|
Lietava Castle
Lietava Castle ( sk, Lietavský hrad, older names , , , ) is an extensive castle ruin in the Súľov Mountains of northern Slovakia, between the villages of Lietava and Lietavská Svinná-Babkov in the Žilina District. History The castle was built after 1241, most likely as an administrative and military centre. It occupies a strategic position alongside the Amber Road, a trade route between Europe and Asia along which amber and other goods were transported. Members of the Balas family are thought to have constructed a four-storey tower, and this was expanded over the years by successive owners. In the early 14th century, it is mentioned with Máté Csák III, one of the powerful magnates in the Kingdom of Hungary. The castle changed hands several times until the 16th century when the Thurzó family gained it. It was reconstructed in the Gothic-Renaissance style and fortified, and given its own military garrison. The weathered remains of this reconstruction are what remains; its ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Súľov Mountains
The Súľov Mountains (in Slovak, ''Súľovské vrchy'') is a rugged mountain range in Slovakia, the northwestern part of the Fatra-Tatra Area of the Inner Western Carpathians. Its highest peak is Veľký Manín, at 890 meters. The Súľov Mountains is the location of: * the Súľov Rocks, a national nature reserve open for hiking and rock-climbing. The highest peak in this area is ''Žibrid'' (867 meters) * the national nature reserves of the Manínska Gorge and the Kostolecká Gorge * the Bosmany natural monument * the extensive castle ruins of the 13th century Lietava Castle Lietava Castle ( sk, Lietavský hrad, older names , , , ) is an extensive castle ruin in the Súľov Mountains of northern Slovakia, between the villages of Lietava and Lietavská Svinná-Babkov in the Žilina District. History The castle was b ... and the 15th century Súľovský Castle A portion of the Súľovs is also protected by the Strážov Mountains Protected Landscape Area. Refere ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Slovakia
Slovakia (; sk, Slovensko ), officially the Slovak Republic ( sk, Slovenská republika, links=no ), is a landlocked country in Central Europe. It is bordered by Poland to the north, Ukraine to the east, Hungary to the south, Austria to the southwest, and the Czech Republic to the northwest. Slovakia's mostly mountainous territory spans about , with a population of over 5.4 million. The capital and largest city is Bratislava, while the second largest city is Košice. The Slavs arrived in the territory of present-day Slovakia in the fifth and sixth centuries. In the seventh century, they played a significant role in the creation of Samo's Empire. In the ninth century, they established the Principality of Nitra, which was later conquered by the Principality of Moravia to establish Great Moravia. In the 10th century, after the dissolution of Great Moravia, the territory was integrated into the Principality of Hungary, which then became the Kingdom of Hungary in 1000. In 1241 a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lietava
Lietava ( hu, Zsolnalitva) is a village and municipality in Žilina District in the Žilina Region of northern Slovakia. Lietava Castle, the third largest castle in Slovakia, is in the village. History In historical records the village was first mentioned in the year 1300 AD. Geography The municipality lies at an altitude of 429 metres and covers an area of 10.005 km². It has a population Population typically refers to the number of people in a single area, whether it be a city or town, region, country, continent, or the world. Governments typically quantify the size of the resident population within their jurisdiction using a ... of about 1450 people. References External links *http://www.obeclietava.sk *https://web.archive.org/web/20181111123615/https://www.hradlietava.sk/ Villages and municipalities in Žilina District {{Žilina-geo-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lietavská Svinná-Babkov
Lietavská Svinná-Babkov ( hu, Litvaszinye-Babkó) is a village and municipality in Žilina District in the Žilina Region of northern Slovakia. History In historical records the village was first mentioned in 1393. Geography The municipality lies at an altitude of 420 metres and covers an area of 18.297 km². It has a population Population typically refers to the number of people in a single area, whether it be a city or town, region, country, continent, or the world. Governments typically quantify the size of the resident population within their jurisdiction using a ... of about 1562 people. References External links *https://web.archive.org/web/20070513023228/http://www.statistics.sk/mosmis/eng/run.html Villages and municipalities in Žilina District {{Žilina-geo-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Žilina District
Žilina District ( sk, Okres Žilina) is an '' okres'' (district) of the Žilina Region in north-western Slovakia. The district was first established in 1923. Its present borders date from 1996. The heart of the district is the Váh and Rajec river valleys. Urbanization has led to the district's becoming one of Slovakia's most highly developed areas. Municipalities * Belá * Bitarová * Brežany * Čičmany * Divina * Divinka * Dlhé Pole * Dolná Tižina * Dolný Hričov * Ďurčiná * Fačkov * Gbeľany * Horný Hričov * Hôrky * Hričovské Podhradie * Jasenové * Kamenná Poruba * Kľače * Konská * Kotrčiná Lúčka * Krasňany * Kunerad * Lietava * Lietavská Lúčka * Lietavská Svinná-Babkov * Lutiše * Lysica * Malá Čierna * Mojš * Nededza * Nezbudská Lúčka * Ovčiarsko * Paština Závada * Podhorie * Porúbka *Rajec *Rajecká Lesná *Rajecké Teplice * Rosina * Stránske * Stráňavy * Stráža * Strečno * Svederník * Šuja * Teplička nad Váhom *Terchová * ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
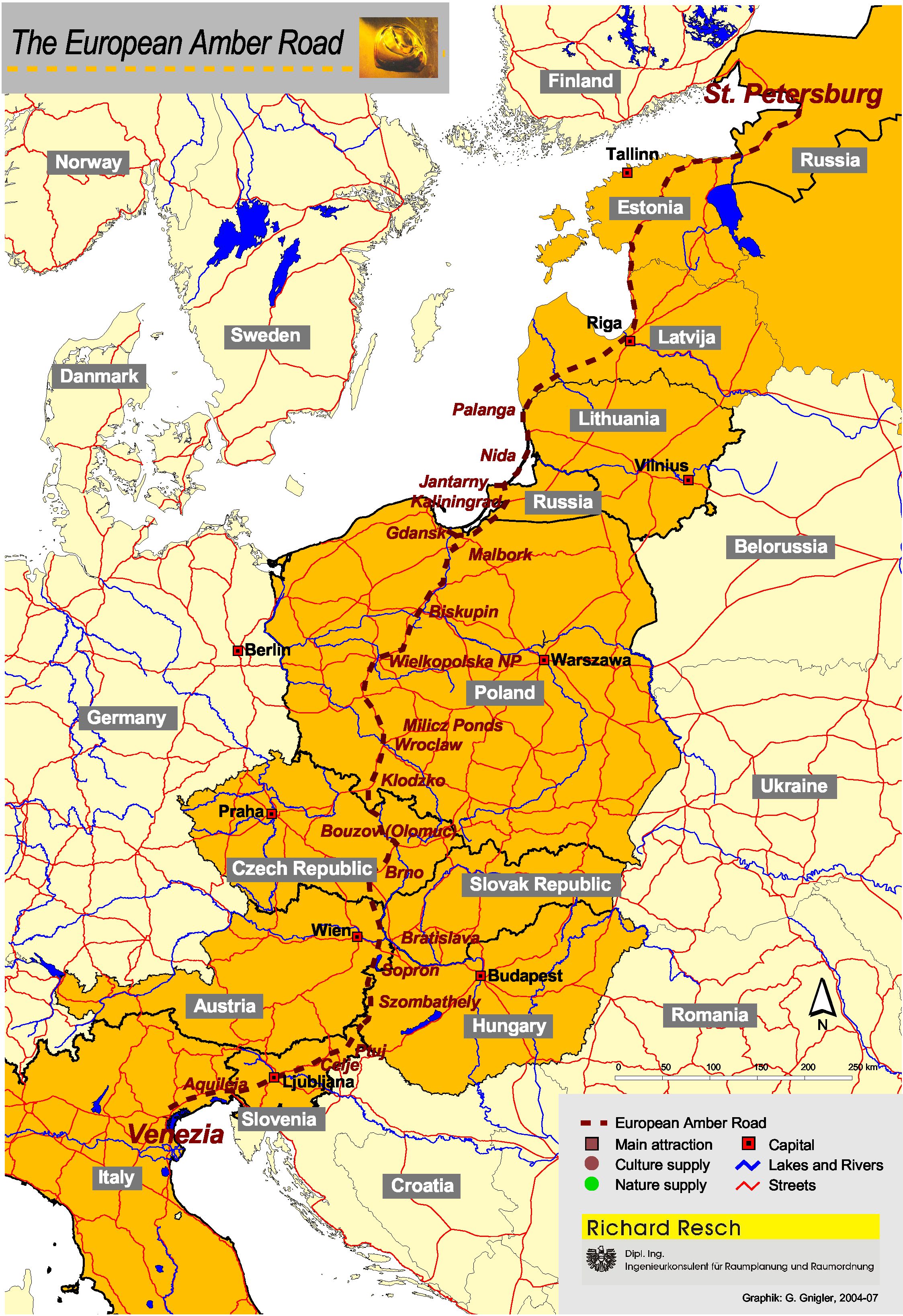
Amber Road
The Amber Road was an ancient trade route for the transfer of amber from coastal areas of the North Sea and the Baltic Sea to the Mediterranean Sea. Prehistoric trade routes between Northern and Southern Europe were defined by the amber trade. As an important commodity, sometimes dubbed "the gold of the north", amber was transported from the North Sea and Baltic Sea coasts overland by way of the Vistula and Dnieper rivers to Italy, Greece, the Black Sea, Syria and Egypt over a period of thousands of years. Antiquity The oldest trade in amber started from Sicily. The Sicilian amber trade was directed to Greece, North Africa and Spain. Sicilian amber was also discovered in Mycenae by the archaeologist Heinrich Schliemann, and it appeared in sites in southern Spain and Portugal. Its distribution is similar to that of ivory, so it is possible that amber from Sicily reached the Iberian Peninsula through contacts with North Africa. After a decline in the consumption and trade of amb ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Amber
Amber is fossilized tree resin that has been appreciated for its color and natural beauty since Neolithic times. Much valued from antiquity to the present as a gemstone, amber is made into a variety of decorative objects."Amber" (2004). In Maxine N. Lurie and Marc Mappen (eds.) ''Encyclopedia of New Jersey'', Rutgers University Press, . Amber is used in jewelry and has been used as a healing agent in folk medicine. There are five classes of amber, defined on the basis of their chemical constituents. Because it originates as a soft, sticky tree resin, amber sometimes contains animal and plant material as inclusions. Amber occurring in coal seams is also called resinite, and the term ''ambrite'' is applied to that found specifically within New Zealand coal seams. Etymology The English word ''amber'' derives from Arabic (ultimately from Middle Persian ''ambar'') via Middle Latin ''ambar'' and Middle French ''ambre''. The word was adopted in Middle English in the 14th century ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Máté Csák III
Mate may refer to: Science * Mate, one of a pair of animals involved in: ** Mate choice, intersexual selection ** Mating * Multi-antimicrobial extrusion protein, or MATE, an efflux transporter family of proteins Person or title * Friendship ** Mateship * Mate (naval officer) ** Chief mate, also known as first mate ** Second mate ** Third mate * Third (curling), also known as a vice, vice-skip, or mate, the team member who delivers the second-to-last pair of a team's stones in an end People Given names * Mate (given name) * Máté (given name) Surname * Máté (surname) Beverages * Mate (drink) (/ˈmɑːte/), made from the yerba mate plant ** Mate, a traditional South American container carved from a dried calabash * Mate de coca, or coca tea Technology * MATE (software) (/ˈmɑːteɪ/) stylised in capitals, a fork of GNOME 2 (desktop shell for desktop hardware) * Mate or mating condition, a synonym for constraints used in computer-aided design (CAD) * Huawei Mate seri ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kingdom Of Hungary
The Kingdom of Hungary was a monarchy in Central Europe that existed for nearly a millennium, from the Middle Ages into the 20th century. The Principality of Hungary emerged as a Christian kingdom upon the coronation of the first king Stephen I at Esztergom around the year 1000;Kristó Gyula – Barta János – Gergely Jenő: Magyarország története előidőktől 2000-ig (History of Hungary from the prehistory to 2000), Pannonica Kiadó, Budapest, 2002, , p. 687, pp. 37, pp. 113 ("Magyarország a 12. század második felére jelentős európai tényezővé, középhatalommá vált."/"By the 12th century Hungary became an important European factor, became a middle power.", "A Nyugat részévé vált Magyarország.../Hungary became part of the West"), pp. 616–644 his family (the Árpád dynasty) led the monarchy for 300 years. By the 12th century, the kingdom became a European middle power within the Western world. Due to the Ottoman occupation of the central and south ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Thurzó Family
Thurzó ( sk, Turzo; pl, Turzonowie) was a Hungarian noble family from the 15th century to the first half of the 17th century. It was in Kraków that the rise of the Thurzó family began, and the family in turn boosted that city into an important center of business, science, and Renaissance high culture. The family's long-term involvement in capitalist enterprises, high-level politics, the affairs of the Church, and its patronage of the arts made the family rich, famous and powerful well beyond the city. Its achievements resembled the Medici family in Italy and France, perhaps the Fugger family in Germany. Key family patriarchs were János Thurzó (1437–1508) and his sons János V (1466–1520), bishop of Wrocław, and Stanislav I (1471–1540), bishop of Olomouc, and Palatine György who founded town Turzovka. Karen Lambrecht argues that the family's most important role was in facilitating "intercultural communications." That is they used their vast network of friends, cli ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Imre Thurzó
Count Imre Thurzó de Bethlenfalva (11 September 1598 – 19 October 1621) was a Hungarian aristocrat, son of Palatine György Thurzó, who served as Perpetual Ispán (Count; ''comes'') of Árva County between 1616 and 1621. Count Imre also functioned as Rector of the University of Wittenberg from 1616 to 1621. He was the last male member of the prestigious Thurzó family. Biography He was born in Nagybiccse, Trencsén County on 11 September 1598. His parents were György Thurzó, Palatine of Hungary and Erzsébet Czobor, daughter of Imre Czobor, who served as Palatinal Governor of Hungary between 1572 and 1581. As the only surviving son of Palatine Thurzó, he received careful and thorough education: firstly in the parental home, then at the University of Wittenberg. His close schoolmate was Juraj V Zrinski, future Ban of Croatia. On Christmas Eve of 1616, György Thurzó died at the age of 49, thus Count Imre inherited the Thurzó prosperity and became Count of Árva. He ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |