|
Leoncito Astronomical Complex
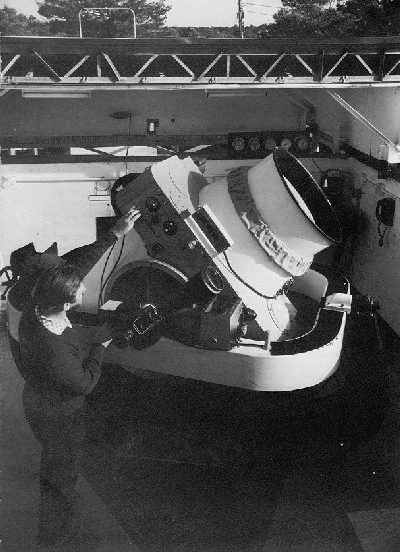
The El Leoncito Astronomical Complex (Spanish: Complejo Astronómico El Leoncito - CASLEO) is an astronomical observatory in the San Juan Province of Argentina. CASLEO is one of two observatories located within El Leoncito National Park, which is in a part of the country which rarely sees cloud cover. The other facility in the park is the Carlos U. Cesco Astronomical Station of the Félix Aguilar Observatory. CASLEO was established in 1983 by an agreement between National Scientific and Technical Research Council (CONICET) of Argentina, the Ministry of Science, Technology and Innovation (MINCYT) of Argentina, the National University of San Juan (UNSJ), the National University of La Plata (UNLP), and the National University of Córdoba (UNC). The facility was dedicated in 1986 and regular observations began in 1987. CASLEO's telescopes are located in two separate areas within the El Leoncito Park. The Jorge Sahade and Submillimeter telescopes are at the main site on the edge of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
National Scientific And Technical Research Council
National may refer to: Common uses * Nation or country ** Nationality – a ''national'' is a person who is subject to a nation, regardless of whether the person has full rights as a citizen Places in the United States * National, Maryland, census-designated place * National, Nevada, ghost town * National, Utah, ghost town * National, West Virginia, unincorporated community Commerce * National (brand), a brand name of electronic goods from Panasonic * National Benzole (or simply known as National), former petrol station chain in the UK, merged with BP * National Car Rental, an American rental car company * National Energy Systems, a former name of Eco Marine Power * National Entertainment Commission, a former name of the Media Rating Council * National Motor Vehicle Company, Indianapolis, Indiana, USA 1900-1924 * National Supermarkets, a defunct American grocery store chain * National String Instrument Corporation, a guitar company formed to manufacture the first resonator g ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Equatorial Mount
An equatorial mount is a mount for instruments that compensates for Earth's rotation by having one rotational axis, the polar axis, parallel to the Earth's axis of rotation. This type of mount is used for astronomical telescopes and cameras. The advantage of an equatorial mount lies in its ability to allow the instrument attached to it to stay fixed on any celestial object with diurnal motion by driving one axis at a constant speed. Such an arrangement is called a sidereal or clock drive. Equatorial mounts achieve this by aligning their rotational axis with the Earth, a process known as polar alignment. Astronomical telescope mounts In astronomical telescope mounts, the equatorial axis (the '' right ascension'') is paired with a second perpendicular axis of motion (known as the '' declination''). The equatorial axis of the mount is often equipped with a motorized "''clock drive''", that rotates that axis one revolution every 23 hours and 56 minutes in exact sync with the appar ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
List Of Astronomical Observatories
This is a list of astronomical observatories ordered by name, along with initial dates of operation (where an accurate date is available) and location. The list also includes a final year of operation for many observatories that are no longer in operation. While other sciences, such as volcanology and meteorology, also use facilities called observatories for research and observations, this list is limited to observatories that are used to observe celestial objects. Astronomical observatories are mainly divided into four categories: space-based, airborne, ground-based, and underground-based. Many modern telescopes and observatories are located in space to observe astronomical objects in wavelengths of the electromagnetic spectrum that cannot penetrate the Earth's atmosphere (such as ultraviolet radiation, X-rays, and gamma rays) and are thus impossible to observe using ground-based telescopes. Being above the atmosphere, these space observatories can also avoid the effects of atmo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
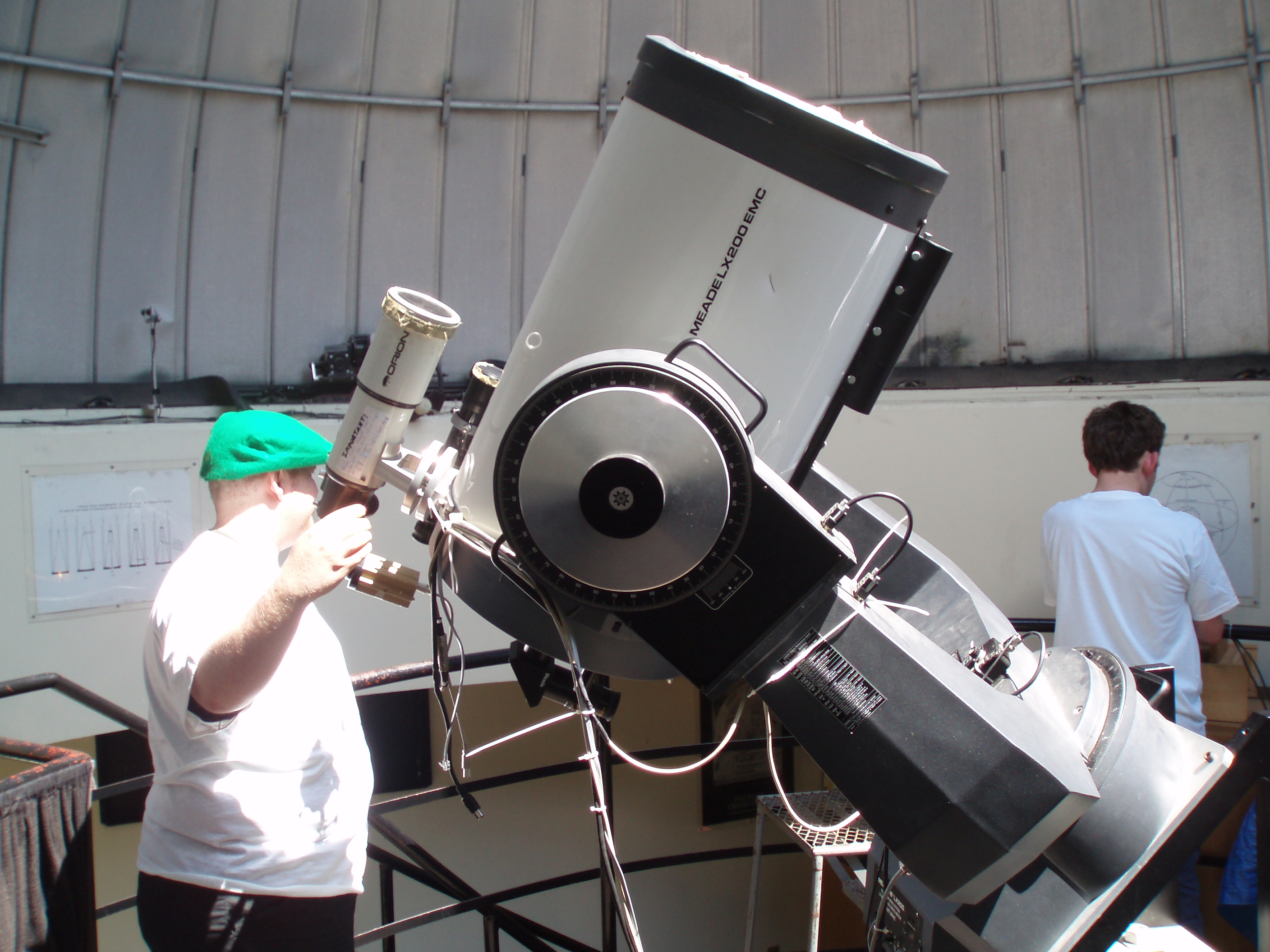
Meade Instruments
The Meade Instruments (also shortened to Meade) is an American multinational company headquartered in Watsonville, California, that manufactures, imports, and distributes telescopes, binoculars, spotting scopes, microscopes, CCD cameras, and telescope accessories for the consumer market. It is the world's largest manufacturer of telescopes. Besides selling under its "Meade" brand name, the company sells solar telescopes under the brand "Coronado". Origins and history Founded in 1972 by John Diebel, Meade started as a mail order seller of small refracting telescopes and telescope accessories manufactured by the Japan-based Towa Optical Manufacturing Company. Meade started manufacturing its own line of products in 1976, introducing 6" and 8" reflecting telescopes models in 1977. In 1980, the company ventured into the Schmidt-Cassegrain market that up to that time had been dominated by Celestron Corporation. Meade has a long history of litigation with other companies over infri ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Helen Sawyer Hogg
Helen Battles Sawyer Hogg (August 1, 1905 – January 28, 1993) was an American-Canadian astronomer who pioneered research into globular clusters and variable stars. She was the first female president of several astronomical organizations and a notable woman of science in a time when many universities would not award scientific degrees to women. Her scientific advocacy and journalism included astronomy columns in the ''Toronto Star'' ("With the Stars", 1951–81) and the ''Journal of the Royal Astronomical Society of Canada'' ("Out of Old Books", 1946–65). She was considered a "great scientist and a gracious person" over a career of sixty years.Shearer, B.F., & Shearer, B.S. (1997). ''Notable Women in the Physical Sciences: A Biographical Dictionary'' Westport, Conn.: Greenwood Press. Early life Born in Lowell, Massachusetts on August 1, 1905, Helen was the second daughter of banker Edward Everett Sawyer and former teacher Carrie Douglass Sawyer. Academically gifted, Helen gr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chile
Chile, officially the Republic of Chile, is a country in the western part of South America. It is the southernmost country in the world, and the closest to Antarctica, occupying a long and narrow strip of land between the Andes to the east and the Pacific Ocean to the west. Chile covers an area of , with a population of 17.5 million as of 2017. It shares land borders with Peru to the north, Bolivia to the north-east, Argentina to the east, and the Drake Passage in the far south. Chile also controls the Pacific islands of Juan Fernández, Isla Salas y Gómez, Desventuradas, and Easter Island in Oceania. It also claims about of Antarctica under the Chilean Antarctic Territory. The country's capital and largest city is Santiago, and its national language is Spanish. Spain conquered and colonized the region in the mid-16th century, replacing Inca rule, but failing to conquer the independent Mapuche who inhabited what is now south-central Chile. In 1818, after declaring in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Las Campanas Observatory
Las Campanas Observatory (LCO) is an astronomical observatory owned and operated by the Carnegie Institution for Science (CIS). It is in the southern Atacama Desert of Chile in the Atacama Region approximately northeast of the city of La Serena. The LCO telescopes and other facilities are near the north end of a long mountain ridge. Cerro Las Campanas, near the southern end and over high, is the future home of the Giant Magellan Telescope. LCO was established in 1969 and is the primary observing facility of CIS. It supplanted Mount Wilson Observatory in that role due to increasing light pollution in the Los Angeles area. The headquarters of Carnegie Observatories is located in Pasadena, California, while the main office in Chile is in La Serena next to the University of La Serena and a short distance from the Association of Universities for Research in Astronomy facility. It is served by Pelicano Airport, to the southwest. Telescopes * The Magellan Telescopes are two i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
University Of Toronto Southern Observatory
The University of Toronto Southern Observatory (UTSO) was an astronomical observatory built by the University of Toronto at the Las Campanas Observatory in Chile. It hosted a single 60 cm Cassegrain telescope and a small cottage for the operators, located amongst the instruments funded by other organizations. The first observational runs started in 1971, and like many smaller instruments, it was later shut down in favor of a partial share in a much larger telescope in 1997. Although small by modern standards, the Southern Observatory nevertheless became famous for its role in the discovery of SN 1987A when UofT astronomer Ian Shelton spotted the supernova while observing with another little-used telescope at the site. History The Southern Observatory came about as a side-effect of problems being caused by the urban sprawl in the Toronto area. Originally located far in the country outside the city, the university's David Dunlap Observatory was being encroached on by new subu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
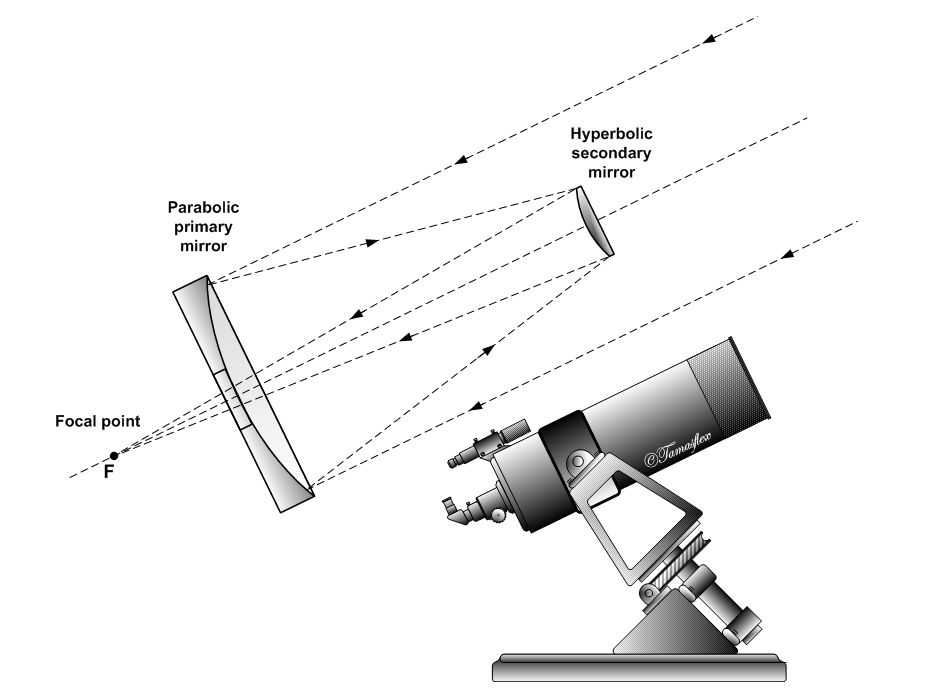
Cassegrain Reflector
The Cassegrain reflector is a combination of a primary concave mirror and a secondary convex mirror, often used in optical telescopes and radio antennas, the main characteristic being that the optical path folds back onto itself, relative to the optical system's primary mirror entrance aperture. This design puts the focal point at a convenient location behind the primary mirror and the convex secondary adds a telephoto effect creating a much longer focal length in a mechanically short system. In a symmetrical Cassegrain both mirrors are aligned about the optical axis, and the primary mirror usually contains a hole in the center, thus permitting the light to reach an eyepiece, a camera, or an image sensor. Alternatively, as in many radio telescopes, the final focus may be in front of the primary. In an asymmetrical Cassegrain, the mirror(s) may be tilted to avoid obscuration of the primary or to avoid the need for a hole in the primary mirror (or both). The classic Cassegrain ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Submillimeter
Submillimetre astronomy or submillimeter astronomy (see spelling differences) is the branch of observational astronomy that is conducted at submillimetre wavelengths (i.e., terahertz radiation) of the electromagnetic spectrum. Astronomers place the submillimetre waveband between the far-infrared and microwave wavebands, typically taken to be between a few hundred micrometres and a millimetre. It is still common in submillimetre astronomy to quote wavelengths in 'microns', the old name for micrometre. Using submillimetre observations, astronomers examine molecular clouds and dark cloud cores with a goal of clarifying the process of star formation from earliest collapse to stellar birth. Submillimetre observations of these dark clouds can be used to determine chemical abundances and cooling mechanisms for the molecules which comprise them. In addition, submillimetre observations give information on the mechanisms for the formation and evolution of galaxies. From the g ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
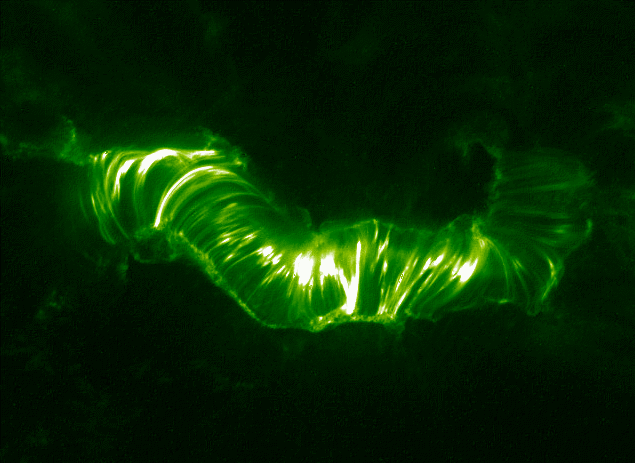
Solar Flares
A solar flare is an intense localized eruption of electromagnetic radiation in the Sun's atmosphere. Flares occur in active regions and are often, but not always, accompanied by coronal mass ejections, solar particle events, and other solar phenomena. The occurrence of solar flares varies with the 11-year solar cycle. Solar flares are thought to occur when stored magnetic energy in the Sun's atmosphere accelerates charged particles in the surrounding plasma. This results in the emission of electromagnetic radiation across the electromagnetic spectrum. High-energy electromagnetic radiation from solar flares is absorbed by the daylight side of Earth's upper atmosphere, in particular the ionosphere, and does not reach the surface. This absorption can temporarily increase the ionization of the ionosphere which may interfere with short-wave radio communication. The prediction of solar flares is an active area of research. Flares also occur on other stars, where the term ''stellar f ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Boller & Chivens
Boller and Chivens was an American manufacturer of high-quality telescopes and spectrographs headquartered in South Pasadena, California. History Founded about 1946 by Harry Berthold Boller (1915-1997) and Clyde Cuthbertson Chivens (1915-2008). the company was acquired in 1965 by Perkin-Elmer. In the 1950s, Boller and Chivens collaborated with Perkin-Elmer to develop and manufacture the large-aperture Baker-Nunn satellite tracking camera for the United States Vanguard space satellite program. In culture A 41-cm (16-inch) Boller and Chivens Cassegrain reflector originally housed at the Harvard-Smithsonian Oak Ridge Observatory in Massachusetts is available for public use at the National Air and Space Museum's Public Observatory Project on the National Mall The National Mall is a Landscape architecture, landscaped park near the Downtown, Washington, D.C., downtown area of Washington, D.C., the capital city of the United States. It contains and borders a number of museums of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |



.jpg)