|
Lifshitz Theory Of Van Der Waals Force
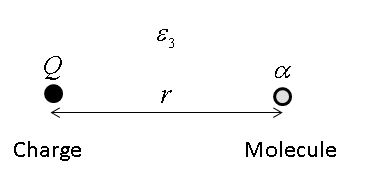
In condensed matter physics and physical chemistry, the Lifshitz theory of van der Waals forces, sometimes called the macroscopic theory of van der Waals forces, is a method proposed by Evgeny Mikhailovich Lifshitz in 1954 for treating van der Waals forces between bodies which does not assume pairwise additivity of the individual intermolecular forces; that is to say, the theory takes into account the influence of neighboring molecules on the interaction between every pair of molecules located in the two bodies, rather than treating each pair independently. Need for a non-pairwise additive theory The van der Waals force between two molecules, in this context, is the sum of the attractive or repulsive forces between them; these forces are primarily electrostatic in nature, and in their simplest form might consist of a force between two charges, two dipoles, or between a charge and a dipole. Thus, the strength of the force may often depend on the net charge, electric dipole moment, o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Condensed Matter Physics
Condensed matter physics is the field of physics that deals with the macroscopic and microscopic physical properties of matter, especially the solid and liquid phases which arise from electromagnetic forces between atoms. More generally, the subject deals with "condensed" phases of matter: systems of many constituents with strong interactions between them. More exotic condensed phases include the superconducting phase exhibited by certain materials at low temperature, the ferromagnetic and antiferromagnetic phases of spins on crystal lattices of atoms, and the Bose–Einstein condensate found in ultracold atomic systems. Condensed matter physicists seek to understand the behavior of these phases by experiments to measure various material properties, and by applying the physical laws of quantum mechanics, electromagnetism, statistical mechanics, and other theories to develop mathematical models. The diversity of systems and phenomena available for study makes condensed matter phy ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Quantum Field Theory
In theoretical physics, quantum field theory (QFT) is a theoretical framework that combines classical field theory, special relativity, and quantum mechanics. QFT is used in particle physics to construct physical models of subatomic particles and in condensed matter physics to construct models of quasiparticles. QFT treats particles as excited states (also called Quantum, quanta) of their underlying quantum field (physics), fields, which are more fundamental than the particles. The equation of motion of the particle is determined by minimization of the Lagrangian, a functional of fields associated with the particle. Interactions between particles are described by interaction terms in the Lagrangian (field theory), Lagrangian involving their corresponding quantum fields. Each interaction can be visually represented by Feynman diagrams according to perturbation theory (quantum mechanics), perturbation theory in quantum mechanics. History Quantum field theory emerged from the wo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lifshitz Van Der Waals Integration 01
Lifshitz (or Lifschitz) is a surname, which may be derived from the Polish city of GĹ‚ubczyce (German: LeobschĂĽtz). The surname has many variants, including: , , Lifshits, Lifshuts, Lefschetz; Lipschitz (Lipshitz), Lipshits, Lipchitz, Lipschutz (LipschĂĽtz), Lipshutz, LĂĽpschĂĽtz; Libschitz; Livshits; Lifszyc, Lipszyc. The surname may refer to: *Asaf Lifshitz (* 1942), Israeli sculptor *Chava Lifshitz (1936–2005), Austrian-Israeli chemist *Dovid Lifshitz (1906-1993), Suvalker Rav, taught at Yeshiva University *Rabbi Eliezer Meir Lifshitz (1879–1946), for whom the Lifshitz College of Education was named *Evgeny Lifshitz (1915–1985), Soviet physicist *Ilya Lifshitz (1917–1982), Soviet physicist (brother of Evgeny) *J.D. Lifshitz (born 1992), American film director *Miguel Lifschitz (1955–2021), Argentine politician, former mayor of the city of Rosario, Santa Fe *Mikhail Lifshitz (1905–1983), Soviet literary critic and aesthetics philosopher *Nechama ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lifshitz Van Der Waals Integration 03
Lifshitz (or Lifschitz) is a surname, which may be derived from the Polish city of GĹ‚ubczyce (German: LeobschĂĽtz). The surname has many variants, including: , , Lifshits, Lifshuts, Lefschetz; Lipschitz (Lipshitz), Lipshits, Lipchitz, Lipschutz (LipschĂĽtz), Lipshutz, LĂĽpschĂĽtz; Libschitz; Livshits; Lifszyc, Lipszyc. The surname may refer to: *Asaf Lifshitz (* 1942), Israeli sculptor *Chava Lifshitz (1936–2005), Austrian-Israeli chemist *Dovid Lifshitz (1906-1993), Suvalker Rav, taught at Yeshiva University *Rabbi Eliezer Meir Lifshitz (1879–1946), for whom the Lifshitz College of Education was named *Evgeny Lifshitz (1915–1985), Soviet physicist *Ilya Lifshitz (1917–1982), Soviet physicist (brother of Evgeny) *J.D. Lifshitz (born 1992), American film director *Miguel Lifschitz (1955–2021), Argentine politician, former mayor of the city of Rosario, Santa Fe *Mikhail Lifshitz (1905–1983), Soviet literary critic and aesthetics philosopher *Nechama ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dielectric Constant
The relative permittivity (in older texts, dielectric constant) is the permittivity of a material expressed as a ratio with the electric permittivity of a vacuum. A dielectric is an insulating material, and the dielectric constant of an insulator measures the ability of the insulator to store electric energy in an electrical field. Permittivity is a material's property that affects the Coulomb force between two point charges in the material. Relative permittivity is the factor by which the electric field between the charges is decreased relative to vacuum. Likewise, relative permittivity is the ratio of the capacitance of a capacitor using that material as a dielectric, compared with a similar capacitor that has vacuum as its dielectric. Relative permittivity is also commonly known as the dielectric constant, a term still used but deprecated by standards organizations in engineering as well as in chemistry. Definition Relative permittivity is typically denoted as (sometimes ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chemical Polarity
In chemistry, polarity is a separation of electric charge leading to a molecule or its chemical groups having an electric dipole moment, with a negatively charged end and a positively charged end. Polar molecules must contain one or more polar bonds due to a difference in electronegativity between the bonded atoms. Molecules containing polar bonds have no molecular polarity if the bond dipoles cancel each other out by symmetry. Polar molecules interact through dipole–dipole intermolecular forces and hydrogen bonds. Polarity underlies a number of physical properties including surface tension, solubility, and melting and boiling points. Polarity of bonds Not all atoms attract electrons with the same force. The amount of "pull" an atom exerts on its electrons is called its electronegativity. Atoms with high electronegativitiessuch as fluorine, oxygen, and nitrogenexert a greater pull on electrons than atoms with lower electronegativities such as alkali metals and alkaline ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hamaker Constant
The Hamaker constant ''A'' can be defined for a van der Waals (vdW) body–body interaction: :A=\pi^2C\rho_1\rho_2, where \rho_1 and \rho_2 are the number densities of the two interacting kinds of particles, and ''C'' is the London coefficient in the particle–particle pair interaction. It is named after H. C. Hamaker. The magnitude of this constant reflects the strength of the vdW-force between two particles, or between a particle and a substrate. The Hamaker constant provides the means to determine the interaction parameter ''C'' from the vdW-pair potential, w(r) = -C/r^6. Hamaker's method and the associated Hamaker constant ignores the influence of an intervening medium between the two particles of interaction. In 1956 Lifshitz developed a description of the vdW energy but with consideration of the dielectric properties of this intervening medium (often a continuous phase). The Van der Waals forces are effective only up to several hundred angstroms. When the interactions a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lifshitz Van Der Waals Integration 02
Lifshitz (or Lifschitz) is a surname, which may be derived from the Polish city of GĹ‚ubczyce (German: LeobschĂĽtz). The surname has many variants, including: , , Lifshits, Lifshuts, Lefschetz; Lipschitz (Lipshitz), Lipshits, Lipchitz, Lipschutz (LipschĂĽtz), Lipshutz, LĂĽpschĂĽtz; Libschitz; Livshits; Lifszyc, Lipszyc. The surname may refer to: *Asaf Lifshitz (* 1942), Israeli sculptor *Chava Lifshitz (1936–2005), Austrian-Israeli chemist *Dovid Lifshitz (1906-1993), Suvalker Rav, taught at Yeshiva University *Rabbi Eliezer Meir Lifshitz (1879–1946), for whom the Lifshitz College of Education was named *Evgeny Lifshitz (1915–1985), Soviet physicist *Ilya Lifshitz (1917–1982), Soviet physicist (brother of Evgeny) *J.D. Lifshitz (born 1992), American film director *Miguel Lifschitz (1955–2021), Argentine politician, former mayor of the city of Rosario, Santa Fe *Mikhail Lifshitz (1905–1983), Soviet literary critic and aesthetics philosopher *Nechama ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nico Van Kampen
Nicolaas 'Nico' Godfried van Kampen (June 22, 1921 – October 6, 2013) was a Dutch theoretical physicist, who worked mainly on statistical mechanics and non-equilibrium thermodynamics. Van Kampen was born in Leiden, and was a nephew of Frits Zernike. He studied physics at Leiden University, where in 1952 under the direction of Hendrik Anthony Kramers he earned his PhD with thesis ''Contributions to the quantum theory of light scattering''. He showed in his thesis how to deal with singularities in quantum mechanical scattering processes, an important step in the development of renormalization, according to Kramers. Van Kampen made fundamental contributions to non-equilibrium processes (in particular on the master equation) and in many-body theory (especially in plasma physics). His work on non-equilibrium processes began in 1953 in the research group of Sybren Ruurds de Groot (the successor to Kramers) in Leiden. In 1955 Van Kampen joined the Institute of Theoretical Physics at Utr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dieter Langbein
Dieter Langbein, Dr. phil. nat., was a German physicist, whose fields of research included solid state physics, fluid physics and microgravity. He was born on 10 February 1932 in Frankfurt am Main, Germany as Werner Dietrich Langbein and died on 25 June 2004 in Bad Homburg, Germany. He was married and had a son and two daughters. Early days In 1951 Dieter Langbein started his studies in mathematics at the Johann Wolfgang Goethe-Universität at Frankfurt am Main, where he met Prof. Friedrich Hund who inspired him to work in theoretical physics. After his diploma in physics in 1956 and his thesis on solid state physics in 1958 he went to the Institute of Theoretical Physics at Göttingen to work with Prof. Hund in investigating galvanomagnetic effects. Research In 1962 he joined Farbwerke Hoechst AG where he worked on thermodynamics and reaction kinetics. Dieter Langbein's scientific career was characterized by working closely with experimental physicists as well as with chemis ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Casimir Effect
In quantum field theory, the Casimir effect is a physical force acting on the macroscopic boundaries of a confined space which arises from the quantum fluctuations of the field. It is named after the Dutch physicist Hendrik Casimir, who predicted the effect for electromagnetic systems in 1948. In the same year, Casimir together with Dirk Polder described a similar effect experienced by a neutral atom in the vicinity of a macroscopic interface which is referred to as the Casimir–Polder force. Their result is a generalization of the London–van der Waals force and includes retardation due to the finite speed of light. Since the fundamental principles leading to the London–van der Waals force, the Casimir and the Casimir–Polder force, respectively, can be formulated on the same footing, the distinction in nomenclature nowadays serves a historical purpose mostly and usually refers to the different physical setups. It was not until 1997 that a direct experiment by S. La ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Refractive Index
In optics, the refractive index (or refraction index) of an optical medium is a dimensionless number that gives the indication of the light bending ability of that medium. The refractive index determines how much the path of light is bent, or refracted, when entering a material. This is described by Snell's law of refraction, , where ''θ''1 and ''θ''2 are the angle of incidence and angle of refraction, respectively, of a ray crossing the interface between two media with refractive indices ''n''1 and ''n''2. The refractive indices also determine the amount of light that is reflected when reaching the interface, as well as the critical angle for total internal reflection, their intensity ( Fresnel's equations) and Brewster's angle. The refractive index can be seen as the factor by which the speed and the wavelength of the radiation are reduced with respect to their vacuum values: the speed of light in a medium is , and similarly the wavelength in that medium is , where ''Π... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |