|
Liberal Period (Dutch East Indies)
The Liberal Period refers to the economic policies instituted in the Dutch East Indies from the mid-19th century. Background: the cultivation system Under the cultivation system (or "tanam paksa" in Indonesian) in place for most of the 19th century, the Dutch colonial government in the Indonesian archipelago required indigenous farmers to deliver, as a sort of tax, fixed amounts of specified crops, such as sugar or coffee. Much of Java became a Dutch plantation, making it a profitable, self-sufficient colony and saving the Netherlands from bankruptcy and helping it become a thriving and modernised bourgeois society. The Cultivation System, however, brought much economic hardship to Javanese peasants, who suffered famine and epidemics in the 1840s, attracting much critical public opinion in the Netherlands. De-regulation of the Indies economy Prior to the late 19th century recession, the Liberal Party had been dominant in policy making in the Netherlands. Its free market phi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
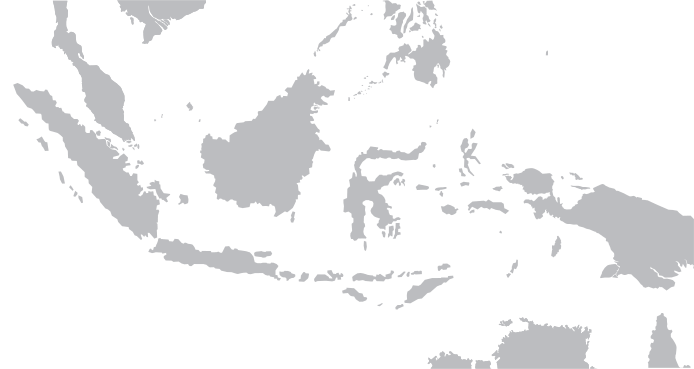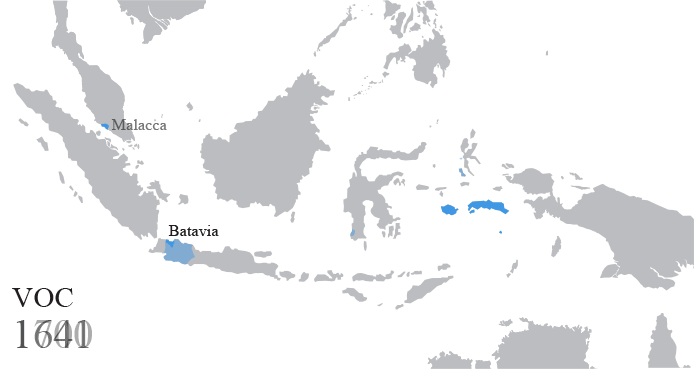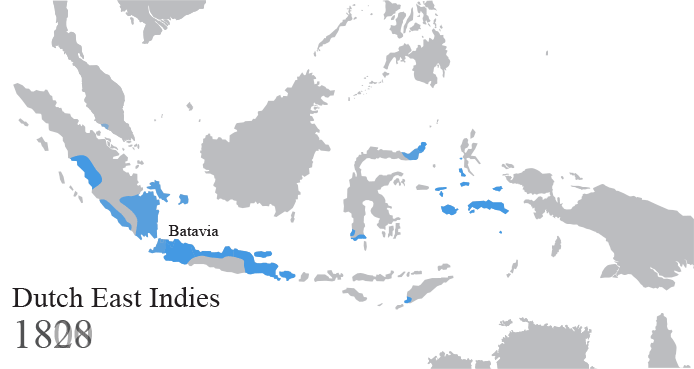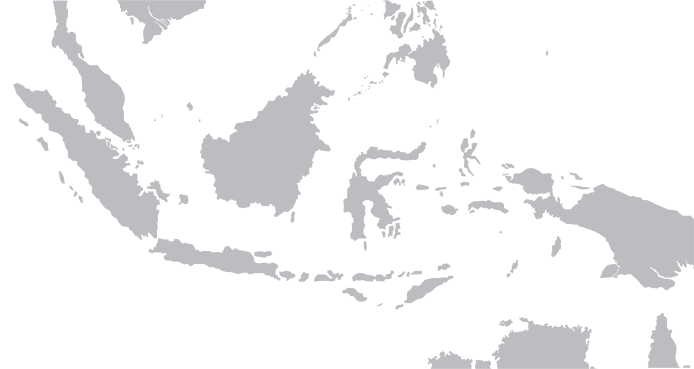
Dutch East Indies
The Dutch East Indies, also known as the Netherlands East Indies ( nl, Nederlands(ch)-Indië; ), was a Dutch colony consisting of what is now Indonesia. It was formed from the nationalised trading posts of the Dutch East India Company, which came under the administration of the Dutch government in 1800. During the 19th century, the Dutch possessions and hegemony expanded, reaching the greatest territorial extent in the early 20th century. The Dutch East Indies was one of the most valuable colonies under European rule, and contributed to Dutch global prominence in spice and cash crop trade in the 19th to early 20th centuries. The colonial social order was based on rigid racial and social structures with a Dutch elite living separate from but linked to their native subjects. The term ''Indonesia'' came into use for the geographical location after 1880. In the early 20th century, local intellectuals began developing the concept of Indonesia as a nation state, and set the stage ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cultivation System
The Cultivation System ( nl, cultuurstelsel) was a Dutch government policy from 1830–1870 for its Dutch East Indies colony (now Indonesia). Requiring a portion of agricultural production to be devoted to export crops, it is referred to by Indonesian historians as ''tanam paksa'' ("enforced planting"). Background Despite increasing returns from the Dutch system of land tax, Dutch finances had been severely affected by the cost of the Java War and Padri Wars. The Belgian Revolution in 1830 and the resulting costs of keeping the Dutch army at a war footing until 1839 brought the Netherlands to the brink of bankruptcy. In 1830, a new governor general, Johannes van den Bosch, was appointed to increase the exploitation of the Dutch East Indies' resources. The Cultivation System was implemented only on land controlled directly by the colonial government, thus exempting the ''Vorstenlanden'' (princely states) and the ''particuliere landerijen'' (private domains). Implementation The ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Java
Java (; id, Jawa, ; jv, ꦗꦮ; su, ) is one of the Greater Sunda Islands in Indonesia. It is bordered by the Indian Ocean to the south and the Java Sea to the north. With a population of 151.6 million people, Java is the world's List of islands by population, most populous island, home to approximately 56% of the Demographics of Indonesia, Indonesian population. Indonesia's capital city, Jakarta, is on Java's northwestern coast. Many of the best known events in Indonesian history took place on Java. It was the centre of powerful Hindu-Buddhist empires, the Islamic sultanates, and the core of the colonial Dutch East Indies. Java was also the center of the History of Indonesia, Indonesian struggle for independence during the 1930s and 1940s. Java dominates Indonesia politically, economically and culturally. Four of Indonesia's eight UNESCO world heritage sites are located in Java: Ujung Kulon National Park, Borobudur Temple, Prambanan Temple, and Sangiran Early Man Site. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Liberal Party (Netherlands)
The Liberal Party (in Dutch: ''Liberale Partij'', LP) was a Dutch conservative liberal political party. The LP played only a marginal role in Dutch politics. Party history The Liberal Party was founded in 1922 by 85-year-old former minister Samuel van Houten in reaction to the foundation of the Liberal State Party which united all liberal parties. Van Houten disagreed with the political course of this new party especially where it came to economic policy and electoral law. Van Houten had started out as an extremely progressive liberal,"uiterst progressief" according tparlement.com/ref> who as an MP in the 1870s had initiated the first forms of social legislation and as a minister in the 1880s had reformed the electoral law. In the 1910s he had become more conservative, opposing encroaching social legislation and the new electoral system. In the 1922 elections the party won one seat. Van Houten was the party's top candidate; he had already announced that he would not take a seat ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kalimantan
Kalimantan () is the Indonesian portion of the island of Borneo. It constitutes 73% of the island's area. The non-Indonesian parts of Borneo are Brunei and East Malaysia. In Indonesia, "Kalimantan" refers to the whole island of Borneo. In 2019, President of Indonesia Joko Widodo proposed that Capital of Indonesia, Indonesia's capital be moved to Kalimantan, and in January 2022 Indonesian legislature approved the proposal. The shift is expected to take up to 10 years. Etymology The name ''Kalimantan'' is derived from the Sanskrit word ''Kalamanthana'', which means "burning weather island", or island with a very hot temperature, referring to its hot and humid tropical climate. It consists of the two words ''Kāla (time), kal[a]'' ("time, season, period") and ''manthan[a]'' ("boiling, churning, burning"). The indigenous people of the eastern region of Borneo referred to their island as ''Pulu K'lemantan'' or "Kalimantan" when the sixteenth century Portuguese explorer Jorge de Meneze ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ethical Period
The Dutch Ethical Policy ( nl, Ethische Politiek) was the official policy of the colonial government of the Dutch East Indies (present-day Indonesia) during the four decades from 1901 until the Japanese occupation of the Dutch East Indies, Japanese occupation of 1942. In 1901, Netherlands, the Dutch Wilhelmina of the Netherlands, Queen Wilhelmina announced that the Netherlands accepted an ethical responsibility for the welfare of their colonial subjects. This announcement was a sharp contrast with the former official doctrine that Indonesia was a ''wingewest'' (region for making profit). It also marked the start of modern human development (humanity), development policy; whereas other colonialism, colonial powers talked of a civilising mission, which mainly involved spreading their culture to colonised peoples. The Policy emphasised improvement in material living conditions. It suffered, however, from severe underfunding, inflated expectations and lack of acceptance in the Dutc ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
History Of Indonesia
The history of Indonesia has been shaped by geographic position, its natural resources, a series of human migrations and contacts, wars of conquest, the spread of Islam from the island of Sumatra in the 7th century AD and the establishment of Islamic kingdoms, as well as by trade Bowls, Jars, Jugs and so on, economics and politics. Indonesia is an archipelago, archipelagic country of 17,000 to 18,000 islands (8,844 named and 922 permanently inhabited) stretching along the equator in South East Asia. The country's strategic sea-lane position fostered inter-island and international trade; trade has since fundamentally shaped Indonesian history. The area of Indonesia is populated by peoples of various migrations, creating a diversity of Culture of Indonesia, cultures, Ethnic groups of Indonesia, ethnicities, and Languages of Indonesia, languages. The archipelago's landforms and climate significantly influenced agriculture and trade, and the formation of states. The boundaries of t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
New Imperialism
In historical contexts, New Imperialism characterizes a period of colonial expansion by European powers, the United States, and Japan during the late 19th and early 20th centuries. Com The period featured an unprecedented pursuit of overseas territorial acquisitions. At the time, states focused on building their empires with new technological advances and developments, expanding their territory through conquest, and exploiting the resources of the subjugated countries. During the era of New Imperialism, the Western powers (and Japan) individually conquered almost all of Africa and parts of Asia. The new wave of imperialism reflected ongoing rivalries among the great powers, the economic desire for new resources and markets, and a "civilizing mission" ethos. Many of the colonies established during this era gained independence during the era of decolonization that followed World War II. The qualifier "new" is used to differentiate modern imperialism from earlier imperi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Economic History Of Indonesia
The economic history of Indonesia is shaped by its geographic location, its natural resources, as well as its people that inhabited the archipelago that today formed the modern nation-state of the Republic of Indonesia. The foreign contact and international trade with foreign counterparts had also shaped and sealed the fate of Indonesian archipelago, as Indians, Chinese, Arabs, and eventually European traders reached the archipelago during the Age of Exploration and participated in the spice trade, war and conquest. By the early 17th century, the Dutch East India Company (VOC), one of the world's earliest multinational companies, had established their base in the archipelago as they monopolised the spice trade. By 1800, the Dutch East Indies colonial state had emerged and benefited from cash crop trades of coffee, tea, quinine, rubber and palm oil from the colony, also from the mining sector: oil, coal, tin and copper. The colonial state would be succeeded by the Indonesian ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
_Java_TMnr_10011707.jpg)


