|
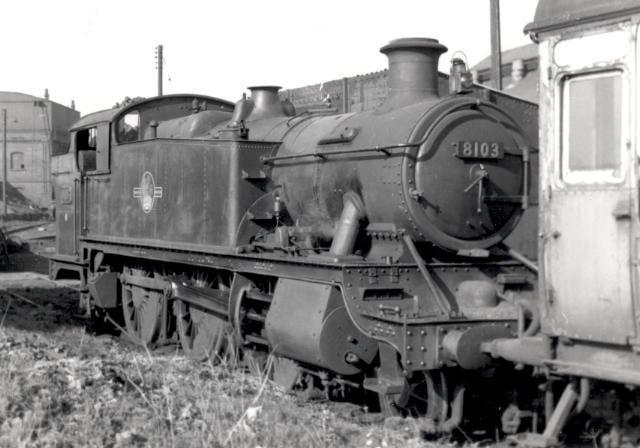
List Of GWR Standard Classes With Two Outside Cylinders
George Jackson Churchward created for the Great Western Railway a family of standard classes of locomotive, based on a limited set of shared dimensions and components, and his principles were followed by his successors. Most of these locomotives had two cylinders, placed outside the frames, and they are listed here, ranging in size from small-wheeled 2-6-2T tank locos to 2-8-0 express freight engines. History of standardisation Standardisation on the GWR started with Daniel Gooch, its first Locomotive Superintendent, who enforced uniformity on third-party suppliers of parts by issuing lithographed copies of drawings and iron templates to check accurate fitting. This was carried through once the GWR built its own works at Swindon, and standard parts were also shared by different classes of locomotive. Joseph Armstrong (and his brother George) used similar techniques at Wolverhampton, and continued Gooch's policy when he replaced him at Swindon. William Dean, Armstrong's succes ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
George Jackson Churchward
George Jackson Churchward (31 January 1857 – 19 December 1933) was an English railway engineer, and was chief mechanical engineer of the Great Western Railway (GWR) in the United Kingdom from 1902 to 1922. Early life Churchward was born at Rowes Farm, Stoke Gabriel, Devon, where his ancestors (the senior line residing at Hill House; his paternal grandfather, Matthew, was the younger son of the head of the family) had been squires since 1457. He was the first son in a family of three sons and two daughters, brothers John (b.1858) and James (b.1860) and sisters Mary (b.1863) and Adelina (b.1870). His father, George Churchward, a farmer, married his cousin, Adelina Mary, daughter of Thomas Churchward, of Paignton, Devon, a corn and cider merchant. He was educated at the Totnes Grammar School, King Edward VI Grammar School, contained within the Mansion House on Fore Street, Totnes, Devon. His father's cousin, Frederick Churchward, head of the family, arranged private tuition at H ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
GWR 6000 Class
The Great Western Railway (GWR) 6000 Class or King Class is a class of 4-6-0 steam locomotives designed for express passenger work and introduced in 1927. They were the largest locomotives built by the GWR, apart from the unique Pacific ( ''The Great Bear''). The class was named after kings of the United Kingdom and of England, beginning with the then reigning monarch, King George V, and going back through history. They handled the principal GWR expresses on the main line from London to the West of England and on the Chiltern line to Birmingham and Wolverhampton, until 1962 when the class was withdrawn. Background and development By 1918, it was apparent to the GWR chief mechanical engineer George Jackson Churchward that his Star Class 4-6-0 locomotives would soon be incapable of handling the heaviest West of England expresses without assistance. He therefore proposed fitting the diameter boiler used on his 4700 Class 2-8-0 on to a 4-6-0 chassis, in 1919, to create a more ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
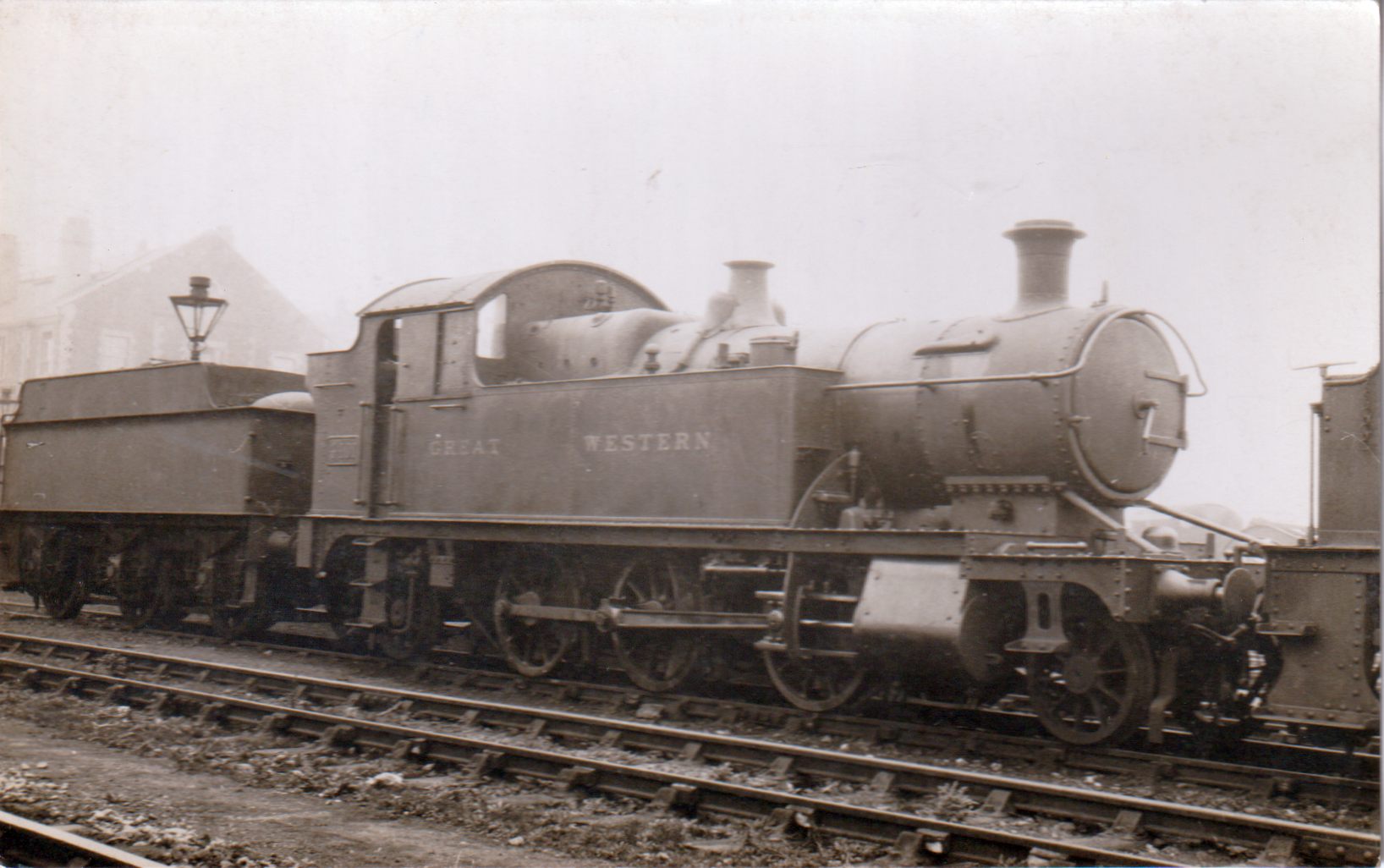
GWR 2221 Class
The Great Western Railway (GWR) 2221 Class or County Tank was a class of 4-4-2T steam locomotive, effectively a tank engine version of the 3800 "County" Class 4-4-0 tender locomotives. The two classes had different boilers, standard no 4 for the tender locomotive, and the smaller (by about ) standard no 2 for the tank. 2230 was fitted with the larger boiler when new, but this was unsuccessful and was quickly altered. Construction Thirty were built between 1905 and 1912 to replace the 3600 "Birdcage" Class. They were built in three batches of ten, the batches having minor differences. In the final batch the drop in the front framing above the cylinders was curved, the cylinders were also lower, superheaters and top feed were fitted from new. Later in life, the earlier members of the class were fitted with superheaters, and some were given larger bunkers in line with other standard tank classes. Use Their work was concentrated on London suburban services. They were replaced by ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
GWR 4400 Class
The Great Western Railway (GWR) 4400 Class was a class of 2-6-2T side tank steam locomotive. History They were introduced in 1904 for work on small branch lines. The 4500 class was a later development with larger driving wheels. The 4400s were particularly used in hilly districts, notably the Princetown and Much Wenlock Branches. All were withdrawn and scrapped between 1949 and 1955. The 4400, 4500 and 4575 classes, which all had stroke cylinders, the Standard 5 boiler and driving wheels under , were collectively known as "Small Prairies", as opposed to the 5100, 3150, 5101, 6100, 3100 and 8100 classes, with stroke cylinders, Standard 2 or 4 boilers and driving wheels over , known as "Large Prairies". See also *GWR 4500 Class *GWR 4575 Class * List of GWR standard classes with two outside cylinders George Jackson Churchward created for the Great Western Railway a family of standard classes of locomotive, based on a limited set of shared dimensions and compone ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
GWR 3800 Class
The Great Western Railway 3800 Class, also known as the County Class, were a class of 4-4-0 steam locomotives for express passenger train work introduced in 1904 in a batch of ten. Two more batches followed in 1906 and 1912 with minor differences. They were designed by George Jackson Churchward, who used standard components to produce a four-coupled version of his Saint Class 4-6-0s. Construction The first locomotive, No. 3473 ''County of Middlesex'', was built at Swindon Works in May 1904, with the following nine completed by October 1904. They were initially fitted with parallel-sided copper-capped chimneys, which were soon replaced by tapered cast iron chimneys. The second batch, of twenty, were built between October and December 1906. This batch had tapered cast iron chimneys from the start. A third and last batch of ten were built between December 1911 and February 1912. On these the footplates had curved drop ends at the cab and front bufferbeam. They were also fitted fro ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
GWR 5100 Class
The Great Western Railway (GWR) GWR 5100 Class (known as the 3100 class between 1912 and 1927) was a class of 2-6-2T side tank steam locomotives. It was the first of a series of broadly similar classes used principally for suburban passenger services. History The class was developed from one of George Jackson Churchward's pioneer designs – No 99 – and a number of derivative classes were built from 1906 to 1950. The development is somewhat convoluted to follow, because of various renumberings and gaps in the number series as listed below. No. 99 was built in 1903 and given an extended trial over the ensuing two years. Fitted with the standard number 2 boiler running at , flat topped tanks and driving wheels of in diameter, it was the forerunner of 289 similar locomotives that were to follow. 39 more examples were built to this initial design. This production batch differed from the prototype only in that the tank tops were sloping to aid visibility and the cab sides were ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
GWR 2884 Class
The Great Western Railway (GWR) 2884 Class is a class of 2-8-0 steam locomotive. They were Collett's development of Churchward's earlier 2800 Class and are sometimes regarded as belonging to that class. History The 2884s were designed for heavy freight work and differed from the original Class 2800 engines (Nos. 2800-2883) in a number of respects, the most obvious being that a more modern Collett side window cab was provided and that they were built with outside steam pipes. Production 83 of the 2884 class were built between 1938 and 1941. Those built during the war did not have the side window to the cab, and the side window on the others was plated over. This was to reduce glare, as a precaution against enemy air attacks. The windows were reinstated after the war. The locomotives were so popular with the ex-Great Western crews that the British Railways Western Region operating authorities wanted more of the class built after nationalisation in 1948; however, this req ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
GWR 2800 Class
The Great Western Railway (GWR) 2800 Class is a class of Churchward-designed 2-8-0 steam locomotive. History The class was designed by George Jackson Churchward for heavy freight work. They were the first 2-8-0 locomotive class in Great Britain. The prototype, originally numbered 97 but later renumbered 2800, appeared in 1903. Construction of the production series commenced in 1905 and continued until 1919. The 2884 Class which appeared in 1938–1942 was developed from the 2800 class and is sometimes classified with it. Prototype No. 97 was originally outshopped in lined black livery and undertook two years of trials before the type went into production. Initial results suggested that only the front end needed further development and where the boiler of No. 97 was parallel for the first four segments, the production series had the familiar taper boiler. Initially the boiler pressure of the 2-8-0 was set at with diameter cylinders. Tractive effort started out at but ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Compound Locomotive
A compound locomotive is a steam locomotive which is powered by a compound engine, a type of steam engine where steam is expanded in two or more stages. The locomotive was only one application of compounding. Two and three stages were used in ships, for example. Compounding became popular for railway locomotives from the early 1880s and by the 1890s were becoming common. Large numbers were constructed, mostly two- and four-cylinder compounds, in France, Germany, Austria, Hungary, and the United States. It declined in popularity due to maintenance issues and because superheating provided similar efficiencies at lower cost. Nonetheless, compound Mallets were built by the Norfolk and Western Railway right up to 1952. Introduction In the usual arrangement for a compound engine the steam is first expanded in one or two high-pressure ''(HP)'' cylinders, then having given up some heat and lost some pressure, it exhausts into a larger-volume low-pressure ''(LP)'' cylinder, (or two, - or ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
GWR 2900 Class
The Great Western Railway 2900 Class or Saint Class, which was built by the Great Western Railway's Swindon Works, incorporated several series of 2-cylinder passenger steam locomotives designed by George Jackson Churchward and built between 1902 and 1913 with differences in the dimensions. The majority of these were built as 4-6-0 locomotives; but thirteen examples were built as 4-4-2 (but converted to 4-6-0 during 1912/13). They proved to be a successful class which established the design principles for GWR 2-cylinder classes over the next fifty years. Background After finally converting the last broad gauge lines in 1892, the Great Western Railway (GWR) began a period of modernization as new cut-off lines shortened its routes to west of England, South Wales and Birmingham. During the first decade of the twentieth century the Chief Mechanical Engineer, George Jackson Churchward, designed or acquired a number of experimental locomotives with different wheel arrangements and boile ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
GWR 3000 Class
The Great Western Railway (GWR) 3000 Class was a class of 2-8-0 steam locomotive consisting of the ex-Railway Operating Division ROD 2-8-0. These were built by North British Locomotive Co. between 1917 and 1918. No examples have been preserved. Initial loans and purchase The GWR borrowed several ROD 2-8-0s during the First World War but these were returned to the government after the end of the war. In 1919, GWR bought 20 virtually new RODs, and numbered them 3000–19. A further 84 were hired in July 1919, and were numbered 3020-99 and 6000–3, but these were returned in October 1922. In 1925, the GWR bought 80 engines (including some previously hired) and numbered them 3020–99. Overhaul and sorting In 1926/7 the GWR sorted the eighty RODs bought in 1925 which had been given nos. 3020–99 into two batches, which involved considerable renumbering. The worst fifty were touched up and returned to traffic with steel fireboxes and painted the original R.O.D. black and renum ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Railway Operating Division
The Railway Operating Division (ROD) was a division of the Royal Engineers formed in 1915 to operate railways in the many theatres of the First World War. It was largely composed of railway employees and operated both standard gauge and narrow gauge railways. The ROD operated their first line on a section of the Hazebrouck–Ypres line. The work was carried out by former employees of the London and North Western Railway. The ROD requisitioned many diverse locomotives from Britain's railway companies and leased several Belgian locomotives sent to France in 1914, but as the war dragged on adopted the Great Central Railway's Robinson Class 8K 2-8-0 as its standard freight locomotive to become the ROD 2-8-0. Some locomotives were also purchased from Baldwin in the United States. They also operated narrow-gauge engines (meter gauge or gauge trains). After the war, requisitioned locomotives returned to their foreign owners. * the ROD 2-8-0 were stored in Great Britain and sold t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
.jpg)

.jpg)