|
Leptosphaeria Maculans
''Leptosphaeria maculans'' (anamorph ''Phoma lingam'') is a fungal pathogen of the phylum Ascomycota that is the causal agent of blackleg disease on ''Brassica'' crops. Its genome has been sequenced, and ''L. maculans'' is a well-studied model phytopathogenic fungus. Symptoms of blackleg generally include basal stem cankers, small grey lesions on leaves, and root rot. The major yield loss is due to stem canker. The fungus is dispersed by the wind as ascospores or rain splash in the case of the conidia. ''L. maculans'' grows best in wet conditions and a temperature range of 5–20 degrees Celsius. Rotation of crops, removal of stubble, application of fungicide, and crop resistance are all used to manage blackleg. The fungus is an important pathogen of ''Brassica napus'' (canola) crops. Host and symptoms ''Leptosphaeria maculans'' causes phoma stem canker or blackleg. Symptoms generally include basal stem cankers, small grey oval lesions on the leaf tissue and root rot (as the fun ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
James Sowerby
James Sowerby (21 March 1757 – 25 October 1822) was an English naturalist, illustrator and mineralogist. Contributions to published works, such as ''A Specimen of the Botany of New Holland'' or ''English Botany'', include his detailed and appealing plates. The use of vivid colour and accessible texts were intended to reach a widening audience in works of natural history. Biography James Sowerby was born in Lambeth, London, his parents were named John and Arabella. Having decided to become a painter of flowers his first venture was with William Curtis, whose ''Flora Londinensis'' he illustrated. Sowerby studied art at the Royal Academy and took an apprenticeship with Richard Wright. He married Anne Brettingham De Carle and they were to have three sons: James De Carle Sowerby (1787–1871), George Brettingham Sowerby I (1788–1854) and Charles Edward Sowerby (1795–1842), the Sowerby family of naturalists. His sons and theirs were to contribute and continue the enormous ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
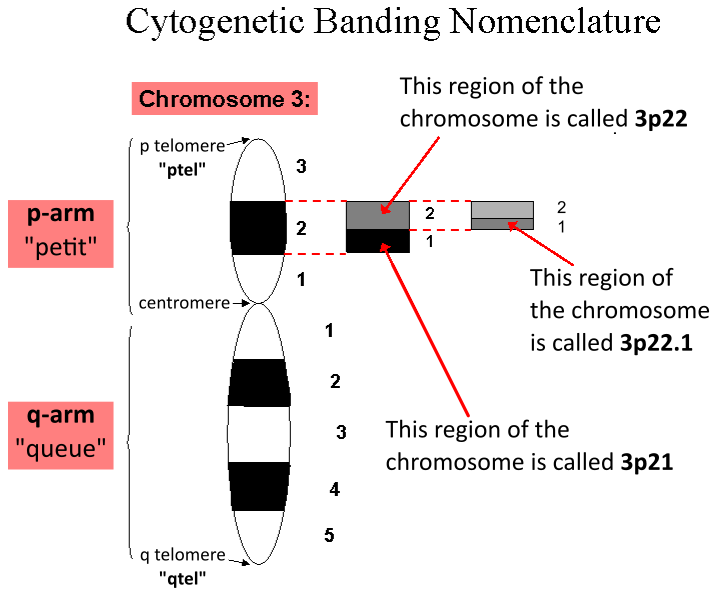
Quantitative Trait Locus
A quantitative trait locus (QTL) is a locus (section of DNA) that correlates with variation of a quantitative trait in the phenotype of a population of organisms. QTLs are mapped by identifying which molecular markers (such as SNPs or AFLPs) correlate with an observed trait. This is often an early step in identifying the actual genes that cause the trait variation. Definition A quantitative trait locus (QTL) is a region of DNA which is associated with a particular phenotypic trait, which varies in degree and which can be attributed to polygenic effects, i.e., the product of two or more genes, and their environment. . These QTLs are often found on different chromosomes. The number of QTLs which explain variation in the phenotypic trait indicates the genetic architecture of a trait. It may indicate that plant height is controlled by many genes of small effect, or by a few genes of large effect. Typically, QTLs underlie continuous traits (those traits which vary continuousl ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ethylene
Ethylene (IUPAC name: ethene) is a hydrocarbon which has the formula or . It is a colourless, flammable gas with a faint "sweet and musky" odour when pure. It is the simplest alkene (a hydrocarbon with carbon-carbon double bonds). Ethylene is widely used in the chemical industry, and its worldwide production (over 150 million tonnes in 2016) exceeds that of any other organic compound. Much of this production goes toward polyethylene, a widely used plastic containing polymer chains of ethylene units in various chain lengths. Ethylene is also an important natural plant hormone and is used in agriculture to force the ripening of fruits. The hydrate of ethylene is ethanol. Structure and properties This hydrocarbon has four hydrogen atoms bound to a pair of carbon atoms that are connected by a double bond. All six atoms that comprise ethylene are coplanar. The H-C-H angle is 117.4°, close to the 120° for ideal sp² hybridized carbon. The molecule is also relatively weak: ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Jasmonic Acid
Jasmonic acid (JA) is an organic compound found in several plants including jasmine. The molecule is a member of the jasmonate class of plant hormones. It is biosynthesized from linolenic acid by the octadecanoid pathway. It was first isolated in 1957 as the methyl ester of jasmonic acid by the Swiss chemist Edouard Demole and his colleagues. Biosynthesis Its biosynthesis starts from the fatty acid linolenic acid, which is oxygenated by lipoxygenase (13-LOX), forming a hydroperoxide. This peroxide then cyclizes in the presence of allene oxide synthase to form an allene oxide. The rearrangement of allene oxide to form 12-oxophytodienoic acid is catalyzed by the enzyme allene oxide cyclase. A series of β-oxidations result in 7-iso-jasmonic acid. In the absence of enzyme, this iso-jasmonic acid isomerizes to jasmonic acid. Function The major function of JA and its various metabolites is regulating plant responses to abiotic and biotic stresses as well as plant growth and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Salicylic Acid
Salicylic acid is an organic compound with the formula HOC6H4CO2H. A colorless, bitter-tasting solid, it is a precursor to and a metabolite of aspirin (acetylsalicylic acid). It is a plant hormone, and has been listed by the EPA Toxic Substances Control Act (TSCA) Chemical Substance Inventory as an experimental teratogen. The name is from Latin '' salix'' for willow tree. It is an ingredient in some anti-acne products. Salts and esters of salicylic acid are known as salicylates. Uses Medicine Salicylic acid as a medication is commonly used to remove the outer layer of the skin. As such, it is used to treat warts, psoriasis, acne vulgaris, ringworm, dandruff, and ichthyosis. Similar to other hydroxy acids, salicylic acid is an ingredient in many skincare products for the treatment of seborrhoeic dermatitis, acne, psoriasis, calluses, Corn (medicine), corns, keratosis pilaris, acanthosis nigricans, ichthyosis, and warts. Uses in manufacturing Salicylic acid is used as ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Phytoalexin
Phytoalexins are antimicrobial substances, some of which are antioxidative as well. They are defined, not by their having any particular chemical structure or character, but by the fact that they are defensively synthesized ''de novo'' by plants that produce the compounds rapidly at sites of pathogen infection. In general phytoalexins are broad spectrum inhibitors; they are chemically diverse, and different chemical classes of compounds are characteristic of particular plant taxa. Phytoalexins tend to fall into several chemical classes, including terpenoids, glycosteroids and alkaloids, however the term applies to any phytochemicals that are induced by microbial infection. Function Phytoalexins are produced in plants to act as toxins to the attacking organism. They may puncture the cell wall, delay maturation, disrupt metabolism or prevent reproduction of the pathogen in question. Their importance in plant defense is indicated by an increase in susceptibility of plant tissue t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Camalexin
Camalexin (3-thiazol-2-yl-indole) is a simple indole alkaloid found in the plant ''Arabidopsis thaliana'' and other crucifers. The secondary metabolite functions as a phytoalexin to deter bacterial and fungal pathogens. Structure The base structure of camalexin consists of an indole ring derived from tryptophan. The ethanamine moiety attached to the 3 position of the indole ring is subsequently rearranged into a thiazole ring. Biosynthesis While the biosynthesis of camalexin ''in planta'' has not been fully elucidated, most of the enzymes involved in the pathway are known and involved in a metabolon complex. The pathway starts with a tryptophan precursor which is subsequently oxidized by two cytochrome P450 enzymes. The indole-3-acetaldoxime is then converted to indole-3-acetonitrile by another cytochrome P450, CYP71A13. A glutathione conjugate followed by a subsequent unknown enzyme is needed to form dihydrocamalexic acid. A final decarboxylation step by cytochrome P450 C ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
T-DNA
The transfer DNA (abbreviated T-DNA) is the transferred DNA of the tumor-inducing (Ti) plasmid of some species of bacteria such as '' Agrobacterium tumefaciens'' and '' Agrobacterium rhizogenes(actually an Ri plasmid)''. The T-DNA is transferred from bacterium into the host plant's nuclear DNA genome. The capability of this specialized tumor-inducing (Ti) plasmid is attributed to two essential regions required for DNA transfer to the host cell. The T-DNA is bordered by 25-base-pair repeats on each end. Transfer is initiated at the right border and terminated at the left border and requires the ''vir'' genes of the Ti plasmid. The bacterial T-DNA is about 24,000 base pairs long and contains plant-expressed genes that code for enzymes synthesizing opines and phytohormones. By transferring the T-DNA into the plant genome, the bacterium essentially reprograms the plant cells to grow into a tumor and produce a unique food source for the bacteria. The synthesis of the plant hormones a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
NOD-like Receptor
The nucleotide-binding oligomerization domain-like receptors, or NOD-like receptors (NLRs) (also known as nucleotide-binding leucine-rich repeat receptors), are intracellular sensors of pathogen-associated molecular patterns (PAMPs) that enter the cell via phagocytosis or pores, and damage-associated molecular patterns (DAMPs) that are associated with cell stress. They are types of pattern recognition receptors (PRRs), and play key roles in the regulation of innate immune response. NLRs can cooperate with toll-like receptors (TLRs) and regulate inflammatory and apoptotic response. They are found in lymphocytes, macrophages, dendritic cells and also in non-immune cells, for example in epithelium. NLRs are highly conserved through evolution. Their homologs have been discovered in many different animal species (APAF1) and also in the plant kingdom ( disease-resistance R protein). Structure NLRs contain 3 domains – central NACHT (NOD or NBD – nucleotide-binding domain) dom ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Interleukin-1 Receptor Family
Members of the very wide interleukin-1 receptor (IL-1R) family are characterized by extracellular immunoglobulin-like domains and intracellular Toll/Interleukin-1R (TIR) domain. It is a group of structurally homologous proteins, conserved throughout the species as it was identified from plants to mammals. Proteins of this family play important role in host defence, injury and stress. There are four main groups of TIR domain-containing proteins in animals; Toll-like receptors, Interleukin-1 receptor (IL-1R), cytosolic adaptor proteins (such as MyD88 adaptor protein) and insect and nematode Toll. Each of these groups is involved mainly in host defence; Toll receptors are also involved in embryogenesis. TIR domain The TIR domain is about 200 amino acids long and consists of 3 conserved boxes and between these boxes there are regions of variable length. If due to some mutation all of the three boxes are damaged, there is no surface expression of the protein. If only boxes one and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Locus (genetics)
In genetics, a locus (plural loci) is a specific, fixed position on a chromosome where a particular gene or genetic marker is located. Each chromosome carries many genes, with each gene occupying a different position or locus; in humans, the total number of protein-coding genes in a complete haploid set of 23 chromosomes is estimated at 19,000–20,000. Genes may possess multiple variants known as alleles, and an allele may also be said to reside at a particular locus. Diploid and polyploid cells whose chromosomes have the same allele at a given locus are called homozygous with respect to that locus, while those that have different alleles at a given locus are called heterozygous. The ordered list of loci known for a particular genome is called a gene map. Gene mapping is the process of determining the specific locus or loci responsible for producing a particular phenotype or biological trait. Association mapping, also known as "linkage disequilibrium mapping", is a method of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mutation
In biology, a mutation is an alteration in the nucleic acid sequence of the genome of an organism, virus, or extrachromosomal DNA. Viral genomes contain either DNA or RNA. Mutations result from errors during DNA replication, DNA or viral replication, mitosis, or meiosis or other types of DNA repair#DNA damage, damage to DNA (such as pyrimidine dimers caused by exposure to ultraviolet radiation), which then may undergo error-prone repair (especially microhomology-mediated end joining), cause an error during other forms of repair, or cause an error during replication (DNA repair#Translesion synthesis, translesion synthesis). Mutations may also result from Insertion (genetics), insertion or Deletion (genetics), deletion of segments of DNA due to mobile genetic elements. Mutations may or may not produce detectable changes in the observable characteristics (phenotype) of an organism. Mutations play a part in both normal and abnormal biological processes including: evolution, cancer ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |