|
Leslie Combs (soldier And Politician)
Leslie Combs (November 28, 1793 – August 22, 1881) was a lawyer and politician from the U.S. state of Kentucky. He served under William Henry Harrison and Green Clay during the War of 1812 and was captured in 1813. After his release, he studied law and was admitted to the bar in 1818. In 1827, he was elected as a Whig to the first of several non-consecutive terms in the Kentucky House of Representatives. He was re-elected in 1833, 1845, and 1857, and served as Speaker of the House in 1846. He lost a bid for a seat in the U.S. House of Representatives to Democrat John C. Breckinridge in 1851. His last political office was clerk of the Kentucky Court of Appeals, which he held from 1860 to 1866, when he retired from public life. He died in 1881 and was buried in Lexington Cemetery. Early life Leslie Combs was born November 28, 1793, in Clark County, Kentucky.Kleber, p. 219 He was the youngest of twelve children born to Benjamin Combs, an officer in the Revolutionary War, and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kentucky Court Of Appeals
The Kentucky Court of Appeals is the lower of Kentucky's two appellate courts, under the Kentucky Supreme Court. Prior to a 1975 amendment to the Kentucky Constitution the Kentucky Court of Appeals was the only appellate court in Kentucky. The Court of Appeals has 14 members. Two members are elected from each of seven districts and serve eight-year terms of office. The Kentucky Court of Appeals judges are elected from districts that mirror the seven districts which elect the seven justices of the Supreme Court of Kentucky. The 14 judges select one colleague to serve as chief judge for a four-year term. The chief judge assigns judges and cases to panels. The current chief judge is Denise G. Clayton. The court usually sits in three judge panels. Membership of the panels rotate so that all judges sit on at least one panel with each of their colleagues in any given year. Usually one judge is chosen to author the majority opinion for each panel in a particular case. The Kentuc ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
John C
John is a common English name and surname: * John (given name) * John (surname) John may also refer to: New Testament Works * Gospel of John, a title often shortened to John * First Epistle of John, often shortened to 1 John * Second Epistle of John, often shortened to 2 John * Third Epistle of John, often shortened to 3 John People * John the Baptist (died c. AD 30), regarded as a prophet and the forerunner of Jesus Christ * John the Apostle (lived c. AD 30), one of the twelve apostles of Jesus * John the Evangelist, assigned author of the Fourth Gospel, once identified with the Apostle * John of Patmos, also known as John the Divine or John the Revelator, the author of the Book of Revelation, once identified with the Apostle * John the Presbyter, a figure either identified with or distinguished from the Apostle, the Evangelist and John of Patmos Other people with the given name Religious figures * John, father of Andrew the Apostle and Saint Peter * Pope Jo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Reading Law
Reading law was the method used in common law countries, particularly the United States, for people to prepare for and enter the legal profession before the advent of law schools. It consisted of an extended internship or apprenticeship under the tutelage or mentoring of an experienced lawyer. The practice largely died out in the early 20th century. A few U.S. states still permit people to become lawyers by reading law instead of attending law school, although the practice is rare. In this sense, "reading law" specifically refers to a means of entering the profession, although in England it is still customary to say that a university undergraduate is "reading" a course, which may be law or any other. __TOC__ History United States In colonial America, as in Britain in that day, law schools did not exist at all until Litchfield Law School was founded in 1773. Within a few years following the American Revolution, some universities such as the College of William and Mary and the Un ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Parole
Parole (also known as provisional release or supervised release) is a form of early release of a prison inmate where the prisoner agrees to abide by certain behavioral conditions, including checking-in with their designated parole officers, or else they may be rearrested and returned to prison. Originating from the French word ''parole'' ("speech, spoken words" but also "promise"), the term became associated during the Middle Ages with the release of prisoners who gave their word. This differs greatly from pardon, amnesty or commutation of sentence in that parolees are still considered to be serving their sentences, and may be returned to prison if they violate the conditions of their parole. Modern development Alexander Maconochie, a Scottish geographer and captain in the Royal Navy, introduced the modern idea of parole when, in 1840, he was appointed superintendent of the British penal colonies in Norfolk Island, Australia. He developed a plan to prepare them for event ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
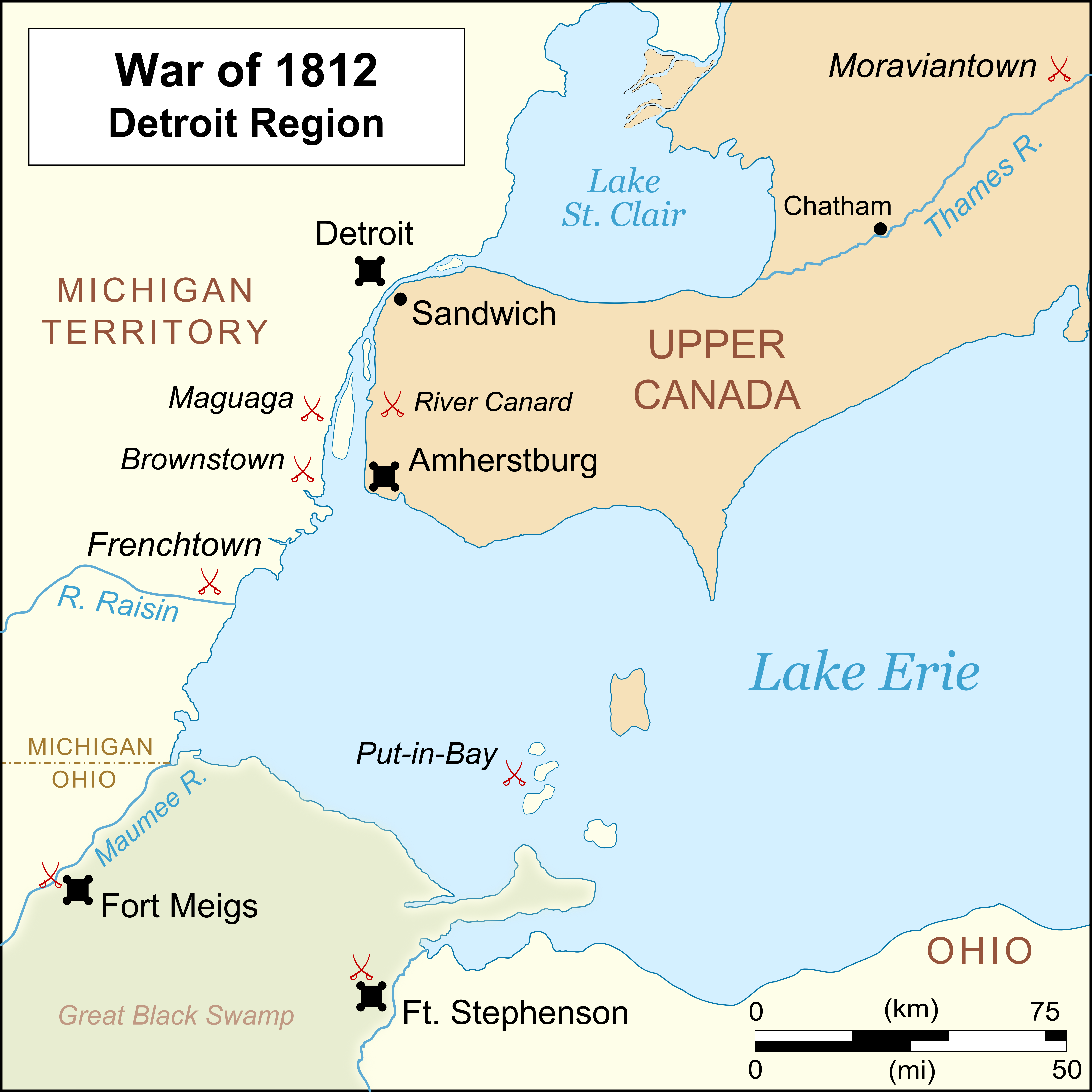
Siege Of Fort Meigs
The siege of Fort Meigs took place in late April to early May 1813 during the War of 1812 in northwestern Ohio, present-day Perrysburg. A small British Army unit with support from Indians attempted to capture the recently constructed fort to forestall an American offensive against Detroit, and its Fort Detroit in the Great Lakes region which the British from the north in Canada had captured the previous year. An American sortie and relief attempt failed with heavy casualties, but the British failed to capture the fort and were forced to raise the siege. Background In the early days of the War of 1812 (1812–1815), an American Army under Brigadier General William Hull (1753–1825), surrendered following the siege of Detroit. To recover the town of Detroit and Fort Detroit, the Americans formed the Army of the Northwest. Brigadier General James Winchester (1752–1826), briefly commanded this army before William Henry Harrison (1773–1841), Congressional delegate and then se ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Potawatomi
The Potawatomi , also spelled Pottawatomi and Pottawatomie (among many variations), are a Native American people of the western Great Lakes region, upper Mississippi River and Great Plains. They traditionally speak the Potawatomi language, a member of the Algonquin family. The Potawatomi call themselves ''Neshnabé'', a cognate of the word ''Anishinaabe''. The Potawatomi are part of a long-term alliance, called the Council of Three Fires, with the Ojibway and Odawa (Ottawa). In the Council of Three Fires, the Potawatomi are considered the "youngest brother" and are referred to in this context as ''Bodwéwadmi'', a name that means "keepers of the fire" and refers to the council fire of three peoples. In the 18th century, they were pushed to the west by European/American encroachment and eventually removed from their lands in the Great Lakes region to reservations in Oklahoma. Under Indian Removal, they eventually ceded many of their lands, and most of the Potawatomi relocated ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Maumee River
The Maumee River (pronounced ) ( sjw, Hotaawathiipi; mia, Taawaawa siipiiwi) is a river running in the United States Midwest from northeastern Indiana into northwestern Ohio and Lake Erie. It is formed at the confluence of the St. Joseph and St. Marys rivers, where Fort Wayne, Indiana has developed, and meanders northeastwardly for U.S. Geological Survey. National Hydrography Dataset high-resolution flowline dataThe National Map, accessed May 19, 2011 through an agricultural region of glacial moraines before flowing into the Maumee Bay of Lake Erie. The city of Toledo is located at the mouth of the Maumee. The Maumee was designated an Ohio State Scenic River on July 18, 1974. The Maumee watershed is Ohio’s breadbasket; it is two-thirds farmland, mostly corn and soybeans. It is the largest watershed of any of the rivers feeding the Great Lakes, and supplies five percent of Lake Erie’s water. History Historically the river was also known as the ''Miami'' in United ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fort Meigs
Fort Meigs was a United States fortification along the Maumee River in what is now Perrysburg, Ohio during the War of 1812. The British Army, supported by Tecumseh's Confederacy, failed to capture the fort during the siege of Fort Meigs. It is named in honor of Ohio governor Return J. Meigs Jr., for his support in providing General William Henry Harrison with militia and supplies for the line of forts along the Old Northwest frontier. History Construction of the fort started in February 1813 by soldiers under the command of General William Henry Harrison (future president) at a site where present-day Perrysburg, Ohio developed. It was to provide a supply depot and staging point for US military operations in Canada that would also command the rapids of the Maumee River. The remnants of the British Fort Miami were across the river downstream, to the northeast. The winter climate was harsh, and the landscape unforgiving. A U.S. sentry froze to death during his two hours of guard dut ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fort Defiance (Ohio)
Fort Defiance was built by General "Mad" Anthony Wayne in the second week of August 1794 at the confluence of the Auglaize and Maumee rivers. It was the one of a line of defenses constructed by American forces in the campaign leading to the Northwest Indian War's Battle of Fallen Timbers on August 20, 1794. Work began on August 9, 1794 and was completed by August 17. The name was derived from a declaration by Charles Scott, who was leading a band of Kentucky militiamen in support of Wayne, that: "I defy the English, Indians, and all the devils of hell to take it."Nelson, p. 246 The post was considered one of the strongest fortifications built in that period. Following the Battle of Fallen Timbers, Wayne ordered the destruction of all Native American villages and their crops within a radius of the fort. Under terms of the Treaty of Greenville, signed on August 3, 1795, the native nations ceded six square miles around the fort and allowed the Americans to maintain a trading ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
William Dudley (colonel)
William Dudley (1766 – May 5, 1813) was a colonel in the 13th Regiment of the Kentucky Militia during the War of 1812. He was born in Fredericksburg, Virginia to Robert and Joyce (Gayle) Dudley. He married Lucy Smith on August 23, 1792. Life in Kentucky As a young man, William went to seek his fortune west of the Appalachian Mountains. He eventually settled in Fayette County, Kentucky. There, he served as the local magistrate for several years. When the War of 1812 broke out, he was a colonel in the 13th Regiment of Kentucky Militia. Military service In the spring of 1813, Dudley was under command of General Green Clay. Clay's forces numbered some 1,200 strong as they travelled up the Maumee River to Fort Meigs. Clay's forces arrived at the fort on May 4, 1813, in the midst of the Siege of Fort Meigs. General William Henry Harrison sent a courier to General Clay ordering him to conduct a raid against the British battery on the other side of the Maumee to drive them away and s ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Colonel (United States)
The colonel () in the United States Army, Marine Corps, Air Force and Space Force, is the most senior field-grade military officer rank, immediately above the rank of lieutenant colonel and just below the rank of brigadier general. Colonel is equivalent to the naval rank of captain in the other uniformed services. By law, an officer previously required at least 22 years of cumulative service and a minimum of three years as a lieutenant colonel before being promoted to colonel. With the signing of the National Defense Authorization Act of 2019 (NDAA 2019), military services now have the authorization to directly commission new officers up to the rank of colonel. The pay grade for colonel is O-6. When worn alone, the insignia of rank seen at right is worn centered on headgear and fatigue uniforms. When worn in pairs, the insignia is worn on the officer's left side while a mirror-image reverse version is worn on the right side, such that both of the eagles' heads face forwa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Jessamine County, Kentucky
Jessamine County () is a County (United States), county located in the U.S. state of Kentucky. As of the 2020 United States census, 2020 census, the population was 52,991. Its county seat is Nicholasville, Kentucky, Nicholasville. The county was founded in December 1798. Jessamine County is part of the Lexington-Fayette, KY Lexington-Fayette, KY Metropolitan Statistical Area, Metropolitan Statistical Area. It is within the Inner Blue Grass region, long a center of farming and blooded stock raising, including thoroughbred horses. The legislature established a commercial wine industry here in the late 18th century. History Jessamine County was established in 1798 from land given by Fayette County, Kentucky, Fayette County. Jessamine was the 36th list of Kentucky counties, Kentucky county in order of formation. The county is claimed to be named for a Jessamine Douglass, the daughter of a pioneer settler, who was either killed by Native Americans or committed suicide after being unlu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |