|
Limelight Diagram
Limelight (also known as Drummond light or calcium light)James R. Smith (2004). ''San Francisco's Lost Landmarks'', Quill Driver Books. is a type of stage lighting once used in theatres and music halls. An intense illumination is created when a flame fed by oxygen and hydrogen is directed at a cylinder of quicklime (calcium oxide), which can be heated to before melting. The light is produced by a combination of incandescence and candoluminescence. Although it has long since been replaced by electric lighting, the term has nonetheless survived, as someone in the public eye is still said to be "in the limelight". The actual lamps are called "limes", a term which has been transferred to electrical equivalents. History Discovery and invention The limelight effect was discovered in the 1820s by Goldsworthy Gurney, based on his work with the "oxy-hydrogen blowpipe", credit for which is normally given to Robert Hare. In 1825, a Scottish engineer, Thomas Drummond (1797–1840), ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Limelight Diagram
Limelight (also known as Drummond light or calcium light)James R. Smith (2004). ''San Francisco's Lost Landmarks'', Quill Driver Books. is a type of stage lighting once used in theatres and music halls. An intense illumination is created when a flame fed by oxygen and hydrogen is directed at a cylinder of quicklime (calcium oxide), which can be heated to before melting. The light is produced by a combination of incandescence and candoluminescence. Although it has long since been replaced by electric lighting, the term has nonetheless survived, as someone in the public eye is still said to be "in the limelight". The actual lamps are called "limes", a term which has been transferred to electrical equivalents. History Discovery and invention The limelight effect was discovered in the 1820s by Goldsworthy Gurney, based on his work with the "oxy-hydrogen blowpipe", credit for which is normally given to Robert Hare. In 1825, a Scottish engineer, Thomas Drummond (1797–1840), ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Clock Tower, Herne Bay
The Clock Tower, Herne Bay (built 1837), is a Grade II listed landmark in Herne Bay, Kent, England. It is believed to be one of the earliest purpose-built, free-standing clock towers in the United Kingdom. It was funded by Mrs Ann Thwaytes, and now serves as a memorial to the fallen of the Second Boer War. The benefactor At the time of the erection of the Clock Tower, Ann Thwaytes (1789–1866) was the rich widow of London grocer William Thwaytes.Mike Bundock, ''Victorian Herne Bay'' (Herne Bay, Kent, Pierhead Publications Ltd, 1 February 2011), p.18, . Between 1834 and 1840 she visited Herne Bay regularly with friends, staying with Mr Camplin who owned number 8 (now 30) Marine Terrace on Central Parade, and became an established town benefactor of Herne Bay.Herne Bay Cultural Trail: Cl ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Timeline Of Hydrogen Technologies
This is a timeline of the history of hydrogen technology. Timeline 16th century * c. 1520 – First recorded observation of hydrogen by Paracelsus through dissolution of metals (iron, zinc, and tin) in sulfuric acid. 17th century * 1625 – First description of hydrogen by Johann Baptista van Helmont. First to use the word "gas". * 1650 – Turquet de Mayerne obtained a gas or "inflammable air" by the action of dilute sulphuric acid on iron. * 1662 – Boyle's law (gas law relating pressure and volume) * 1670 – Robert Boyle produced hydrogen by reacting metals with acid. * 1672 – "New Experiments touching the Relation between Flame and Air" by Robert Boyle. * 1679 – Denis Papin – safety valve * 1700 – Nicolas Lemery showed that the gas produced in the sulfuric acid/iron reaction was explosive in air 18th century * 1755 – Joseph Black confirmed that different gases exist. / Latent heat * 1766 – Henry Cavendish published in "On Factitious Airs" a description of " ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nineteenth-century Theatrical Scenery
Theatre in the nineteenth century was noted for its changing philosophy from the Romanticism and Neoclassicism that dominated Europe since the late 18th century to Realism and Naturalism in the latter half of the 19th century before it eventually gave way to the rise of Modernism in the 20th century. Scenery in theater at the time closely mirrored these changes, and with the onset of the Industrial Revolution and technological advancement throughout the century, dramatically changed the aesthetics of the theater. Realism Theatrical realism was a general movement in 19th-century theatre from the time period of 1870-1960 that developed a set of dramatic and theatrical conventions with the aim of bringing a greater fidelity of real life to texts and performances. Part of a broader artistic movement, it included a focus on everyday middle-class drama, ordinary speech, and simple settings. This idea of representing subject matter truthfully, was evident in the changes that were made to ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
List Of Light Sources
This is a list of sources of light, the visible part of the electromagnetic spectrum. Light sources produce photons from another energy source, such as heat, chemical reactions, or conversion of mass or a different frequency of electromagnetic energy, and include light bulbs and stars like the Sun. Reflectors (such as the moon, cat's eyes, and mirrors) do not actually produce the light that comes from them. Incandescence Incandescence is the emission of light from a hot body as a result of its temperature. * * Combustion Lamps * (obsolete) * * * * (error) * * * * *s *s * (obsolete) *s * Other * * * *s * * * * * * * * * Nuclear and high-energy particle * * ** ** * * * * * Celestial and atmospheric *Astronomical objects **Sun (sunlight, solar radiation) *** *** **Star (Starlight) ***Nova / supernova / hypernova *** **** *** ** *** *** *** *** *** * **Meteor *** ** *** *Lightning (Plasma) ** ** ** ** * * Luminescence Luminescence is emissio ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Klieg Light
A Klieg light is an intense carbon arc lamp especially used in filmmaking. It is named after inventor John Kliegl and his brother Anton Kliegl. Klieg lights usually have a Fresnel lens with a spherical reflector or an ellipsoidal reflector with a lens train containing two plano-convex lenses or a single step lens. Film The carbon-arc source was so bright that it allowed film directors to shoot daytime scenes at night. The ultraviolet rays produced by the light also led to some actors developing an eye inflammation referred to as " Klieg eye". Stage In the early days of spotlights, the name "Klieg light" became synonymous with any ellipsoidal reflector spotlight (ERS), other carbon-arc sources or any bright source. Initially developed for film, the Klieg light was adapted for use as an incandescent stage fixture in 1911. Although not completely certain, the title of the first ellipsoidal reflector spotlight often goes to the 1933 Klieglight, which was first used to light an ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
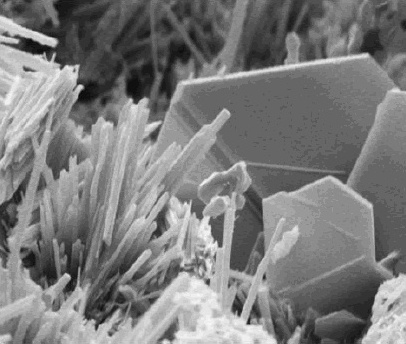
Calcium Hydroxide
Calcium hydroxide (traditionally called slaked lime) is an inorganic compound with the chemical formula Ca( OH)2. It is a colorless crystal or white powder and is produced when quicklime (calcium oxide) is mixed or slaked with water. It has many names including hydrated lime, caustic lime, builders' lime, slaked lime, cal, and pickling lime. Calcium hydroxide is used in many applications, including food preparation, where it has been identified as E number E526. Limewater, also called milk of lime, is the common name for a saturated solution of calcium hydroxide. Properties Calcium hydroxide is poorly soluble in water, with a retrograde solubility increasing from 0.66 g/L at 100 °C to 1.89 g/L at 0 °C. With a solubility product ''K''sp of 5.02 at 25 °C, its dissociation in water is large enough that its solutions are basic according to the following dissolution reaction: : Ca(OH)2 → Ca2+ + 2 OH− At ambient temperature, calcium hydroxide (portlandite) ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Arc Lamp
An arc lamp or arc light is a lamp that produces light by an electric arc (also called a voltaic arc). The carbon arc light, which consists of an arc between carbon electrodes in air, invented by Humphry Davy in the first decade of the 1800s, was the first practical electric light. It was widely used starting in the 1870s for street and large building lighting until it was superseded by the incandescent light in the early 20th century. It continued in use in more specialized applications where a high intensity point light source was needed, such as searchlights and movie projectors until after World War II. The carbon arc lamp is now obsolete for most of these purposes, but it is still used as a source of high intensity ultraviolet light. The term is now used for gas discharge lamps, which produce light by an arc between metal electrodes through a gas in a glass bulb. The common fluorescent lamp is a low-pressure mercury arc lamp. The xenon arc lamp, which produces a high ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Confederate States Army
The Confederate States Army, also called the Confederate Army or the Southern Army, was the military land force of the Confederate States of America (commonly referred to as the Confederacy) during the American Civil War (1861–1865), fighting against the United States forces to win the independence of the Southern states and uphold the institution of slavery. On February 28, 1861, the Provisional Confederate Congress established a provisional volunteer army and gave control over military operations and authority for mustering state forces and volunteers to the newly chosen Confederate president, Jefferson Davis. Davis was a graduate of the U.S. Military Academy, and colonel of a volunteer regiment during the Mexican–American War. He had also been a United States senator from Mississippi and U.S. Secretary of War under President Franklin Pierce. On March 1, 1861, on behalf of the Confederate government, Davis assumed control of the military situation at Charleston, South C ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Union (American Civil War)
During the American Civil War, the Union, also known as the North, referred to the United States led by President Abraham Lincoln. It was opposed by the secessionist Confederate States of America (CSA), informally called "the Confederacy" or "the South". The Union is named after its declared goal of preserving the United States as a constitutional union. "Union" is used in the U.S. Constitution to refer to the founding formation of the people, and to the states in union. In the context of the Civil War, it has also often been used as a synonym for "the northern states loyal to the United States government;" in this meaning, the Union consisted of 20 free states and five border states. The Union Army was a new formation comprising mostly state units, together with units from the regular U.S. Army. The border states were essential as a supply base for the Union invasion of the Confederacy, and Lincoln realized he could not win the war without control of them, especially Maryla ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
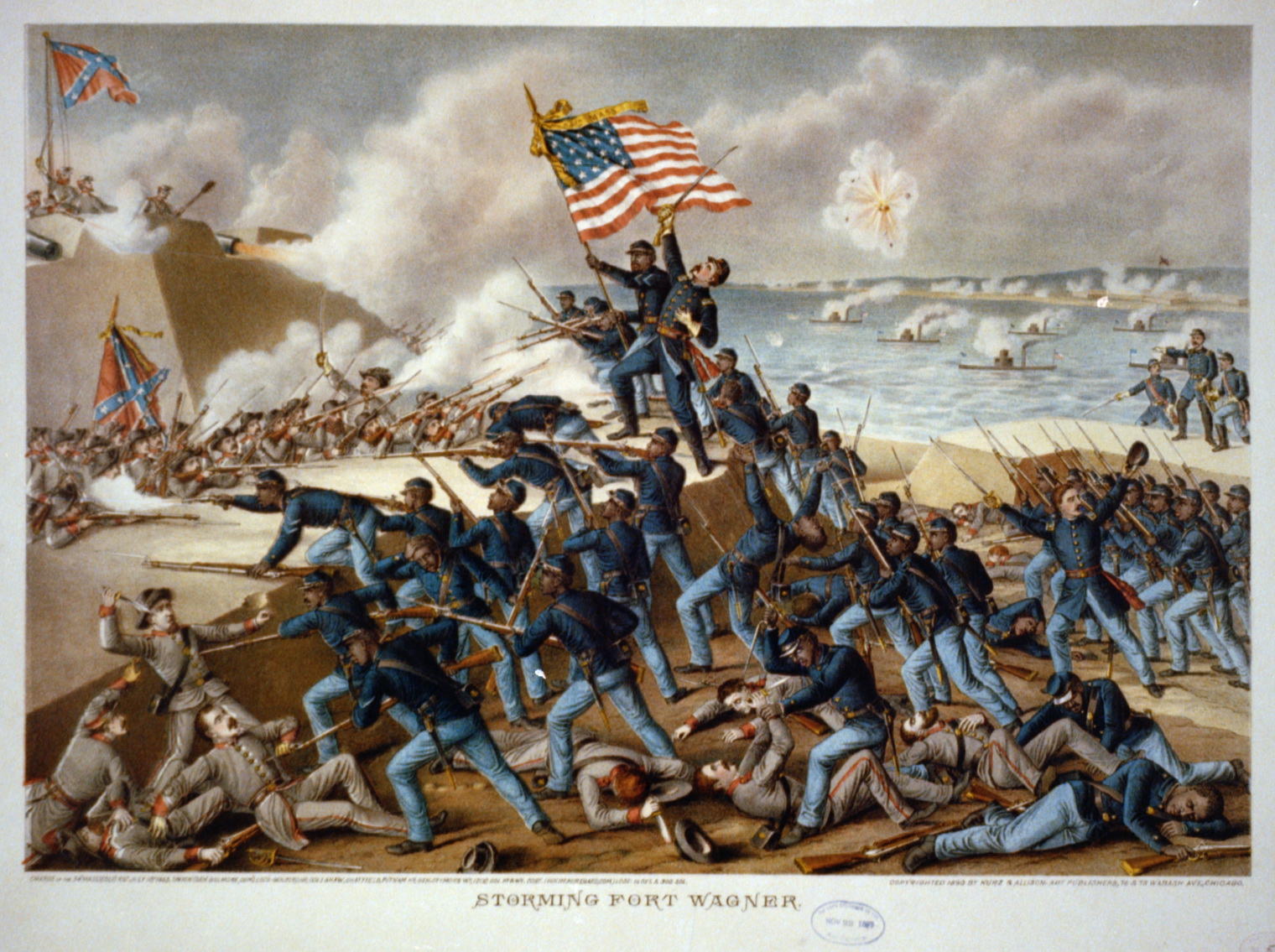
Fort Wagner
Fort Wagner or Battery Wagner was a beachhead fortification on Morris Island, South Carolina, that covered the southern approach to Charleston Harbor. It was the site of two American Civil War battles in the campaign known as Operations Against the Defenses of Charleston in 1863, in which United States forces took heavy casualties while trying to seize the fort. Construction Named for deceased Lt. Col. Thomas M. Wagner, Fort Wagner measured by , and spanned an area between the Atlantic on the east and an impassable swamp on the west. Its walls, composed of sand and earth, rose above the level beach and were supported by palmetto logs and sandbags. The fort's arsenal included fourteen cannons, the largest a Columbiad that fired a 128-pound shell. It was a large structure capable of sheltering nearly 1,000 of the fort's 1,700-man garrison and provided substantial protection against naval shelling. The fort's land face was protected by a water-filled trench, wide and dee ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
American Civil War
The American Civil War (April 12, 1861 – May 26, 1865; also known by other names) was a civil war in the United States. It was fought between the Union ("the North") and the Confederacy ("the South"), the latter formed by states that had seceded. The central cause of the war was the dispute over whether slavery would be permitted to expand into the western territories, leading to more slave states, or be prevented from doing so, which was widely believed would place slavery on a course of ultimate extinction. Decades of political controversy over slavery were brought to a head by the victory in the 1860 U.S. presidential election of Abraham Lincoln, who opposed slavery's expansion into the west. An initial seven southern slave states responded to Lincoln's victory by seceding from the United States and, in 1861, forming the Confederacy. The Confederacy seized U.S. forts and other federal assets within their borders. Led by Confederate President Jefferson Davis, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |