the Industrial Revolution. Overview When an object's velocity is held constant at one metre per second against a constant opposing force of one Newton (unit), newton, the rate at which Work (physics), work is done is one watt. : \mathrm In terms of electromagnetism, one watt is the rate at which electrical work is performed when a current of one ampere (A) flows across an electrical potentia ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Geographic Coordinate System
The geographic coordinate system (GCS) is a spherical or ellipsoidal coordinate system for measuring and communicating positions directly on the Earth as latitude and longitude. It is the simplest, oldest and most widely used of the various spatial reference systems that are in use, and forms the basis for most others. Although latitude and longitude form a coordinate tuple like a cartesian coordinate system, the geographic coordinate system is not cartesian because the measurements are angles and are not on a planar surface. A full GCS specification, such as those listed in the EPSG and ISO 19111 standards, also includes a choice of geodetic datum (including an Earth ellipsoid), as different datums will yield different latitude and longitude values for the same location. History The invention of a geographic coordinate system is generally credited to Eratosthenes of Cyrene, who composed his now-lost ''Geography'' at the Library of Alexandria in the 3rd century ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Snare River
The Snare River is a river in the Northwest Territories, Canada. It is connected to Great Slave Lake via Marian Lake and Frank Channel and hosts the Snare Hydro System, four hydroelectric plants about northwest of Yellowknife which it powers along with the nearby communities of Behchokǫ̀ and Dettah. It is located close to the Snare River Airport, owned by the Northwest Territories Power Corporation The Northwest Territories Power Corporation (NTPC) is an electric utility in the Northwest Territories of Canada. NTPC was formed in 1988 to acquire and operate the former assets of the Northern Canada Power Commission in the Northwest Territories ..., which serves the hydro system. References Rivers of the Northwest Territories {{NorthwestTerritories-river-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |

.jpg)
_Generator_Set.jpg)
