|
List Of Geological Features On Proteus
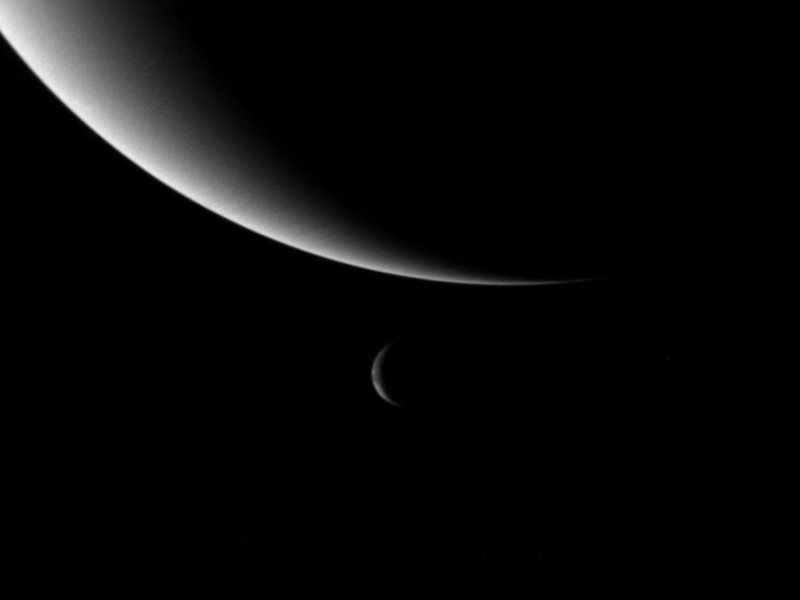
Proteus (), also known as Neptune VIII, is the second-largest Neptune, Neptunian natural satellite, moon, and Neptune's largest Inner moon, inner satellite. Discovered by ''Voyager 2'' spacecraft in 1989, it is named after Proteus, the shape-changing sea god of Greek mythology. Proteus orbits Neptune in a nearly equatorial orbit at a distance of about 4.75 times the radius of Neptune's equator. Despite being a predominantly icy body more than in diameter, Proteus's shape deviates significantly from an ellipsoid. It is shaped more like an irregular polyhedron with several slightly concave facets and relief as high as . Its surface is dark, neutral in color, and heavily cratered. Proteus's largest crater is Pharos (crater), Pharos, which is more than in diameter. There are also a number of Cliff, scarps, grooves, and valleys related to large craters. Proteus is probably not an original body that formed with Neptune. It could have accreted later from the debris formed when th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Voyager 2
''Voyager 2'' is a space probe launched by NASA on August 20, 1977, to study the outer planets and interstellar space beyond the Sun's heliosphere. As a part of the Voyager program, it was launched 16 days before its twin, ''Voyager 1'', on a trajectory that took longer to reach gas giants Jupiter and Saturn but enabled further encounters with ice giants Uranus and Neptune. ''Voyager 2'' remains the only spacecraft to have visited either of the ice giant planets. ''Voyager 2'' was the fourth of five spacecraft to achieve Solar escape velocity, which allowed it to leave the Solar System. ''Voyager 2'' successfully fulfilled its primary mission of visiting the Jovian system in 1979, the Saturnian system in 1981, Uranian system in 1986, and the Neptunian system in 1989. The spacecraft is now in its extended mission of studying interstellar space. It has been operating for as of ; , it has reached a distance of from Earth. The probe entered interstellar space on November 5, 2 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ellipsoid
An ellipsoid is a surface that may be obtained from a sphere by deforming it by means of directional scalings, or more generally, of an affine transformation. An ellipsoid is a quadric surface; that is, a surface that may be defined as the zero set of a polynomial of degree two in three variables. Among quadric surfaces, an ellipsoid is characterized by either of the two following properties. Every planar cross section is either an ellipse, or is empty, or is reduced to a single point (this explains the name, meaning "ellipse-like"). It is bounded, which means that it may be enclosed in a sufficiently large sphere. An ellipsoid has three pairwise perpendicular axes of symmetry which intersect at a center of symmetry, called the center of the ellipsoid. The line segments that are delimited on the axes of symmetry by the ellipsoid are called the ''principal axes'', or simply axes of the ellipsoid. If the three axes have different lengths, the figure is a triaxial ellipsoid (r ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Synchronous Orbit
A synchronous orbit is an orbit in which an orbiting body (usually a satellite) has a period equal to the average rotational period of the body being orbited (usually a planet), and in the same direction of rotation as that body. Simplified meaning A synchronous orbit is an orbit in which the orbiting object (for example, an artificial satellite or a moon) takes the same amount of time to complete an orbit as it takes the object it is orbiting to rotate once. Properties A satellite in a synchronous orbit that is both equatorial and circle, circular will appear to be suspended motionless above a point on the orbited planet's equator. For synchronous satellites orbiting Earth, this is also known as a geostationary orbit. However, a synchronous orbit need not be equatorial; nor circular. A body in a non-equatorial synchronous orbit will appear to oscillate north and south above a point on the planet's equator, whereas a body in an ellipse, elliptical orbit will appear to oscillate ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tidal Locking
Tidal locking between a pair of co-orbiting astronomical bodies occurs when one of the objects reaches a state where there is no longer any net change in its rotation rate over the course of a complete orbit. In the case where a tidally locked body possesses synchronous rotation, the object takes just as long to rotate around its own axis as it does to revolve around its partner. For example, the same side of the Moon always faces the Earth, although there is some variability because the Moon's orbit is not perfectly circular. Usually, only the satellite is tidally locked to the larger body. However, if both the difference in mass between the two bodies and the distance between them are relatively small, each may be tidally locked to the other; this is the case for Pluto and Charon. Alternative names for the tidal locking process are gravitational locking, captured rotation, and spin–orbit locking. The effect arises between two bodies when their gravitational interaction sl ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Orbital Eccentricity
In astrodynamics, the orbital eccentricity of an astronomical object is a dimensionless parameter that determines the amount by which its orbit around another body deviates from a perfect circle. A value of 0 is a circular orbit, values between 0 and 1 form an elliptic orbit, 1 is a parabolic escape orbit (or capture orbit), and greater than 1 is a hyperbola. The term derives its name from the parameters of conic sections, as every Kepler orbit is a conic section. It is normally used for the isolated two-body problem, but extensions exist for objects following a rosette orbit through the Galaxy. Definition In a two-body problem with inverse-square-law force, every orbit is a Kepler orbit. The eccentricity of this Kepler orbit is a non-negative number that defines its shape. The eccentricity may take the following values: * circular orbit: ''e'' = 0 * elliptic orbit: 0 < ''e'' < 1 * [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bradford A
Bradford is a city status in the United Kingdom, city and the administrative centre of the City of Bradford district in West Yorkshire, England. The city is in the Pennines' eastern foothills on the banks of the Bradford Beck. Bradford had a population of 349,561 at the 2011 Census for England and Wales, 2011 census; the second-largest population centre in the county after Leeds, which is to the east of the city. It shares West Yorkshire Built-up Area, a continuous built-up area with the towns of Shipley, West Yorkshire, Shipley, Silsden, Bingley and Keighley in the district as well as with the metropolitan county's other districts. Its name is also given to Bradford Beck. It became a West Riding of Yorkshire municipal borough in 1847 and received its city charter in 1897. Since Local Government Act 1972, local government reform in 1974, the city is the administrative centre of a wider metropolitan district, city hall is the meeting place of Bradford City Council. The district ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Provisional Designation
Provisional designation in astronomy is the naming convention applied to astronomical objects immediately following their discovery. The provisional designation is usually superseded by a permanent designation once a reliable orbit has been calculated. Approximately 47% of the more than 1,100,000 known minor planets remain provisionally designated, as hundreds of thousands have been discovered in the last two decades. __TOC__ Minor planets The current system of provisional designation of minor planets (asteroids, centaurs and trans-Neptunian objects) has been in place since 1925. It superseded several previous conventions, each of which was in turn rendered obsolete by the increasing numbers of minor planet discoveries. A modern or new-style provisional designation consists of the year of discovery, followed by two letters and, possibly, a suffixed number. New-style provisional designation For example, the provisional designation stands for the 3910th body identified dur ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nereid (moon)
Nereid, or Neptune II, is the third-largest moon of Neptune. It has the most eccentric orbit of all known moons in the Solar System. It was the second moon of Neptune to be discovered, by Gerard Kuiper in 1949. Discovery and naming Nereid was discovered on 1 May 1949 by Gerard P. Kuiper on photographic plates taken with the 82-inch telescope at the McDonald Observatory. He proposed the name in the report of his discovery. It is named after the Nereids, sea-nymphs of Greek mythology and attendants of the god Neptune. It was the second and last moon of Neptune to be discovered before the arrival of ''Voyager 2'' (not counting a single observation of an occultation by Larissa in 1981). Physical characteristics Nereid is third-largest of Neptune's satellites, and has a mean radius of about . It is rather large for an irregular satellite. The shape of Nereid is unknown. Nereid is around half the size and mass of Saturn's moon Mimas, though Nereid is slightly denser. Since 1987 s ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Moon Of Neptune
The planet Neptune has 14 known moons, which are named for minor water deities in Greek mythology. By far the largest of them is Triton, discovered by William Lassell on October 10, 1846, 17 days after the discovery of Neptune itself; over a century passed before the discovery of the second natural satellite, Nereid. Neptune's outermost moon Neso, which has an orbital period of about 26 Julian years, orbits farther from its planet than any other moon in the Solar System. Triton is unique among moons of planetary mass in that its orbit is retrograde to Neptune's rotation and inclined relative to Neptune's equator, which suggests that it did not form in orbit around Neptune but was instead gravitationally captured by it. The next-largest satellite in the Solar System suspected to be captured, Saturn's moon Phoebe, has only 0.03% of Triton's mass. The capture of Triton, probably occurring some time after Neptune formed a satellite system, was a catastrophic event for Nept ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hubble Space Telescope
The Hubble Space Telescope (often referred to as HST or Hubble) is a space telescope that was launched into low Earth orbit in 1990 and remains in operation. It was not the first space telescope, but it is one of the largest and most versatile, renowned both as a vital research tool and as a public relations boon for astronomy. The Hubble telescope is named after astronomer Edwin Hubble and is one of NASA's Great Observatories. The Space Telescope Science Institute (STScI) selects Hubble's targets and processes the resulting data, while the Goddard Space Flight Center (GSFC) controls the spacecraft. Hubble features a mirror, and its five main instruments observe in the ultraviolet, visible, and near-infrared regions of the electromagnetic spectrum. Hubble's orbit outside the distortion of Earth's atmosphere allows it to capture extremely high-resolution images with substantially lower background light than ground-based telescopes. It has recorded some of the most detaile ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Triton (moon)
Triton is the largest natural satellite of the planet Neptune, and was the first Neptunian moon to be discovered, on October 10, 1846, by English astronomer William Lassell. It is the only large moon in the Solar System with a retrograde orbit, an orbit in the direction opposite to its planet's rotation. Because of its retrograde orbit and composition similar to Pluto, Triton is thought to have been a dwarf planet, captured from the Kuiper belt. At in diameter, it is the seventh-largest moon in the Solar System, the only satellite of Neptune massive enough to be in hydrostatic equilibrium, the second-largest planetary moon in relation to its primary (after Earth's Moon), and larger than Pluto. Triton is one of the few moons in the Solar System known to be geologically active (the others being Jupiter's Io and Europa, and Saturn's Enceladus and Titan). As a consequence, its surface is relatively young, with few obvious impact craters. Intricate cryovolcanic and tectonic te ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Valley
A valley is an elongated low area often running between Hill, hills or Mountain, mountains, which will typically contain a river or stream running from one end to the other. Most valleys are formed by erosion of the land surface by rivers or streams over a very long period. Some valleys are formed through erosion by glacier, glacial ice. These glaciers may remain present in valleys in high mountains or polar areas. At lower latitudes and altitudes, these glaciation, glacially formed valleys may have been created or enlarged during ice ages but now are ice-free and occupied by streams or rivers. In desert areas, valleys may be entirely dry or carry a watercourse only rarely. In karst, areas of limestone bedrock, dry valleys may also result from drainage now taking place cave, underground rather than at the surface. Rift valleys arise principally from tectonics, earth movements, rather than erosion. Many different types of valleys are described by geographers, using terms th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
.jpg)