|
Linxia City
Linxia City (, Xiao'erjing: لٍِثِيَا شِ), once known as Hezhou (, Xiao'erjing: حَجِوْ), is a county-level city in the province of Gansu of the China, People's Republic of China and the capital of the multi-ethnic Linxia Hui Autonomous Prefecture. It is located in the valley of the Daxia River (a right tributary of the Yellow River), (by China National Highway 213, road) southwest of the provincial capital Lanzhou.Linxia City brief info, on the web site of the prefectural government (The page itself is dated April 2008, but does not state the dates for which population estimates have been made) The population of the entire county-level city of Linxia (which includes both the central city and some rural area) is estimated at 250,000; of which, 58.4% is class ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
County-level City
A county-level municipality (), county-level city or county city, formerly known as prefecture-controlled city (1949–1970: ; 1970–1983: ), is a Administrative divisions of China#County level (3rd), county-level administrative division of the China, People's Republic of China. County-level cities have judiciary, judicial but no legislature, legislative rights over their own local ordinance, local law and are usually governed by Administrative divisions of China#Prefectural level (2nd), prefecture-level divisions, but a few are governed directly by Administrative divisions of China#Provincial level (1st), province-level divisions. A county-level city is a "city" () and "county" () that have been merged into one unified jurisdiction. As such it is simultaneously a city, which is a municipal entity and a county which is an administrative division of a prefecture. Most county-level cities were created in the 1980s and 1990s by replacing denser populated Counties of Chin ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Salar People
The Salar people ( zh, c=撒拉族, p=Sālāzú) are a Turkic ethnic minority of China who largely speak the Salar language, an Oghuz language. The Salar people numbered 130,607 people in the last census of 2010. The Salars live mostly in the Qinghai-Gansu border region, on both sides of the Yellow River, namely in Xunhua Salar Autonomous County, Hualong Hui Autonomous County of Qinghai and the adjacent Jishishan Bonan, Dongxiang and Salar Autonomous County of Gansu and in some parts of Henan and Shanxi. There are also Salars in Northern Xinjiang (in the Ili Kazakh Autonomous Prefecture). They are a patriarchal agricultural society and are predominantly Muslim. Salars live in Gansu's Lintan County and Xining, Linxia County and Qinghai's Hualong Hui autonomous county and Xunhua Salar autonomous county. History Origin According to Salar tradition and Chinese chronics, the Salars are the descendants of the Salur tribe, belonging to the Oghuz Turk tribe of the Western Turkic K ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Town (China)
When referring to political divisions of China, town is the standard English translation of the Chinese (traditional: ; ). The Constitution of the People's Republic of China classifies towns as third-level administrative units, along with for example townships (). A township is typically smaller in population and more remote than a town. Similarly to a higher-level administrative units, the borders of a town would typically include an urban core (a small town with the population on the order of 10,000 people), as well as rural area with some villages (, or ). Map representation A typical provincial map would merely show a town as a circle centered at its urban area and labeled with its name, while a more detailed one (e.g., a map of a single county-level division) would also show the borders dividing the county or county-level city into towns () and/or township () and subdistrict (街道) units. The town in which the county level government, and usually the division's mai ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Jiedao
A subdistrict ()' is one of the smaller administrative divisions of China. It is a form of township-level division which is typically part of a larger urban area, as opposed to a discrete town (zhèn, 镇) surrounded by rural areas, or a rural township (xiāng, 乡). In general, urban areas are divided into subdistricts and a subdistrict is sub-divided into several residential communities or neighbourhood A neighbourhood (British English, Irish English, Australian English and Canadian English) or neighborhood (American English; see spelling differences) is a geographically localised community within a larger city, town, suburb or rural are ...s as well as into villagers' groups (居民区/居住区, 小区/社区, 村民小组). The subdistrict's administrative agency is the subdistrict office ()"【街道办事处】 jiēdào bànshìchù 市辖区、不设区的市的人民政府派出机关。在上一级政府领导下,负责本辖区内的社区服务、经� ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dongxiang Autonomous County
Dongxiang Autonomous County (; Santa: Dunxianzu Zizhixien) is an autonomous county in the Linxia Hui Autonomous Prefecture, province of Gansu of the People's Republic of China. It was established as a Dongxiang ethnic autonomous area in 1950. Historically, Dongxiang has long been directly under the jurisdiction of Linxia. During the Republic of China (1912–1949) period, its area was divided between the surrounding counties. Its population in 2020 was 381,700, 88% of whom belonging to the Dongxiang minority group. As of 1993, half of the total Dongxiang minority population lived in the county. At least until the end of the 20th century, Dongxiang County was very impoverished and undeveloped, having a literacy rate of just 15%, the lowest in China. In 2017, it had the highest poverty rate of Gansu, already the poorest province in China. Dongxiang County has a typical Loess Plateau landscape, with numerous gullies and mountains and a dry climate. Administrative divisions Dong ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Linxia County
Linxia County (, Xiao'erjing: ) is a county in the Linxia Hui Autonomous Prefecture, province of Gansu of the People's Republic of China. Geography Linxia County is located in central and south-western parts of the Linxia Hui Autonomous Prefecture, extending from the shores of Liujiaxia Reservoir in the north (at 1735 m elevation above the sea level, the lowest part of the county), to Taizu Mountains in the south and Dalijia Mountain (, ) (at 4613 m elevation above the sea level, the highest point in the county) in the west. The county's river network is formed primarily by small rivers that flow to the northeast and north from the mountains that line the county's southwestern border toward the Yellow River (i.e., these days, the Liujiaxia Reservoir) near the northern end of the county. The largest of these rivers is the Daxia River (, ), which flows from the Gannan Tibetan Autonomous Prefecture to cross Linxia County. The river's lower course forms the border between Linxia ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
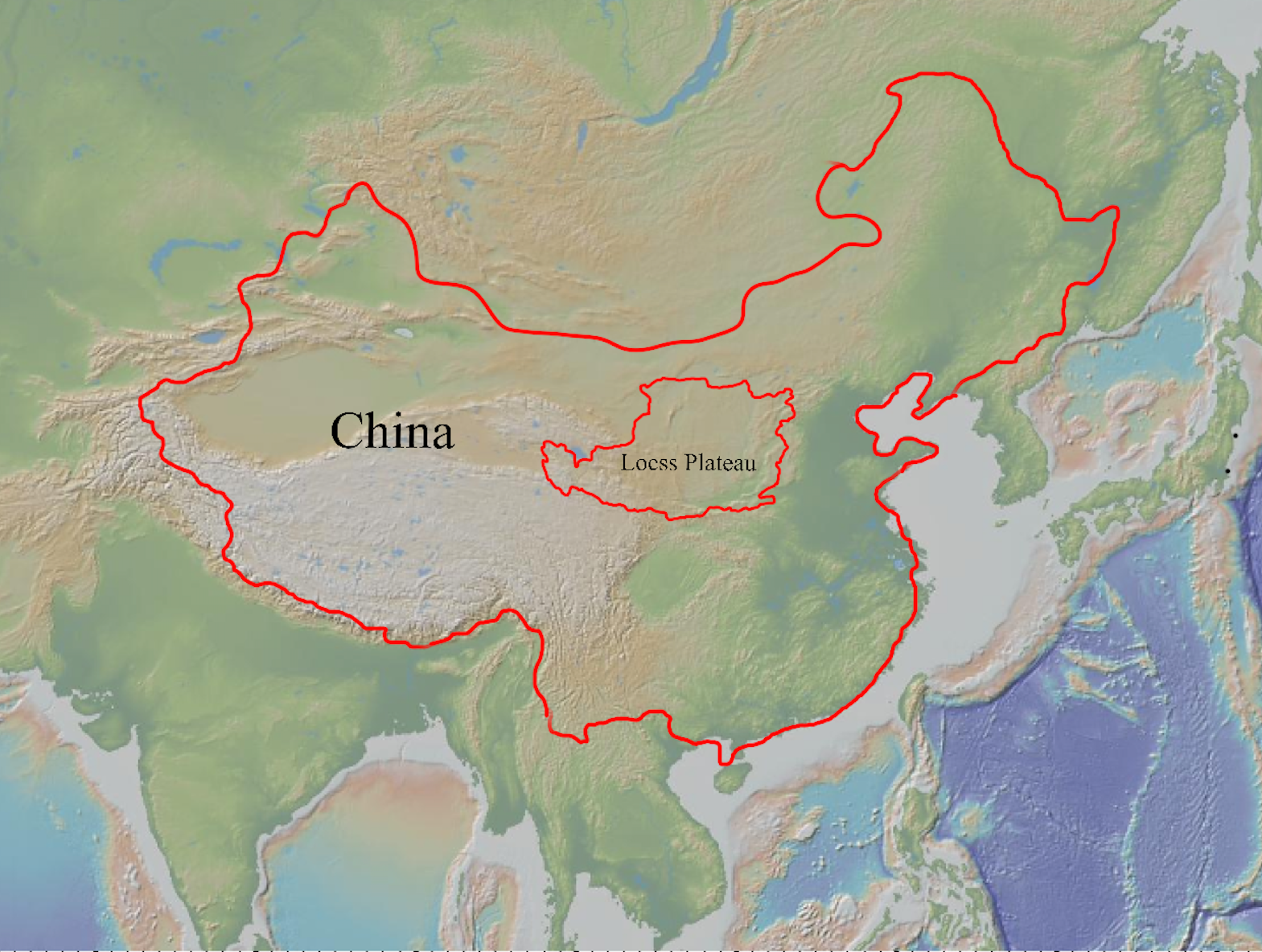
Loess Plateau
The Chinese Loess Plateau, or simply the Loess Plateau, is a plateau in north-central China formed of loess, a clastic silt-like sediment formed by the accumulation of wind-blown dust. It is located southeast of the Gobi Desert and is surrounded by the Yellow River. It includes parts of the Chinese provinces of Gansu, Shaanxi and Shanxi. The depositional setting of the Chinese Loess Plateau was shaped by the tectonic movement in the Neogene period, after which strong southeast winds caused by the East Asian Monsoon transported sediment to the plateau during the Quaternary period. The three main morphological types in the Loess Plateau are loess platforms, ridges and hills, formed by the deposition and erosion of loess. Most of the loess comes from the Gobi Desert and other nearby deserts. The sediments were transported to the Loess Plateau during interglacial periods by southeasterly prevailing winds and winter monsoon winds. After the deposition of sediments on the plateau ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
5703-Linxia-City-Worshippers-leaving-a-mosque-near-Daxia-River-SW-of-downtown , a semi-automatic pistol
{{Numberdis ...
57 may refer to: * 57 (number) * one of the years 57 BC, AD 57, 1957, 2057 * "57" (song), a song by Biffy Clyro * "Fifty Seven", a song by Karma to Burn from the album ''Arch Stanton'', 2014 * "57" (album), a studio album by Klaus Major Heuser Band in 2014 * "57 Live" (album), a live double-album by Klaus Major Heuser Band in 2015 * Heinz 57 (varieties), a former advertising slogan * Maybach 57, a car * American Base Hospital No. 57 * Swift Current 57's, baseball team in the Western Canadian Baseball League * FN Five-Seven The FN Five-seven (stylized as Five-seveN) is a semi-automatic pistol designed and manufactured by FN Herstal in Belgium. The pistol is named for its 5.7×28mm (.224 in) bullet diameter, and the trademark capitalization style is intended to ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
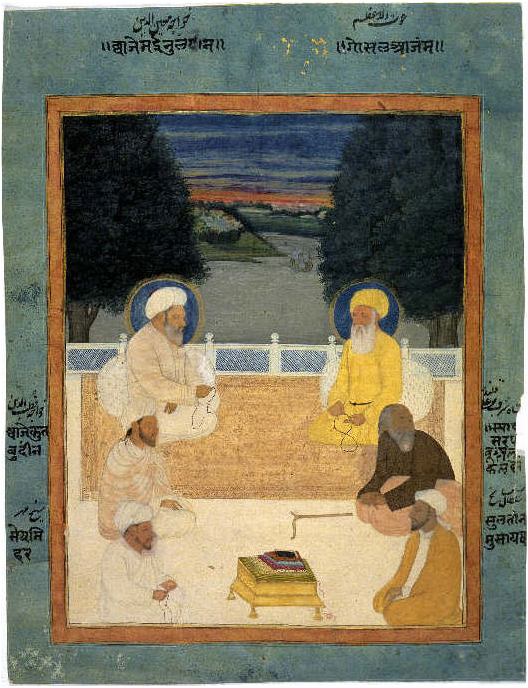
Jahriyya
Jahriyya (also spelled Jahrīya or Jahriyah) is a ''menhuan'' (Sufi order) in China, commonly called the New Teaching (''Xinjiao''). Founded in the 1760s by Ma Mingxin, it was active in the late 18th and 19th centuries in what was then Gansu Province (also including parts of today's Qinghai and Ningxia), when its followers were involved in a number of conflicts with other Muslim groups and in several rebellions against China's ruling Qing dynasty. The name comes from the Arabic word ''jahr'' (جهر), referring to their practice of vocally performing the ''dhikr'' (invocation of the name of God). This contrasted with the more typical Naqshbandi practice of performing it silently, as observed by the Khufiyya or Old Teaching. Ma Mingxin opposed the practice of saint veneration which had become popular in China. History Foundation and principles The Jahriya order was founded by the Gansu Chinese-speaking Muslim scholar Ma Mingxin soon after his return to China in 1761, after 16 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ma Mingxin
Ma Mingxin (1719–1781) () was a Chinese Sufi master, the founder of the Jahriyya ''menhuan'' (Naqshbandi Sufi order). Names Ma Mingxin's Arabic given name was Ibrāhīm. After returning to China from Arabia he started calling himself 'Azīz. He was also called Muhammad Emin ( ar, محمد أمين}). Followers of the Jahriyyah sometimes refer to him by the title of Wiqāyatullāh (: وقاية الله)Life A[...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sufism
Sufism ( ar, ''aṣ-ṣūfiyya''), also known as Tasawwuf ( ''at-taṣawwuf''), is a mystic body of religious practice, found mainly within Sunni Islam but also within Shia Islam, which is characterized by a focus on Islamic spirituality, ritualism, asceticism and esotericism. It has been variously defined as "Islamic mysticism",Martin Lings, ''What is Sufism?'' (Lahore: Suhail Academy, 2005; first imp. 1983, second imp. 1999), p.15 "the mystical expression of Islamic faith", "the inward dimension of Islam", "the phenomenon of mysticism within Islam", the "main manifestation and the most important and central crystallization" of mystical practice in Islam, and "the interiorization and intensification of Islamic faith and practice". Practitioners of Sufism are referred to as "Sufis" (from , ), and historically typically belonged to "orders" known as (pl. ) – congregations formed around a grand who would be the last in a chain of successive teachers linking back to Muham ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Khufiyya
Khufiyya (; Arabic: خفيه, the silent ones) is a Sufist order of Chinese Islam. It was the first Sufist order to be established within China and, along with Jahriyya, Qadiriyya and Kubrawiyyah, is acknowledged as one of the four orders of Chinese Sufism. Adherents of Khufiyya dwell mainly in Northwestern China, especially Gansu Province. The order follows the school of Hanafi in terms of jurisprudence. Traditional beliefs within the order claim the origin of Khufiyya to be Abu Bakr. In addition, the doctrines of Khufiyya are influenced by Confucianism, the Confucian approach or way of expounding Islamic sacred texts known as "Yiru Quanjing" (以儒詮經). History The origin of Khufiyya can be traced to the Naqshbandis of Central Asia, a Sunni spiritual order of Sufism, which in turn has its roots in Sham. Their missions gave rise to the prosperity of Sufis in Bukhara and Samarkand. Makhdumi Azam, a 17th-century Naqshbandi leader, settled in Kashgar where his offsprin ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |