|
List Of Super Why! Episodes
''Super Why!'' is a CGI-animated superhero preschool television series created by Angela C. Santomero for PBS Kids and aimed for preschoolers ages 3 to 6. The show aired from September 3, 2007 to May 12, 2016. Its episodes are shown below. Series overview Episodes Pilot (2000) Season 1 (2007–2010) Season 2 (2011–2012) Nicholas Kaegi replaces Nicholas Castel Vanderburgh in the role of Whyatt Beanstalk / Super Why. Season 3 (2015–2016) Johnny Orlando replaces Nicholas Kaegi in the role of Whyatt Beanstalk / Super Why, Samuel Faraci replaces Zachary Bloch in the role of Pig / Alpha Pig, and T.J. McGibbon replaces Siera Florindo in the role of Red / Wonder Red. References {{DISPLAYTITLE:List of ''Super Why!'' episodes Super Why! Super Why! ''Super Why!'' (stylized as ''Super WHY!'') is a CGI-animated superhero preschool television series created by Angela C. Santomero (who also created ''Blue's Clues'') for PBS Kids and aimed for preschoolers ages 3 to 6 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Super Why!
''Super Why!'' (stylized as ''Super WHY!'') is a CGI-animated superhero preschool television series created by Angela C. Santomero (who also created ''Blue's Clues'') for PBS Kids and aimed for preschoolers ages 3 to 6. Produced by New York City-based Out of the Blue Enterprises, and Toronto-based C.O.R.E. Toons (animation for season 1 only, being the company's final show produced before their closure on March 15, 2010) and DHX Media (originally through its Decode Entertainment division for seasons one and two), it was distributed by PBS in the United States, Decode Enterprises for seasons 1 and 2, and DHX Distribution for season 3. Originally created as a stop motion pilot in 1999 by Cuppa Coffee Animation that was pitched to Nickelodeon/Nick Jr. but later shown at the 2000 Annecy Film Festival, the show was eventually picked up by PBS Kids, changing the animation to CGI and debuted on September 3, 2007, ending on May 12, 2016 after nearly a decade with a total of 103 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
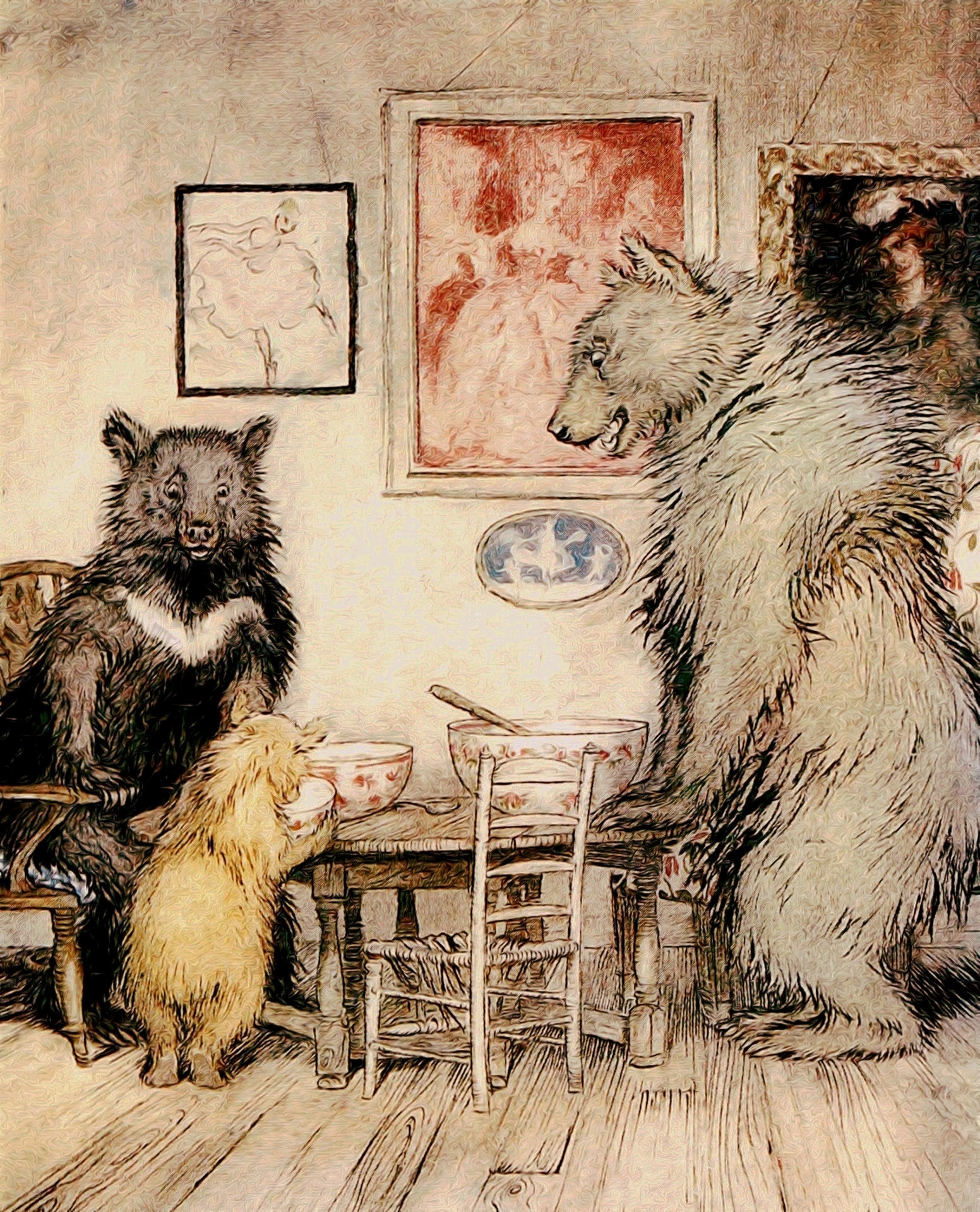
Goldilocks And The Three Bears
"Goldilocks and the Three Bears" (originally titled "The Story of the Three Bears") is a 19th-century English fairy tale of which three versions exist. The original version of the tale tells of an obscene old woman who enters the forest home of three bachelor bears while they are away. She eats some of their porridge, sits down on one of their chairs and breaks it, and sleeps in one of their beds. When the bears return and discover her, she wakes up, jumps out of the window, and is never seen again. The second version replaced the old woman with a young girl named Goldilocks, and the third and by far best-known version replaced the original bear trio with Papa Bear, Mama Bear, and Baby Bear. What was originally a frightening oral tale became a cosy family story with only a hint of menace. The story has elicited various interpretations and has been adapted to film, opera, and other media. "Goldilocks and the Three Bears" is one of the most popular fairy tales in the English la ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tom Thumb
Tom Thumb is a character of English folklore. ''The History of Tom Thumb'' was published in 1621 and was the first fairy tale printed in English. Tom is no bigger than his father's thumb, and his adventures include being swallowed by a cow, tangling with giants, and becoming a favourite of King Arthur. The earliest allusions to Tom occur in various 16th-century works such as Reginald Scot's ''Discovery of Witchcraft'' (1584), where Tom is cited as one of the supernatural folk employed by servant maids to frighten children. Tattershall in Lincolnshire, England, reputedly has the home and grave of Tom Thumb. Aside from his own tales, Tom figures in Henry Fielding's 1730 play ''Tom Thumb'', a companion piece to his ''The Author's Farce''. It was expanded into a single 1731 piece titled '' The Tragedy of Tragedies, or the History of Tom Thumb the Great''. In the mid-18th century, books began to be published specifically for children (some with their authorship attributed to "Tommy Th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Little Red Riding Hood
"Little Red Riding Hood" is a European fairy tale about a young girl and a sly wolf. Its origins can be traced back to several pre-17th century European folk tales. The two best known versions were written by Charles Perrault and the Brothers Grimm. The story has been changed considerably in various retellings and subjected to numerous modern adaptations and readings. Other names for the story are: "Little Red Cap" or simply "Red Riding Hood". It is number 333 in the Aarne–Thompson classification system for folktales. Tale The story revolves around a girl called Little Red Riding Hood. In Perrault's versions of the tale, she is named after her red hooded cape/cloak that she wears. The girl walks through the woods to deliver food to her sickly grandmother (wine and cake depending on the translation). In the Grimms' version, her mother had ordered her to stay strictly on the path. A stalking wolf wants to eat the girl and the food in the basket. He asks her where she is ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
The Princess And The Pea
"The Princess and the Pea" ( da, "Prinsessen paa Ærten"; direct translation: "The Princess on the Pea") is a literary fairy tale by Hans Christian Andersen about a young woman whose royal ancestry is established by a test of her sensitivity. The tale was first published with three others by Andersen in an inexpensive booklet on 8 May 1835 in Copenhagen by C. A. Reitzel. Andersen had heard the story as a child, and it likely has its source in folk material, possibly originating from Sweden, as it is unknown in the Danish oral tradition. Neither "The Princess and the Pea" nor Andersen's other tales of 1835 were well received by Danish critics, who disliked their casual, chatty style and their lack of morals. The tale is classified in the Aarne–Thompson–Uther Index as ATU 704, "The Princess and the Pea". Plot The story tells of a prince who wants to marry a princess but is having difficulty finding a suitable wife. Something is always wrong with those he meets and he ca ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
The Frog Prince
"The Frog Prince; or, Iron Henry" (german: Der Froschkönig oder der eiserne Heinrich, literally "The Frog King or the Iron Henry") is a German fairy tale collected by the Brothers Grimm and published in 1812 in ''Grimm's Fairy Tales'' (KHM 1). Traditionally, it is the first story in their folktale collection. The tale is classified as Aarne-Thompson type 440. Origin Editions The story is best known through the rendition of the Brothers Grimms, who published it in their 1812 edition of ''Kinder- und Hausmärchen'' (''Grimm's Fairy Tales''), as tale no. 1. An older, moralistic version was included in the Grimms' handwritten Ölenberg Manuscript from 1810. Jack Zipes noted in 2016 that the Grimms greatly treasured this tale, considering it to be one of the "oldest and most beautiful in German-speaking regions." Sources The Grimms' source is unclear, but it apparently comes from an oral tradition of Dortchen Wild's family in Kassel. The volume 2 of the first edition of ''Kin ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
The Little Red Hen
''The Little Red Hen'' is an American fable first collected by Mary Mapes Dodge in ''St. Nicholas Magazine'' in 1874. The story is meant to teach children the importance of hard work and personal initiative. The story A hen living on a farm finds some wheat and decides to make bread with it. She asks the other farmyard animals to help her plant it, but they refuse. The hen then harvests and mills the wheat into flour before baking it into bread; at each stage she again asks the animals for help and they refuse. Finally, with her task complete, the hen asks who will help her eat the bread. This time the animals accept eagerly, but the hen refuses them stating that no one helped her with her work and decides to eat the bread herself. She then runs away with it. Background and adaptations The tale is based on a story Dodge's mother often told her. Originally the other animals besides the hen consist of a rat, a cow, a cat, a dog, a duck, and a pig. Later adaptations often reduce ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
The Ant And The Grasshopper
The Ant and the Grasshopper, alternatively titled The Grasshopper and the Ant (or Ants), is one of Aesop's Fables, numbered 373 in the Perry Index. The fable describes how a hungry grasshopper begs for food from an ant when winter comes and is refused. The situation sums up moral lessons about the virtues of hard work and planning for the future. Even in Classical times, however, the advice was mistrusted by some and an alternative story represented the ant's industry as mean and self-serving. Jean de la Fontaine's delicately ironic retelling in French later widened the debate to cover the themes of compassion and charity. Since the 18th century the grasshopper has been seen as the type of the artist and the question of the place of culture in society has also been included. Argument over the fable's ambivalent meaning has generally been conducted through adaptation or reinterpretation of the fable in literature, arts, and music. Fable and counter-fable The fable concerns a gra ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Brian Perkins
Brian Perkins (born 11 September 1943 in Wanganui, New Zealand) is a former senior newsreader on BBC Radio 4. Career He first started working in 1962 in Christchurch on radio stations of the New Zealand Broadcasting Service (NZBS), and its successor, the New Zealand Broadcasting Corporation (NZBC). He worked on 3YA, 3YC and sometimes on 3ZB, and in those days all the work was continuity functions. When he came to Wellington at the end of 1962 he started reading the news both on television and on radio. The NZBC introduced him to many forms of radio including compiling programmes, commentary and other functions. In 1965 he moved to London, and obtained a role announcing and newsreading for the BBC. A keen musician, he began by learning the cello and changed to a double bass. While in London he attended the Guildhall School of Music. In 1969 he went back to New Zealand to play the double bass with the New Zealand Symphony Orchestra. Nine years later he returned to Britain to ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cinderella
"Cinderella",; french: link=no, Cendrillon; german: link=no, Aschenputtel) or "The Little Glass Slipper", is a folk tale with thousands of variants throughout the world.Dundes, Alan. Cinderella, a Casebook. Madison, Wis: University of Wisconsin Press, 1988. The protagonist is a young woman living in forsaken circumstances that are suddenly changed to remarkable fortune, with her ascension to the throne via marriage. The story of Rhodopis, recounted by the Greek geographer Strabo sometime between around 7 BC and AD 23, about a Greek slave girl who marries the king of Egypt, is usually considered to be the earliest known variant of the Cinderella story.Roger Lancelyn Green: ''Tales of Ancient Egypt'', Penguin UK, 2011, , chapter "The Land of Egypt" The first literary European version of the story was published in Italy by Giambattista Basile in his ''Pentamerone'' in 1634; the version that is now most widely known in the English-speaking world was published in French by Charles ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Little Miss Muffet
"Little Miss Muffet" is an English nursery rhyme of uncertain origin, first recorded in 1805. It has a Roud Folk Song Index number of 20605. Wording The rhyme first appeared in print in ''Songs for the Nursery'' (1805), and there have been many variants since. ''The Oxford Dictionary of Nursery Rhymes'' gives the following: :Little Miss Muffet :Sat on a tuffet, :Eating her curds and whey; :There came a big spider, :Who sat down beside her :And frightened Miss Muffet away. Older versions sometimes use "of" rather than "her" in line 3, and refer to a "little spider" as in this example dating between 1837 and 1845: :Little Miss Muffet :She sat on a tuffet, :Eating of curds and whey; :There came a little spider, :Who sat down beside her, :And frighten'd Miss Muffet away. There are several early-published versions with significant variations including "Little Mary Ester sat upon a tester" (1812) and "Little Miss Mopsey, Sat in the shopsey" (1842). Other collected variants ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
The Elves And The Shoemaker
"The Elves and The Shoemaker" (German: ''Die Wichtelmänner'') is a set of fairy tales collected by the Brothers Grimm (KHM 39) about a poor shoemaker who receives much-needed help from three young helpful elves. The original story is the first of three fairy tales contained as entry 39 in the German ''Grimm's Fairy Tales'' under the common title "Die Wichtelmänner". In her translation of 1884 Margaret Hunt chose ''The Elves'' as title for these three stories. The first tale is of Aarne-Thompson (AT) type 503* ('Helpful Elves'), also classified as a migratory legend (AT-7015). The second is of AT 476* type ('A Widwife r Godmotherfor the Elves'), also categorized as a migratory legend (AT 5070). The third tale is of AT 504 type ('The Changeling'), also categorized as a migratory legend (AT 5085). Origin The set of related tales was published by the Brothers Grimm in the first edition of ''Kinder- und Hausmärchen'' (1812), as tale no. 39. Their versions of the three stories a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |