|
List Of Distinct Cell Types In The Adult Human Body
There are many different types of cells in the human body. Cells derived primarily from endoderm Exocrine secretory epithelial cells * Brunner's gland cell in duodenum (enzymes and alkaline mucus) *Insulated goblet cell of respiratory and digestive tracts (mucus secretion) *Stomach **Foveolar cell (mucus secretion) **Chief cell ( pepsinogen secretion) **Parietal cell (hydrochloric acid secretion) * Pancreatic acinar cell (bicarbonate and digestive enzyme secretion) *Paneth cell of small intestine (lysozyme secretion) *Type II pneumocyte of lung ( surfactant secretion) *Club cell of lung Barrier cells *Type I pneumocyte (lung) * Gall bladder epithelial cell * Centroacinar cell (pancreas) *Intercalated duct cell (pancreas) *Intestinal brush border cell (with microvilli) Hormone-secreting cells *Enteroendocrine cell **K cell (secretes gastric inhibitory peptide) **L cell (secretes glucagon-like peptide-1, peptide YY3-36, oxyntomodulin, and glucagon-like peptide-2) **I ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cells Of The Human Body By Count
Cell most often refers to: * Cell (biology), the functional basic unit of life Cell may also refer to: Locations * Monastic cell, a small room, hut, or cave in which a religious recluse lives, alternatively the small precursor of a monastery with only a few monks or nuns * Prison cell, a room used to hold people in prisons Groups of people * Cell, a group of people in a cell group, a form of Christian church organization * Cell, a unit of a clandestine cell system, a penetration-resistant form of a secret or outlawed organization * Cellular organizational structure, such as in business management Science, mathematics, and technology Computing and telecommunications * Cell (EDA), a term used in an electronic circuit design schematics * Cell (microprocessor), a microprocessor architecture developed by Sony, Toshiba, and IBM * Memory cell (computing), the basic unit of (volatile or non-volatile) computer memory * Cell, a unit in a database table or spreadsheet, formed by the int ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Alkaline Mucus
Alkaline mucus is a thick fluid produced by animals which confers tissue protection in an acidic environment, such as in the stomach. Properties Mucus that serves a protective function against acidic environments generally has a high viscosity, though the thickness and viscosity of the mucus layer can vary due to several factors. For example, alkaline mucus in the stomach increases in thickness when the stomach is distended. The pH level of the mucus also plays a role in its viscosity, as higher pH levels tend to alter the thickness of the mucus, making it less viscous. Because of this, invading agents such as ''Helicobacter pylori'', a bacterium that causes stomach ulcers, can alter the pH of the mucus to make the mucus pliable enough to move through. Exposure to atmospheric air also tends to increase the pH level of alkaline mucus. In humans In humans, alkaline mucus is present in several organs and provides protection by way of its alkalinity and high viscosity. Alkaline mu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
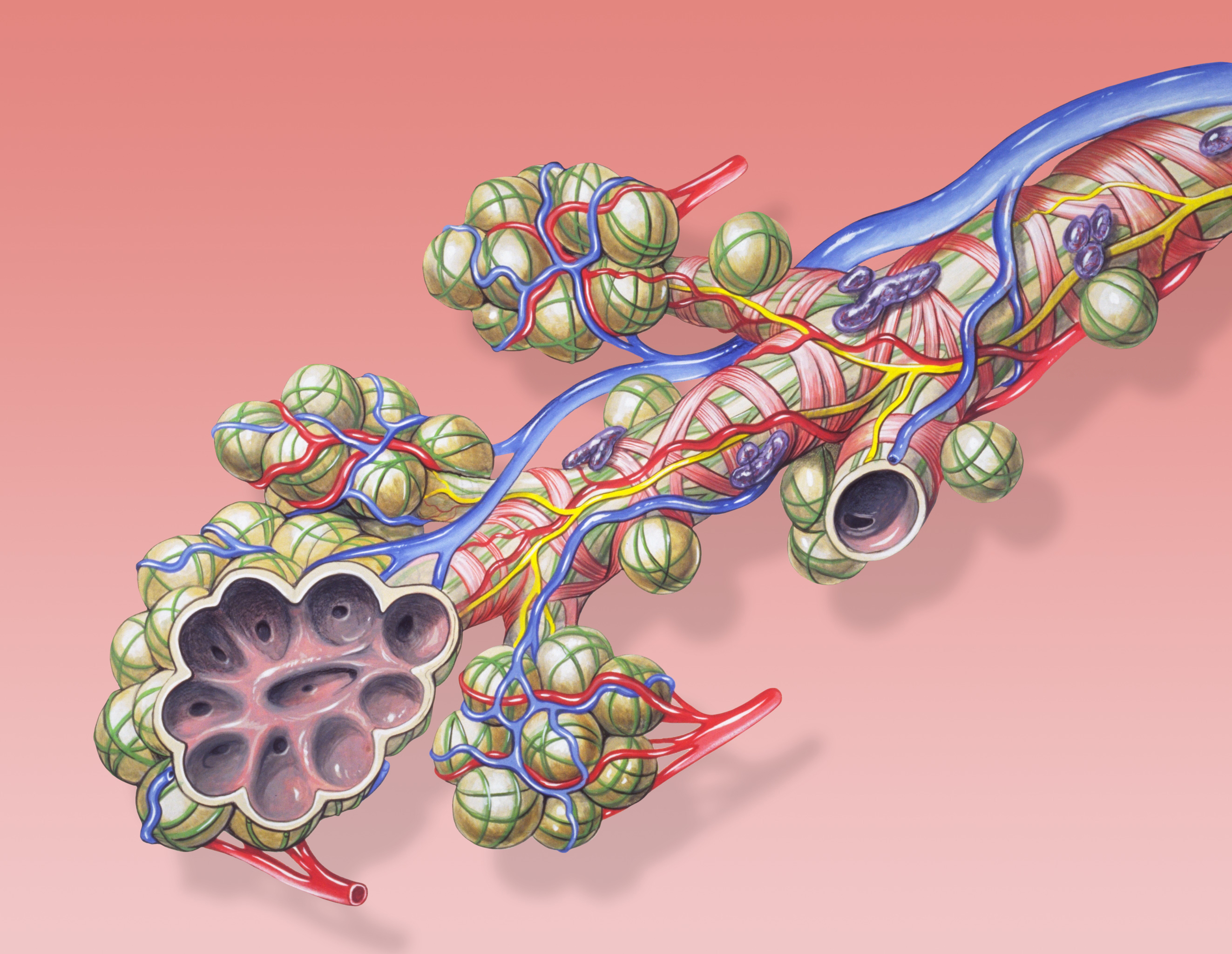
Pneumocyte
A pulmonary alveolus (plural: alveoli, from Latin ''alveolus'', "little cavity"), also known as an air sac or air space, is one of millions of hollow, distensible cup-shaped cavities in the lungs where oxygen is exchanged for carbon dioxide. Alveoli make up the functional tissue of the mammalian lungs known as the lung parenchyma, which takes up 90 percent of the total lung volume. Alveoli are first located in the respiratory bronchioles that mark the beginning of the respiratory zone. They are located sparsely in these bronchioles, line the walls of the alveolar ducts, and are more numerous in the blind-ended alveolar sacs. The acini are the basic units of respiration, with gas exchange taking place in all the alveoli present. The alveolar membrane is the gas exchange surface, surrounded by a network of capillaries. Across the membrane oxygen is diffused into the capillaries and carbon dioxide released from the capillaries into the alveoli to be breathed out. Alveoli are part ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lysozyme
Lysozyme (EC 3.2.1.17, muramidase, ''N''-acetylmuramide glycanhydrolase; systematic name peptidoglycan ''N''-acetylmuramoylhydrolase) is an antimicrobial enzyme produced by animals that forms part of the innate immune system. It is a glycoside hydrolase that catalyzes the following process: : Hydrolysis of (1→4)-β-linkages between ''N''-acetylmuramic acid and ''N''-acetyl-D-glucosamine residues in a peptidoglycan and between ''N''-acetyl-D-glucosamine residues in chitodextrins Peptidoglycan is the major component of gram-positive bacterial cell wall. This hydrolysis in turn compromises the integrity of bacterial cell walls causing lysis of the bacteria. Lysozyme is abundant in secretions including tears, saliva, human milk, and mucus. It is also present in cytoplasmic granules of the macrophages and the polymorphonuclear neutrophils (PMNs). Large amounts of lysozyme can be found in egg white. C-type lysozymes are closely related to α-lactalbumin in sequence and structure ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Intestine
The gastrointestinal tract (GI tract, digestive tract, alimentary canal) is the tract or passageway of the digestive system that leads from the mouth to the anus. The GI tract contains all the major organs of the digestive system, in humans and other animals, including the esophagus, stomach, and intestines. Food taken in through the mouth is digested to extract nutrients and absorb energy, and the waste expelled at the anus as feces. ''Gastrointestinal'' is an adjective meaning of or pertaining to the stomach and intestines. Most animals have a "through-gut" or complete digestive tract. Exceptions are more primitive ones: sponges have small pores ( ostia) throughout their body for digestion and a larger dorsal pore (osculum) for excretion, comb jellies have both a ventral mouth and dorsal anal pores, while cnidarians and acoels have a single pore for both digestion and excretion. The human gastrointestinal tract consists of the esophagus, stomach, and intestines, and is ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Paneth Cell
Paneth cells are cells in the small intestine epithelium, alongside goblet cells, enterocytes, and enteroendocrine cells. Some can also be found in the cecum and appendix. They are below the intestinal stem cells in the intestinal glands (also called crypts of Lieberkühn) and the large eosinophilic refractile granules that occupy most of their cytoplasm. These granules consist of several anti-microbial compounds and other compounds that are known to be important in immunity and host-defense. When exposed to bacteria or bacterial antigens, Paneth cells secrete some of these compounds into the lumen of the intestinal gland, thereby contributing to maintenance of the gastrointestinal barrier. Paneth cells are named after 19th-century pathologist Joseph Paneth. Structure Paneth cells are found throughout the small intestine and the appendix at the base of the intestinal glands. The Paneth cell increase in numbers towards the end of the small intestine. Like the other epithelial ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Digestive Enzyme
Digestive enzymes are a group of enzymes that break down polymeric macromolecules into their smaller building blocks, in order to facilitate their absorption into the cells of the body. Digestive enzymes are found in the digestive tracts of animals (including humans) and in the tracts of carnivorous plants, where they aid in the digestion of food, as well as inside cells, especially in their lysosomes, where they function to maintain cellular survival. Digestive enzymes of diverse specificities are found in the saliva secreted by the salivary glands, in the secretions of cells lining the stomach, in the pancreatic juice secreted by pancreatic exocrine cells, and in the secretions of cells lining the small and large intestines. Digestive enzymes are classified based on their target substrates: * Lipases split fatty acids into fats and oils. *Proteases and peptidases split proteins into small peptides and amino acids. *Amylases split carbohydrates such as starch and sugars into s ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bicarbonate
In inorganic chemistry, bicarbonate (IUPAC-recommended nomenclature: hydrogencarbonate) is an intermediate form in the deprotonation of carbonic acid. It is a polyatomic anion with the chemical formula . Bicarbonate serves a crucial biochemical role in the physiological pH buffering system. The term "bicarbonate" was coined in 1814 by the English chemist William Hyde Wollaston. The name lives on as a trivial name. Chemical properties The bicarbonate ion (hydrogencarbonate ion) is an anion with the empirical formula and a molecular mass of 61.01 daltons; it consists of one central carbon atom surrounded by three oxygen atoms in a trigonal planar arrangement, with a hydrogen atom attached to one of the oxygens. It is isoelectronic with nitric acid . The bicarbonate ion carries a negative one formal charge and is an amphiprotic species which has both acidic and basic properties. It is both the conjugate base of carbonic acid ; and the conjugate acid of , ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pancreas
The pancreas is an organ of the digestive system and endocrine system of vertebrates. In humans, it is located in the abdomen behind the stomach and functions as a gland. The pancreas is a mixed or heterocrine gland, i.e. it has both an endocrine and a digestive exocrine function. 99% of the pancreas is exocrine and 1% is endocrine. As an endocrine gland, it functions mostly to regulate blood sugar levels, secreting the hormones insulin, glucagon, somatostatin, and pancreatic polypeptide. As a part of the digestive system, it functions as an exocrine gland secreting pancreatic juice into the duodenum through the pancreatic duct. This juice contains bicarbonate, which neutralizes acid entering the duodenum from the stomach; and digestive enzymes, which break down carbohydrates, proteins, and fats in food entering the duodenum from the stomach. Inflammation of the pancreas is known as pancreatitis, with common causes including chronic alcohol use and gallstones. Becaus ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hydrochloric Acid
Hydrochloric acid, also known as muriatic acid, is an aqueous solution of hydrogen chloride. It is a colorless solution with a distinctive pungent smell. It is classified as a strong acid Acid strength is the tendency of an acid, symbolised by the chemical formula HA, to dissociate into a proton, H+, and an anion, A-. The dissociation of a strong acid in solution is effectively complete, except in its most concentrated solutions .... It is a component of the gastric acid in the digestive systems of most animal species, including humans. Hydrochloric acid is an important laboratory reagent and industrial chemical. History In the early tenth century, the Persian physician and alchemist Abu Bakr al-Razi ( 865–925, Latin: Rhazes) conducted experiments with sal ammoniac (ammonium chloride) and vitriol (hydrated sulfates of various metals), which he distilled together, thus producing the gas hydrogen chloride. In doing so, al-Razi may have stumbled upon a primitive method ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pepsinogen
Pepsin is an endopeptidase that breaks down proteins into smaller peptides. It is produced in the gastric chief cells of the stomach lining and is one of the main digestive enzymes in the digestive systems of humans and many other animals, where it helps digest the proteins in food. Pepsin is an aspartic protease, using a catalytic aspartate in its active site. It is one of three principal endopeptidases (enzymes cutting proteins in the middle) in the human digestive system, the other two being chymotrypsin and trypsin. There are also exopeptidases which remove individual amino acids at both ends of proteins (carboxypeptidases produced by the pancreas and aminopeptidases secreted by the small intestine). During the process of digestion, these enzymes, each of which is specialized in severing links between particular types of amino acids, collaborate to break down dietary proteins into their components, i.e., peptides and amino acids, which can be readily absorbed by the small ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gastric Glands
The gastric glands are glands in the lining of the stomach that play an essential role in the process of digestion. All of the glands have mucus-secreting foveolar cells. Mucus lines the entire stomach, and protects the stomach lining from the effects of hydrochloric acid released from other cells in the glands. There are two types of gland in the stomach, the oxyntic gland, and the pyloric gland. The major type of gastric gland is the oxyntic gland that is present in 80 per cent of the stomach, and is often referred to simply as the ''gastric gland''. The oxyntic gland is an exocrine gland and contains the parietal cells that produce hydrochloric acid, and intrinsic factor. Intrinsic factor is necessary for the absorption of vitamin B12. The other type of gland in the stomach is the pyloric gland found in the pyloric region taking up the remaining 20 per cent of the stomach area. The pyloric gland secretes gastrin from its G cells. Pyloric glands are similar in structure to t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |