|
Linking Verb
In traditional grammar and guide books, a linking verb is a verb that describes the subject by connecting it to a predicate adjective or predicate noun A noun () is a word that generally functions as the name of a specific object or set of objects, such as living creatures, places, actions, qualities, states of existence, or ideas.Example nouns for: * Living creatures (including people, alive, ... (collectively known as subject complements). Unlike the majority of verbs, they do not describe any direct action taken or controlled by the subject. Linking verbs include copulas such as the English verb ''be'' and its various forms, as well as verbs of perception such as ''look'', ''sound'', or ''taste'' and some other verbs that describe the subject, such as ''seem'', ''become'', or ''remain''. In addition to predicate adjectives and predicate nouns, English allows for predicate prepositional phrases as well: ''John is behind the cocktail cabinet''. The following sentences incl ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
List Of English Copulae
This is a non-exhaustive list of copulae in the English language, i.e. words used to link the subject of a sentence with a predicate (a subject complement). Because many of these copulative verbs may be used non-copulatively, examples are provided. Also, there can be other copulative verbs depending on the context and the meaning of the specific verb used. Therefore, this list is not an exhaustive one. *'' act'' "Tom ''acted'' suspicious." *'' appear'' "Tom ''appears'' satisfied, but really is not." *'' be'' "Tom ''is'' a coward." *'' become'' (inchoative) "Tom ''became'' wealthy." *'' call in'' "Tom ''called in'' sick." *''come'' "The prediction ''came'' true;" "the belt ''came'' loose;" "the characters in the story ''come'' alive" *'' come out'' "It ''came out'' burnt." *'' constitute'' "Verbs ''constitute'' one of the main word classes in the English language" *'' die'' "He ''died'' poor." *'' eat'' "Tom ''eats'' healthy." *'' emerge'' "Tom ''emerged'' unharmed after the i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Traditional Grammar
Traditional grammar (also known as classical grammar) is a framework for the description of the structure of a language. The roots of traditional grammar are in the work of classical Greek language, Greek and Latin language, Latin Philology, philologists. The formal study of grammar based on these models became popular during the Renaissance. Traditional grammars may be contrasted with more modern theories of grammar in theoretical linguistics, which grew out of traditional descriptions. While traditional grammars seek to describe how particular languages are used, or to teach people to speak or read them, grammar frameworks in contemporary linguistics often seek to explain the nature of language knowledge and ability. Traditional grammar is often prescriptive, and may be regarded as unscientific by those working in linguistics. Traditional Western grammars classify words into parts of speech. They describe the patterns for word inflection, and the rules of syntax by which those ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Verb
A verb () is a word ( part of speech) that in syntax generally conveys an action (''bring'', ''read'', ''walk'', ''run'', ''learn''), an occurrence (''happen'', ''become''), or a state of being (''be'', ''exist'', ''stand''). In the usual description of English, the basic form, with or without the particle ''to'', is the infinitive. In many languages, verbs are inflected (modified in form) to encode tense, aspect, mood, and voice. A verb may also agree with the person, gender or number of some of its arguments, such as its subject, or object. Verbs have tenses: present, to indicate that an action is being carried out; past, to indicate that an action has been done; future, to indicate that an action will be done. For some examples: * I ''washed'' the car yesterday. * The dog ''ate'' my homework. * John ''studies'' English and French. * Lucy ''enjoys'' listening to music. *Barack Obama ''became'' the President of the United States in 2009. ''(occurrence)'' * Mike T ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Adjective
In linguistics, an adjective (abbreviated ) is a word that generally modifies a noun or noun phrase or describes its referent. Its semantic role is to change information given by the noun. Traditionally, adjectives were considered one of the main parts of speech of the English language, although historically they were classed together with nouns. Nowadays, certain words that usually had been classified as adjectives, including ''the'', ''this'', ''my'', etc., typically are classed separately, as determiners. Here are some examples: * That's a funny idea. ( attributive) * That idea is funny. ( predicative) * * The good, the bad, and the funny. ( substantive) Etymology ''Adjective'' comes from Latin ', a calque of grc, ἐπίθετον ὄνομα, epítheton ónoma, additional noun (whence also English '' epithet''). In the grammatical tradition of Latin and Greek, because adjectives were inflected for gender, number, and case like nouns (a process called declension), th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Noun
A noun () is a word that generally functions as the name of a specific object or set of objects, such as living creatures, places, actions, qualities, states of existence, or ideas.Example nouns for: * Living creatures (including people, alive, dead or imaginary): ''mushrooms, dogs, Afro-Caribbeans, rosebushes, Nelson Mandela, bacteria, Klingons'', etc. * Physical objects: ''hammers, pencils, Earth, guitars, atoms, stones, boots, shadows'', etc. * Places: ''closets, temples, rivers, Antarctica, houses, Grand Canyon, utopia'', etc. * Actions: ''swimming, exercises, diffusions, explosions, flight, electrification, embezzlement'', etc. * Qualities: ''colors, lengths, deafness, weights, roundness, symmetry, warp speed,'' etc. * Mental or physical states of existence: ''jealousy, sleep, heat, joy, stomachache, confusion, mind meld,'' etc. Lexical categories ( parts of speech) are defined in terms of the ways in which their members combine with other kinds of expressions. Th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Subject Complement
In grammar, a subject complement or predicative of the subject is a predicative expression that follows a linking verb ( copula) and that complements the subject of the sentence by either (1) renaming it or (2) describing it. It completes the meaning of the subject. In the former case, a renaming noun phrase such as a noun or pronoun is called a predicative nominal. An adjective following the copula and describing the subject is called a predicative adjective. In either case the predicative complement in effect mirrors the subject. Subject complements are used with a small class of verbs called linking verbs or copulas, of which ''be'' is the most common. Since linking verbs are intransitive, subject complements are not affected by any action of the verb. Subject complements are typically neither clause arguments nor adjuncts. A predicative complement can be either a subject complement or an object complement. A predicate nominative does not determine the verb. When there is a d ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
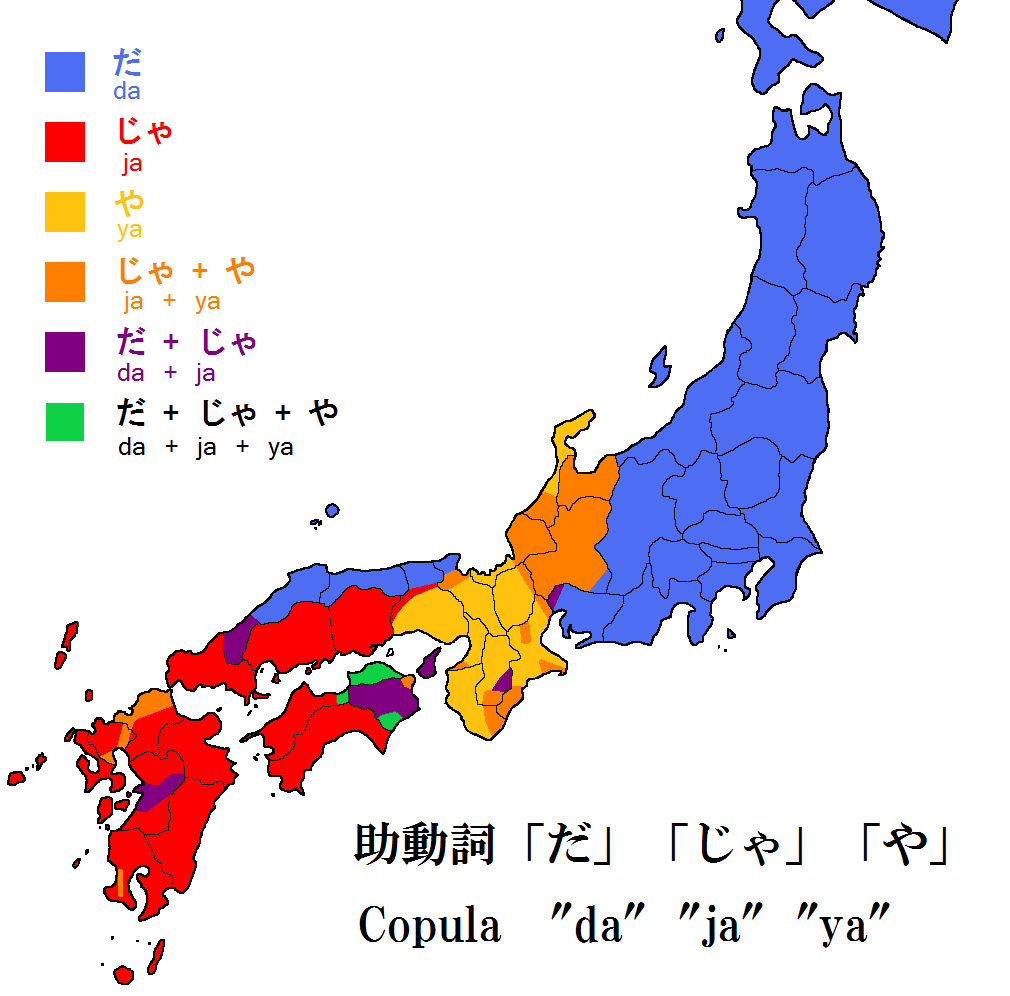
Copula (linguistics)
In linguistics, a copula (plural: copulas or copulae; abbreviated ) is a word or phrase that links the subject of a sentence to a subject complement, such as the word ''is'' in the sentence "The sky is blue" or the phrase ''was not being'' in the sentence "It was not being co-operative." The word ''copula'' derives from the Latin noun for a "link" or "tie" that connects two different things. A copula is often a verb or a verb-like word, though this is not universally the case. A verb that is a copula is sometimes called a copulative or copular verb. In English primary education grammar courses, a copula is often called a linking verb. In other languages, copulas show more resemblances to pronouns, as in Classical Chinese and Guarani, or may take the form of suffixes attached to a noun, as in Korean, Beja, and Inuit languages. Most languages have one main copula, although some (like Spanish, Portuguese and Thai) have more than one, while others have none. In the case ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |