|
List Of Inventions Named After People
This is a list of inventions followed by name of the inventor (or whomever else it is named after). For other lists of eponyms (names derived from people) see Lists of etymologies. The list A to F * Abney level – William de Wiveleslie Abney * Aldis lamp – Arthur Cyril Webb Aldis * Aldrin – Kurt Alder * Alexanderson alternator – Ernst Alexanderson * Algorithm – Muḥammad ibn Mūsā al-Khwārizmī * Anderson shelter – John Anderson, 1st Viscount Waverley * Anderton Shearer Loader – James Anderton * Appertization – Nicolas Appert * Archimedes' screw – Archimedes * Argand lamp – Aimé Argand * Armstrong breech-loading gun – William Armstrong, 1st Baron Armstrong * Armstrong's acid – Henry Edward Armstrong * Austenite – William Chandler Roberts-Austen * Auston switch - David H. Auston * Avtomat Kalashnikova (AK-47) – Mikhail Kalashnikov * Bailey bridge – Donald Bailey * Bakelite – Leo Baekeland * Barlow lens, Barlow's wheel – Peter ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Invention
An invention is a unique or novel device, method, composition, idea or process. An invention may be an improvement upon a machine, product, or process for increasing efficiency or lowering cost. It may also be an entirely new concept. If an idea is unique enough either as a stand alone invention or as a significant improvement over the work of others, it can be patented. A patent, if granted, gives the inventor a proprietary interest in the patent over a specific period of time, which can be licensed for financial gain. An inventor creates or discovers an invention. The word ''inventor'' comes from the Latin verb ''invenire'', ''invent-'', to find. Although inventing is closely associated with science and engineering, inventors are not necessarily engineers or scientists. Due to advances in artificial intelligence, the term "inventor" no longer exclusively applies to an occupation (see human computers). Some inventions can be patented. The system of patents was established ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
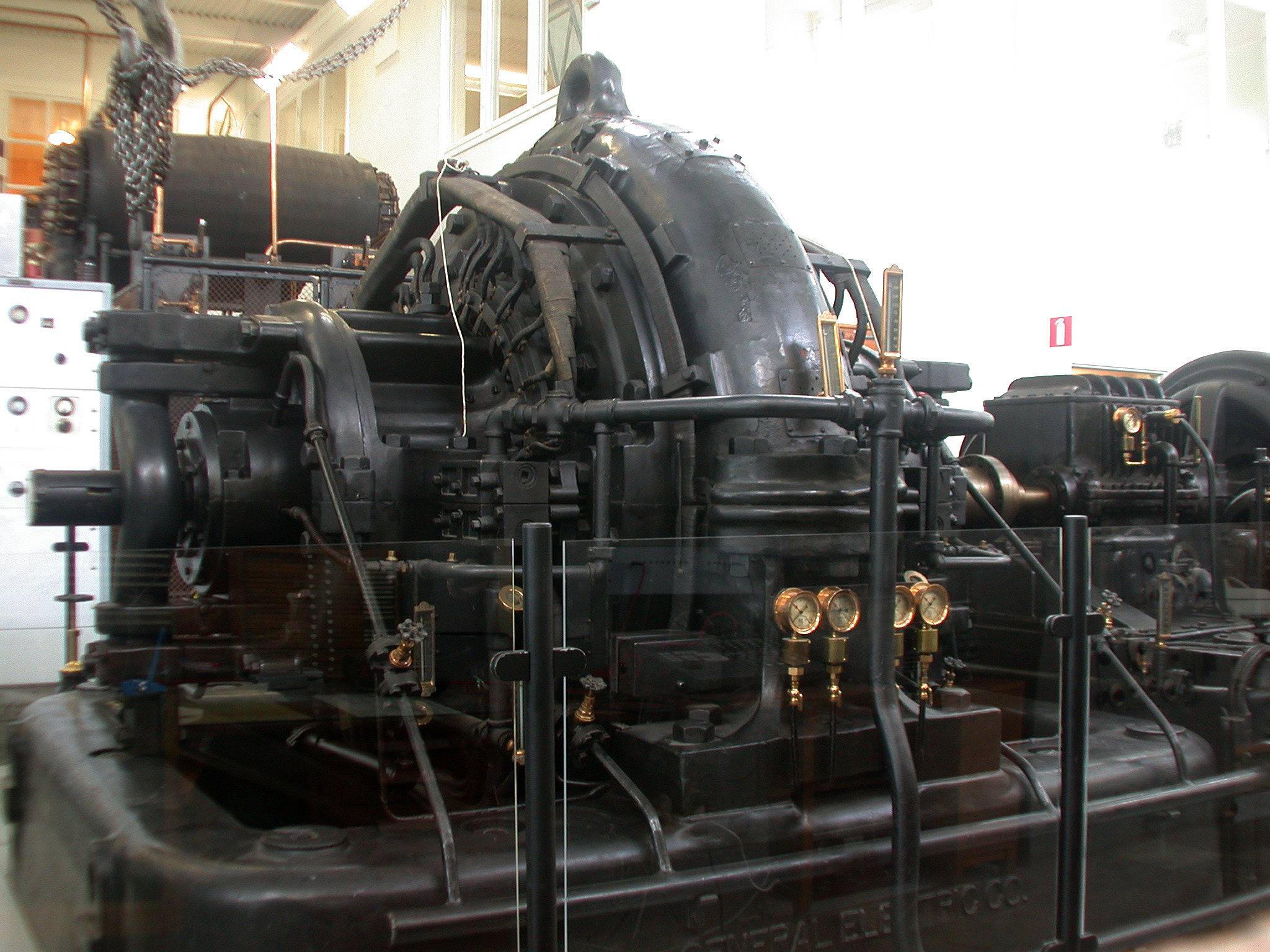
Alexanderson Alternator
An Alexanderson alternator is a rotating machine invented by Ernst Alexanderson in 1904 for the generation of high-frequency alternating current for use as a radio transmitter. It was one of the first devices capable of generating the continuous radio waves needed for transmission of amplitude modulated signals by radio. It was used from about 1910 in a few "superpower" longwave radiotelegraphy stations to transmit transoceanic message traffic by Morse code to similar stations all over the world. Although superceded in the early 1920s by the development of vacuum-tube transmitters, the Alexanderson alternator continued to be used until World War II. It is on the list of IEEE Milestones as a key achievement in electrical engineering. History Prior developments After radio waves were discovered in 1887, the first generation of radio transmitters, the spark gap transmitters, produced strings of ''damped waves'', pulses of radio waves which died out to zero quickly. By the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
William Armstrong, 1st Baron Armstrong
William George Armstrong, 1st Baron Armstrong, (26 November 1810 – 27 December 1900) was an English engineer and industrialist who founded the Armstrong Whitworth manufacturing concern on Tyneside. He was also an eminent scientist, inventor and philanthropist. In collaboration with the architect Richard Norman Shaw, he built Cragside in Northumberland, the first house in the world to be lit by hydroelectricity. He is regarded as the inventor of modern artillery. Armstrong was knighted in 1859 after giving his gun patents to the government. In 1887, in Queen Victoria's golden jubilee year, he was raised to the peerage as Baron Armstrong of Cragside. Early life Armstrong was born in Newcastle upon Tyne at 9 Pleasant Row, Shieldfield, about a mile from the city centre. Although the house in which he was born no longer exists, an inscribed granite tablet marks the site where it stood. At that time the area, next to thPandon Dene was rural. His father, also called William, wa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Rifled Breech Loader
A rifled breech loader (RBL) is an artillery piece which, unlike the smoothbore cannon and rifled muzzle loader (RML) which preceded it, has rifling in the barrel and is loaded from the breech at the rear of the gun. The spin imparted by the gun's rifling gives projectiles directional stability and increased range. Loading from the rear of the gun leaves the crew less exposed to enemy fire, allows smaller gun emplacements or turrets, and allows a faster rate of fire. Overview The major problem to be solved with breechloading artillery was obturation: the sealing of the breech after firing to ensure that none of the gases generated by the burning of the propellant (initially gunpowder) escaped rearwards through the breech. This was both a safety issue and one of gun performance – all the propellant gas was needed to accelerate the projectile along the barrel. The second problem was speed of operation – how to close the breech before firing and open it after firing as quickly ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Aimé Argand
François-Pierre-Amédée Argand, known as Ami Argand (5 July 1750 – 14 or 24 October 1803) was a Genevan physicist and chemist. He invented the Argand lamp, a great improvement on the traditional oil lamp. Early years Francois-Pierre-Amédée Argand was born in Geneva, Republic of Geneva, the ninth of ten children. His father was a watchmaker, who intended for him to enter the clergy. However, he had an aptitude more for science, and became a pupil of the noted botanist and meteorologist Horace-Bénédict de Saussure. He published several scientific papers on meteorological subjects while in Paris in his late twenties. He took a teaching post in chemistry and developed some ideas for improving the distillation of wine into brandy, and, with his brother, successfully built a large distillery. The invention During this period, in 1780, he started to invent improvements on the conventional oil lamp. The basic idea was to have a cylindrical wick which air could flow through and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
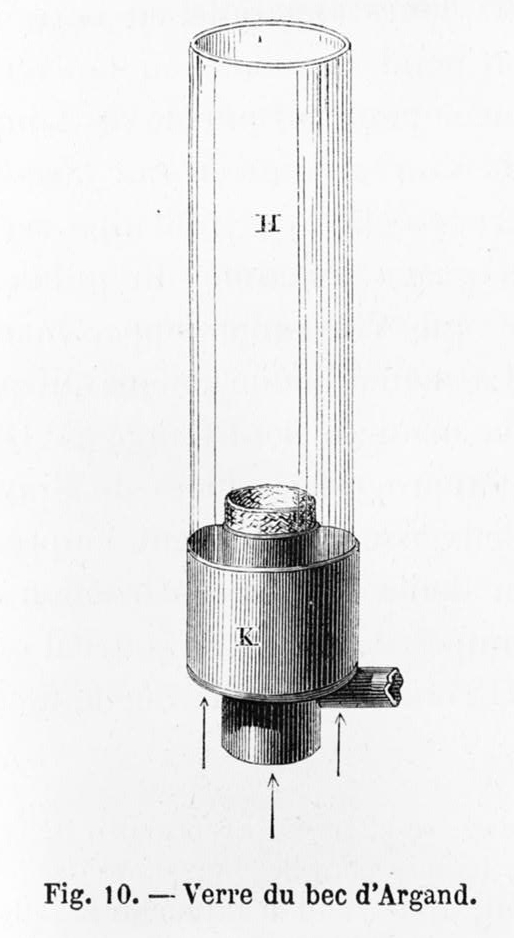
Argand Lamp
The Argand lamp is a type of oil lamp invented in 1780 by Aimé Argand. Its output is 6 to 10 candelas, brighter than that of earlier lamps. Its more complete combustion of the candle wick and oil than in other lamps required much less frequent trimming of the wick. In France, the lamp is called "Quinquet", after Antoine-Arnoult Quinquet, a pharmacist in Paris, who used the idea originated by Argand and popularized it in France. Quinquet sometimes is credited with the addition of the glass chimney to the lamp. Design The Argand lamp had a sleeve-shaped wick mounted so that air can pass both through the center of the wick and also around the outside of the wick before being drawn into a cylindrical chimney which steadies the flame and improves the flow of air. Early models used ground glass which was sometimes tinted around the wick. An Argand lamp used whale oil, seal oil, colza, olive oil or other vegetable oil as fuel which was supplied by a gravity feed from a reservoir mou ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Archimedes
Archimedes of Syracuse (;; ) was a Greek mathematician, physicist, engineer, astronomer, and inventor from the ancient city of Syracuse in Sicily. Although few details of his life are known, he is regarded as one of the leading scientists in classical antiquity. Considered the greatest mathematician of ancient history, and one of the greatest of all time,* * * * * * * * * * Archimedes anticipated modern calculus and analysis by applying the concept of the infinitely small and the method of exhaustion to derive and rigorously prove a range of geometrical theorems. These include the area of a circle, the surface area and volume of a sphere, the area of an ellipse, the area under a parabola, the volume of a segment of a paraboloid of revolution, the volume of a segment of a hyperboloid of revolution, and the area of a spiral. Heath, Thomas L. 1897. ''Works of Archimedes''. Archimedes' other mathematical achievements include deriving an approximation of pi, defining and in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Archimedes' Screw
The Archimedes screw, also known as the Archimedean screw, hydrodynamic screw, water screw or Egyptian screw, is one of the earliest hydraulic machines. Using Archimedes screws as water pumps (Archimedes screw pump (ASP) or screw pump) dates back many centuries. As a machine used for pump, transferring water from a low-lying body of water into irrigation ditches, water is pumped by turning a screw-shaped surface inside a pipe. In the modern world, Archimedes screw pumps are widely used in wastewater treatment plants and for dewatering low-lying regions. Screw turbine, Archimedes Screws Turbines (ASTs) are a new form of small hydroelectric powerplant that can be applied even in low head sites. Screw turbine, Archimedes screw generators operate in a wide range of flows (0.01 m^3/s to 14.5 m^3/s) and heads (0.1 m to 10 m), including low heads and moderate flow rates that is not ideal for traditional turbines and not occupied by high performance technologies. The Archimedes screw is a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nicolas Appert
Nicolas Appert (17 November 1749 – 1 June 1841) was the French inventor of airtight food preservation. Appert, known as the " father of Food Science", was a confectioner. Appert described his invention as a way "of conserving all kinds of food substances in containers". Early life Appert was born in Châlons-en-Champagne, the ninth of eleven children. His family ran an inn in the town and he worked in the family business until the age of twenty, when he opened a brewery with one of his brothers. He then served as head chef to Christian IV, Count Palatine of Zweibrücken for thirteen years. Appert was a confectioner and chef in Paris from 1784 to 1795. During this period, he married Elisabeth Benoist and the couple had four children. Appert was active during the French Revolution and even took part in the execution of King Louis XVI. However, he fell under suspicion during the subsequent Reign of Terror and was arrested in April 1794, but he was able to avoid being executed him ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Anderton Shearer Loader
The Anderton Shearer Loader is a coal cutting machine which was used in the UK coal industry after 1953. The Anderton Power Loader with its cutting drum up to five feet in diameter was patented in 1953. It was successfully used throughout the British coalfields and by 1966 cut half the coal produced and by 1977 it produced 80% of the coal mined in Britain. The Shearer Loader was mainly developed by James Anderton OBE, who was the National Coal Board ( St Helens Area) production manager and later chairman of the NCB's North-Western Division. The first Anderton shearer loader was commissioned in 1954. It was utilised by Anderton's employers at Groves Ravenhead Colliery in St Helens. The machine works by "shearing" coal from a longwall coal face as it moved along the face. The shear drum is around 0.5 metres in diameter and the machine travels on an armoured conveyor with a prop-free front. The machine shears going one way and the coal at the front is deflected by a plough onto the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
John Anderson, 1st Viscount Waverley
John Anderson, 1st Viscount Waverley, (8 July 1882 – 4 January 1958) was a Scottish civil servant and politician who is best known for his service in the War Cabinet during the Second World War, for which he was nicknamed the "Home Front Prime Minister". He served as Home Secretary, Lord President of the Council and Chancellor of the Exchequer. The Anderson shelters are named after him. A graduate of the University of Edinburgh and the University of Leipzig where he studied the chemistry of uranium, Anderson joined the Civil Service in 1905, and worked in the West African Department of the Colonial Office. During the Great War he headed the staff of the Ministry of Shipping. He served as Under-Secretary for Ireland from 1921 to 1922 during its transition to independence, and as the Permanent Under-Secretary of State at the Home Office from 1922 to 1931 he had to deal with the General Strike of 1926. As Governor of Bengal from 1932 to 1937, he instituted social and financia ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Air-raid Shelter
Air raid shelters are structures for the protection of non-combatants as well as combatants against enemy attacks from the air. They are similar to bunkers in many regards, although they are not designed to defend against ground attack (but many have been used as defensive structures in such situations). During World War II, many types of structures were used as air raid shelters, such as cellars, Hochbunkers (in Germany), basements, and underpasses. Bombing raids during World War I led the UK to build 80 specially adapted London Underground stations as shelters. However, during World War II, the government initially ruled out using these as shelters. After Londoners flooded into underground stations during The Blitz, the government reversed its policy. The UK began building street communal shelters as air raid shelters in 1940. Anderson shelters, designed in 1938 and built to hold up to six people, were in common use in the UK. Indoor shelters known as Morrison shelters were int ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |




_by_Thomas_Degeorge.png)




