|
Lissencephaly
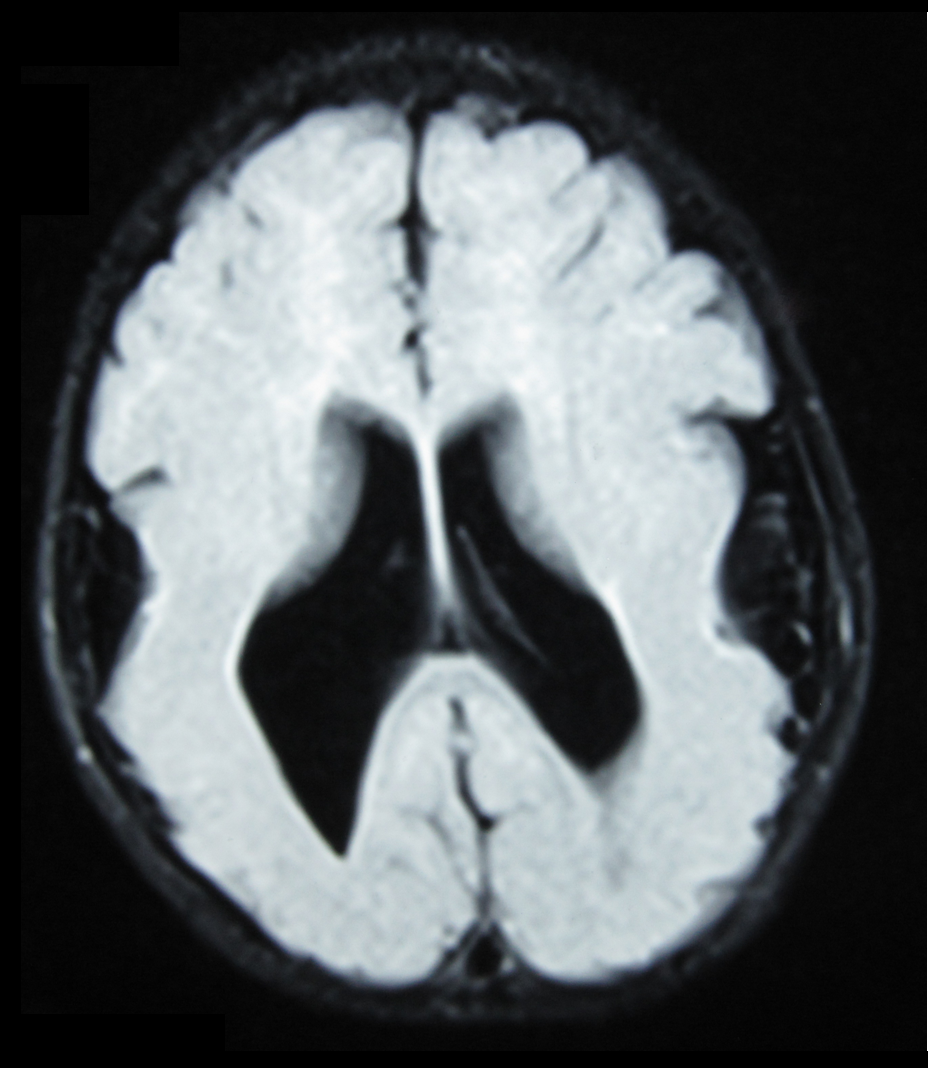
Lissencephaly (, meaning "smooth brain") is a set of rare brain disorders whereby the whole or parts of the surface of the brain appear smooth. It is caused by defective neuronal migration during the 12th to 24th weeks of gestation resulting in a lack of development of brain folds (gyri) and grooves (sulci). It is a form of cephalic disorder. Terms such as ''agyria'' (no gyri) and ''pachygyria'' (broad gyri) are used to describe the appearance of the surface of the brain. Children with lissencephaly generally have significant developmental delays, but these vary greatly from child to child depending on the degree of brain malformation and seizure control. Life expectancy can be shortened, generally due to respiratory problems. Symptoms and signs Affected children display severe psychomotor impairment, failure to thrive, seizures, and muscle spasticity or hypotonia. Other symptoms of the disorder may include unusual facial appearance, difficulty swallowing, and anomalies of the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lissencephaly
Lissencephaly (, meaning "smooth brain") is a set of rare brain disorders whereby the whole or parts of the surface of the brain appear smooth. It is caused by defective neuronal migration during the 12th to 24th weeks of gestation resulting in a lack of development of brain folds (gyri) and grooves (sulci). It is a form of cephalic disorder. Terms such as ''agyria'' (no gyri) and ''pachygyria'' (broad gyri) are used to describe the appearance of the surface of the brain. Children with lissencephaly generally have significant developmental delays, but these vary greatly from child to child depending on the degree of brain malformation and seizure control. Life expectancy can be shortened, generally due to respiratory problems. Symptoms and signs Affected children display severe psychomotor impairment, failure to thrive, seizures, and muscle spasticity or hypotonia. Other symptoms of the disorder may include unusual facial appearance, difficulty swallowing, and anomalies of the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
LIS1
Platelet-activating factor acetylhydrolase IB subunit alpha is an enzyme that in humans is encoded by the ''PAFAH1B1'' gene. The protein is often referred to as Lis1 and plays an important role in regulating the motor protein Dynein. Function PAFAH1B1 was identified as encoding a gene that when mutated or lost caused the lissencephaly associated with Miller–Dieker syndrome. PAFAH1B1 encodes the non-catalytic alpha subunit of the intracellular Ib isoform of platelet-activating factor acetylhydrolase, a heterotrimeric enzyme that specifically catalyzes the removal of the acetyl group at the SN-2 position of platelet-activating factor (identified as 1-O-alkyl-2-acetyl-sn-glyceryl-3-phosphorylcholine). Two other isoforms of intracellular platelet-activating factor acetylhydrolase exist: one composed of multiple subunits, the other, a single subunit. In addition, a single-subunit isoform of this enzyme is found in serum. According to one study, PAFAH1B1 interacts with VLDLR rece ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pachygyria
Pachygyria (from the Greek "pachy" meaning "thick" or "fat" gyri) is a congenital malformation of the cerebral hemisphere. It results in unusually thick convolutions of the cerebral cortex. Typically, children have developmental delay and seizures, the onset and severity depending on the severity of the cortical malformation. Infantile spasms are common in affected children, as is intractable epilepsy. Presentation The term 'pachygyria' does not directly relate to a specific malformation but rather is used to generally describe physical characteristics of the brain in association with several neuronal migration disorders; most commonly disorders relating to varied degrees of lissencephaly. Lissencephaly is present in 1 of 85,470 births and the life span of those affected is short as only a few survive past the age of 20. Pachygyria is a condition identified by a type of cortical genetic malformation. Clinicians will subjectively determine the malformation based on the degree of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
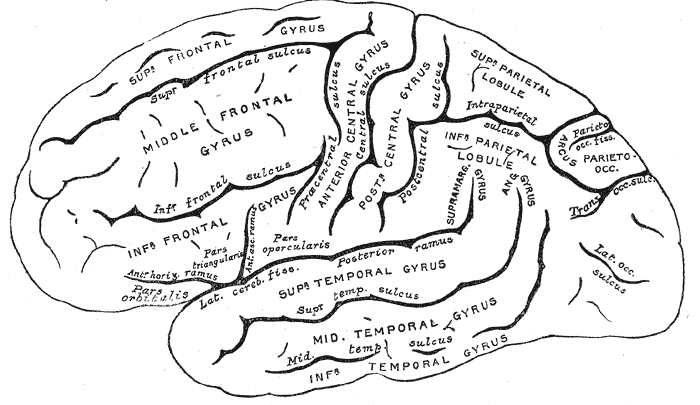
Gyrus
In neuroanatomy, a gyrus (pl. gyri) is a ridge on the cerebral cortex. It is generally surrounded by one or more sulci (depressions or furrows; sg. ''sulcus''). Gyri and sulci create the folded appearance of the brain in humans and other mammals. Structure The gyri are part of a system of folds and ridges that create a larger surface area for the human brain and other mammalian brains. Because the brain is confined to the skull, brain size is limited. Ridges and depressions create folds allowing a larger cortical surface area, and greater cognitive function, to exist in the confines of a smaller cranium. Development The human brain undergoes gyrification during fetal and neonatal development. In embryonic development, all mammalian brains begin as smooth structures derived from the neural tube. A cerebral cortex without surface convolutions is lissencephalic, meaning 'smooth-brained'. As development continues, gyri and sulci begin to take shape on the fetal brain, with ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gyri
In neuroanatomy, a gyrus (pl. gyri) is a ridge on the cerebral cortex. It is generally surrounded by one or more sulci (depressions or furrows; sg. ''sulcus''). Gyri and sulci create the folded appearance of the brain in humans and other mammals. Structure The gyri are part of a system of folds and ridges that create a larger surface area for the human brain and other mammalian brains. Because the brain is confined to the skull, brain size is limited. Ridges and depressions create folds allowing a larger cortical surface area, and greater cognitive function, to exist in the confines of a smaller cranium. Development The human brain undergoes gyrification during fetal and neonatal development. In embryonic development, all mammalian brains begin as smooth structures derived from the neural tube. A cerebral cortex without surface convolutions is lissencephalic, meaning 'smooth-brained'. As development continues, gyri and sulci begin to take shape on the fetal brain, with ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gyrification
Gyrification is the process of forming the characteristic folds of the cerebral cortex. The peak of such a fold is called a ''gyrus'' (pl. ''gyri''), and its trough is called a '' sulcus'' (pl. ''sulci''). The neurons of the cerebral cortex reside in a thin layer of gray matter, only 2–4 mm thick, at the surface of the brain. Much of the interior volume is occupied by white matter, which consists of long axonal projections to and from the cortical neurons residing near the surface. Gyrification allows a larger cortical surface area and hence greater cognitive functionality to fit inside a smaller cranium. In most mammals, gyrification begins during fetal development. Primates, cetaceans, and ungulates have extensive cortical gyri, with a few species exceptions, while rodents generally have none. Gyrification in some animals, for example the ferret, continues well into postnatal life. Gyrification during human brain development As fetal development proceeds, gyri ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Reelin
Reelin, encoded by the ''RELN'' gene, is a large secreted extracellular matrix glycoprotein that helps regulate processes of neuronal migration and positioning in the developing brain by controlling cell–cell interactions. Besides this important role in early development, reelin continues to work in the adult brain. It modulates synaptic plasticity by enhancing the induction and maintenance of long-term potentiation. It also stimulates dendrite and dendritic spine development and regulates the continuing migration of neuroblasts generated in adult neurogenesis sites like the subventricular and subgranular zones. It is found not only in the brain but also in the liver, thyroid gland, adrenal gland, Fallopian tube, breast and in comparatively lower levels across a range of anatomical regions. Reelin has been suggested to be implicated in pathogenesis of several brain diseases. The expression of the protein has been found to be significantly lower in schizophrenia and psycho ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Neuronal Migration Disorder
Neuronal migration disorder (NMD) refers to a heterogenous group of disorders that, it is supposed, share the same etiopathological mechanism: a variable degree of disruption in the migration of neuroblasts during neurogenesis. The neuronal migration disorders are termed cerebral dysgenesis disorders, brain malformations caused by primary alterations during neurogenesis; on the other hand, brain malformations are highly diverse and refer to any insult to the brain during its formation and maturation due to intrinsic or extrinsic causes that ultimately will alter the normal brain anatomy. However, there is some controversy in the terminology because virtually any malformation will involve neuroblast migration, either primarily or secondarily. Symptoms and signs Symptoms vary according to the abnormality, but often feature poor muscle tone and motor function, seizures, developmental delays, mental retardation Intellectual disability (ID), also known as general learning disabilit ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
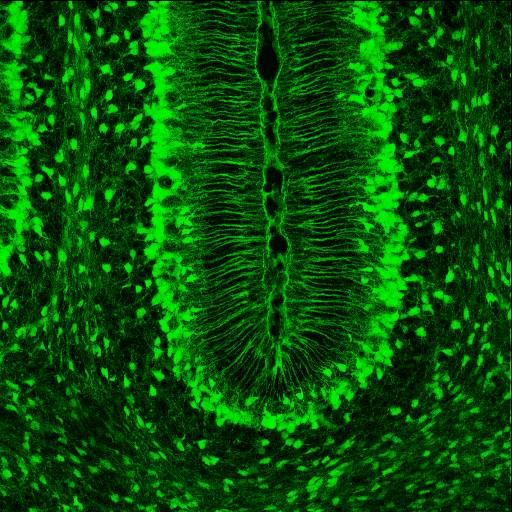
Radial Glia
Radial glial cells, or radial glial progenitor cells (RGPs), are bipolar-shaped progenitor cells that are responsible for producing all of the neurons in the cerebral cortex. RGPs also produce certain lineages of glia, including astrocytes and oligodendrocytes. Their cell bodies (somata) reside in the embryonic ventricular zone, which lies next to the developing ventricular system. During development, newborn neurons use radial glia as scaffolds, traveling along the radial glial fibers in order to reach their final destinations. Despite the various possible fates of the radial glial population, it has been demonstrated through clonal analysis that most radial glia have restricted, unipotent or multipotent, fates. Radial glia can be found during the neurogenic phase in all vertebrates (studied to date). The term "radial glia" refers to the morphological characteristics of these cells that were first observed: namely, their radial processes and their similarity to astrocytes, a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chromosome 7
Chromosome 7 is one of the 23 pairs of chromosomes in humans, who normally have two copies of this chromosome. Chromosome 7 spans about 159 million base pairs (the building material of DNA) and represents between 5 and 5.5 percent of the total DNA in cells. Genes Number of genes The following are some of the gene count estimates of human chromosome 7. Because researchers use different approaches to genome annotation their predictions of the number of genes on each chromosome varies (for technical details, see gene prediction). Among various projects, the collaborative consensus coding sequence project ( CCDS) takes an extremely conservative strategy. So CCDS's gene number prediction represents a lower bound on the total number of human protein-coding genes. Gene list The following is a partial list of genes on human chromosome 7. For complete list, see the link in the infobox on the right. Diseases and disorders The following diseases are some of those related to genes ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Doublecortin
Neuronal migration protein doublecortin, also known as doublin or lissencephalin-X is a protein that in humans is encoded by the DCX gene. Function Doublecortin (DCX) is a microtubule-associated protein expressed by neuronal precursor cells and immature neurons in embryonic and adult cortical structures. Neuronal precursor cells begin to express DCX while actively dividing, and their neuronal daughter cells continue to express DCX for 2–3 weeks as the cells mature into neurons. Downregulation of DCX begins after 2 weeks, and occurs at the same time that these cells begin to express NeuN, a neuronal marker. Due to the nearly exclusive expression of DCX in developing neurons, this protein has been used increasingly as a marker for neurogenesis. Indeed, levels of DCX expression increase in response to exercise, and that increase occurs in parallel with increased BrdU labeling, which is currently a "gold standard" in measuring neurogenesis. Doublecortin was found to bind to th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cephalic Disorder
Cephalic disorders () are congenital conditions that stem from damage to, or abnormal development of, the budding nervous system. Cephalic disorders are not necessarily caused by a single factor, but may be influenced by hereditary or genetic conditions, nutritional deficiencies, or by environmental exposures during pregnancy, such as medication taken by the mother, maternal infection, or exposure to radiation. Some cephalic disorders occur when the cranial sutures (the fibrous joints that connect the bones of the skull) join prematurely. Most cephalic disorders are caused by a disturbance that occurs very early in the development of the fetal nervous system. The human nervous system develops from a small, specialized plate of cells on the surface of the embryo. Early in development, this plate of cells forms the neural tube, a narrow sheath that closes between the third and fourth weeks of pregnancy to form the brain and spinal cord of the embryo. Four main processes are resp ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |