|
Lingqu Canal
The Lingqu () is a canal in Xing'an County, near Guilin, in the northwestern corner of Guangxi, China. It connects the Xiang River (which flows north into the Yangtze) with the Li River (Guangxi), Li River (which flows south into the Gui River and Xijiang), and thus is part of a historical waterway between the Yangtze and the Pearl River Delta. It was the first canal in the world to connect two river valleys and enabled boats to travel from Beijing to Hong Kong. History In 214 BC, Qin Shi Huang, the First Emperor of the Qin dynasty (221–206 BC), ordered the construction of a canal connecting the Xiang and the Li rivers, in order to Qin invasion of Guangdong, attack the Baiyue tribes in the south. The architect who designed the canal was Shi Lu (). It is the oldest contour canal in the world, receiving its water from the Xiang. Its length reaches 36.4 km and it was fitted with thirty-seven Flash lock, flash locks by 825 AD and there is a clear description of pound locks ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lingqu Canal
The Lingqu () is a canal in Xing'an County, near Guilin, in the northwestern corner of Guangxi, China. It connects the Xiang River (which flows north into the Yangtze) with the Li River (Guangxi), Li River (which flows south into the Gui River and Xijiang), and thus is part of a historical waterway between the Yangtze and the Pearl River Delta. It was the first canal in the world to connect two river valleys and enabled boats to travel from Beijing to Hong Kong. History In 214 BC, Qin Shi Huang, the First Emperor of the Qin dynasty (221–206 BC), ordered the construction of a canal connecting the Xiang and the Li rivers, in order to Qin invasion of Guangdong, attack the Baiyue tribes in the south. The architect who designed the canal was Shi Lu (). It is the oldest contour canal in the world, receiving its water from the Xiang. Its length reaches 36.4 km and it was fitted with thirty-seven Flash lock, flash locks by 825 AD and there is a clear description of pound locks ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Baiyue
The Baiyue (, ), Hundred Yue, or simply Yue (; ), were various ethnic groups who inhabited the regions of East China, South China and Northern Vietnam during the 1st millennium BC and 1st millennium AD. They were known for their short hair, body tattoos, fine swords, and naval prowess. During the Warring States period, the word "Yue" referred to the State of Yue in Zhejiang. The later kingdoms of Minyue in Fujian and Nanyue in Guangdong were both considered Yue states. Meacham (1996:93) notes that, during the Zhou and Han dynasties, the Yue lived in a vast territory from Jiangsu to Yunnan, while Barlow (1997:2) indicates that the Luoyue occupied the southwest Guangxi and northern Vietnam. The ''Book of Han'' describes the various Yue tribes and peoples can be found from the regions of Kuaiji to Jiaozhi. The Yue tribes were gradually displaced or assimilated into Chinese culture as the Han empire expanded into what is now Southern China and Northern Vietnam. Many modern ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Qin (state)
Qin () was an ancient Chinese state during the Zhou dynasty. Traditionally dated to 897 BC, it took its origin in a reconquest of western lands previously lost to the Rong; its position at the western edge of Chinese civilization permitted expansion and development that was unavailable to its rivals in the North China Plain. Following extensive "Legalist" reform in the fourth century BC, Qin emerged as one of the dominant powers of the Seven Warring States and unified the seven states of China in 221 BC under Qin Shi Huang. It established the Qin dynasty, which was short-lived but greatly influenced later Chinese history. History Founding According to the 2nd century BC historical text ''Records of the Grand Historian'' by Sima Qian, the Qin state traced its origin to Zhuanxu, one of the legendary Five Emperors in ancient times. One of his descendants, Boyi, was granted the family name of Yíng by Emperor Shun. During the Xia and Shang dynasties, the Yíng clan split ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Major National Historical And Cultural Sites In Guangxi
Major (commandant in certain jurisdictions) is a military rank of commissioned officer status, with corresponding ranks existing in many military forces throughout the world. When used unhyphenated and in conjunction with no other indicators, major is one rank above captain, and one rank below lieutenant colonel. It is considered the most junior of the field officer ranks. Background Majors are typically assigned as specialised executive or operations officers for battalion-sized units of 300 to 1,200 soldiers while in some nations, like Germany, majors are often in command of a company. When used in hyphenated or combined fashion, the term can also imply seniority at other levels of rank, including ''general-major'' or ''major general'', denoting a low-level general officer, and ''sergeant major'', denoting the most senior non-commissioned officer (NCO) of a military unit. The term ''major'' can also be used with a hyphen to denote the leader of a military band such as i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Geography Of Guilin
Geography (from Greek: , ''geographia''. Combination of Greek words ‘Geo’ (The Earth) and ‘Graphien’ (to describe), literally "earth description") is a field of science devoted to the study of the lands, features, inhabitants, and phenomena of Earth. The first recorded use of the word γεωγραφία was as a title of a book by Greek scholar Eratosthenes (276–194 BC). Geography is an all-encompassing discipline that seeks an understanding of Earth and its human and natural complexities—not merely where objects are, but also how they have changed and come to be. While geography is specific to Earth, many concepts can be applied more broadly to other celestial bodies in the field of planetary science. One such concept, the first law of geography, proposed by Waldo Tobler, is "everything is related to everything else, but near things are more related than distant things." Geography has been called "the world discipline" and "the bridge between the human and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chinese Inventions
China has been the source of many innovations, scientific discoveries and inventions. This includes the ''Four Great Inventions'': papermaking, the compass, gunpowder, and printing (both woodblock and movable type). The list below contains these and other inventions in ancient and modern China attested by archaeological or historical evidence, excluding prehistoric inventions of Neolithic and early Bronze Age China. The historical region now known as China experienced a history involving mechanics, hydraulics and mathematics applied to horology, metallurgy, astronomy, agriculture, engineering, music theory, craftsmanship, naval architecture and warfare. Use of the plow during the Neolithic period Longshan culture (c. 3000–c. 2000 BC) allowed for high agricultural production yields and rise of Chinese civilization during the Shang Dynasty (c. 1600–c. 1050 BC). Later inventions such as the multiple-tube seed drill and the heavy moldboard iron plow enabled China to s ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Canals In China
The history of canals in China connecting its major rivers and centers of agriculture and population extends from the legendary exploits of Yu the Great in his attempts control the flooding of the Yellow River to the present infrastructure projects of the People's Republic of China. From the Spring and Autumn period (8th–5th centuriesBCE) onward, the canals of China were used for army transportation and supply, as well as colonization of new territories. From the Qin (3rd century BCE) to the Qing (17th–20th centuriesCE), China's canal network was also essential to imperial taxation-in-kind. Control of shipbuilding and internal tariffs were also administered along the canals. History Spring and Autumn and Warring States periods In 647BCE, the State of Jin suffered major crop failure. Duke Mu of Qin despatched a large fleet of ships manned by Corvée labour from his capital at Yong (雍) in modern-day Fengxiang County, Shaanxi Province. The ships carried several thousands ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Zhengguo Canal
The Zhengguo Canal, Zhengguoqu or Chengkuo Canal (), named after its designer, Zheng Guo, is a large canal located in Shaanxi province, China. The canal irrigates the Guanzhong plain, north of Xi'an. Together with the Dujiangyan Irrigation System and Lingqu Canal, it is one of the three biggest water conservation projects built before the Qin dynasty in ancient China. The canal connects the Jing river and Luo river, northern tributaries of the Wei River. History Historian Sima Qian in his Records of the Grand Historian wrote of the Zhengguo Canal: The plan to drain the resources of the State of Qin back-fired as Qin successfully completed the canal, which irrigated c. 27,000 square kilometres of additional agricultural land, providing the kingdom with sufficient resources to increase the size of its already massive armies. To this day the land surrounding the Zhengguo Canal is extremely fertile. By the time of its completion in 246 BC, during the Han dynasty ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
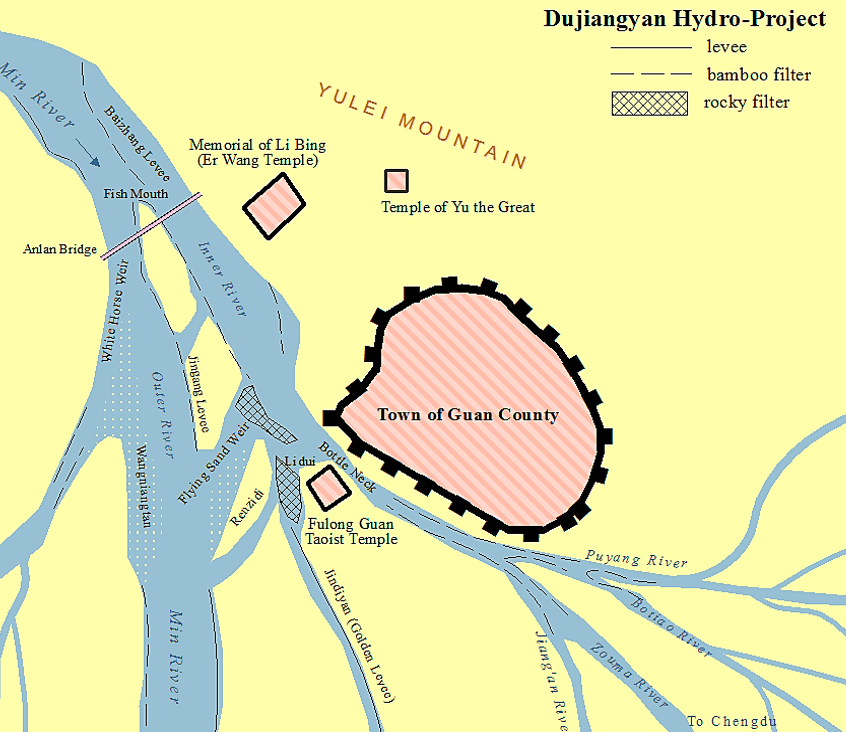
Dujiangyan
The Dujiangyan () is an ancient irrigation system in Dujiangyan City, Sichuan, China. Originally constructed around 256 BC by the State of Qin (state), Qin as an irrigation and flood control project, it is still in use today. The system's infrastructure develops on the Min River (Sichuan), Min River (Minjiang), the longest tributary of the Yangtze. The area is in the west part of the Chengdu Plain, between the Sichuan Basin and the Tibetan Plateau. Originally, the Min would rush down from the Min Mountains and slow down abruptly after reaching the Chengdu Plain, filling the watercourse with silt, thus making the nearby areas extremely prone to floods. King Zhao of Qin commissioned the project, and the construction of the Dujiangyan harnessed the river using a new method of channeling and dividing the water rather than simply damming it. The water management scheme is still in use today to irrigate over of land in the region. The Dujiangyan, the Zhengguo Canal in Shaanxi and the Li ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Grand Canal (China)
The Grand Canal, known to the Chinese as the Jing–Hang Grand Canal (, or more commonly, as the「大运河」("Grand Canal")), a UNESCO World Heritage Site, is the longest canal or artificial river in the world. Starting in Beijing, it passes through Tianjin and the provinces of Hebei, Shandong, Jiangsu, and Zhejiang to the city of Hangzhou, linking the Yellow River and Yangtze River. The oldest parts of the canal date back to the 5th century BC, but the various sections were first connected during the Sui dynasty (581–618 AD). Dynasties in 1271–1633 significantly restored and rebuilt the canal and altered its route to supply their capital. The Grand Canal played a major role in reunifying north and south China. The canal was built by conscripted laborers and connected the Yellow River in the north with the Yangtze River in the south, which made it much easier to transport grain from the south to the centers of political and military power in north China. The total length ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
History Of Canals In China
The history of canals in China connecting its major rivers and centers of agriculture and population extends from the legendary exploits of Yu the Great in his attempts control the flooding of the Yellow River to the present infrastructure projects of the People's Republic of China. From the Spring and Autumn period (8th–5th centuriesBCE) onward, the canals of China were used for army transportation and supply, as well as colonization of new territories. From the Qin (3rd century BCE) to the Qing (17th–20th centuriesCE), China's canal network was also essential to imperial taxation-in-kind. Control of shipbuilding and internal tariffs were also administered along the canals. History Spring and Autumn and Warring States periods In 647BCE, the State of Jin suffered major crop failure. Duke Mu of Qin despatched a large fleet of ships manned by Corvée labour from his capital at Yong (雍) in modern-day Fengxiang County, Shaanxi Province. The ships carried several thousands ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
World Heritage Sites
A World Heritage Site is a landmark or area with legal protection by an international convention administered by the UNESCO, United Nations Educational, Scientific and Cultural Organization (UNESCO). World Heritage Sites are designated by UNESCO for having cultural, historical, scientific or other form of significance. The sites are judged to contain "cultural heritage, cultural and natural heritage, natural heritage around the world considered to be of outstanding value to Human, humanity". To be selected, a World Heritage Site must be a somehow unique landmark which is geographically and historically identifiable and has special cultural or physical significance. For example, World Heritage Sites might be ancient ruins or historical structures, buildings, cities, deserts, forests, islands, lakes, monuments, mountains, or wilderness areas. A World Heritage Site may signify a remarkable accomplishment of humanity, and serve as evidence of our intellectual history on the planet, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |