|
Leen Ritmeyer
Leen Ritmeyer (b. 1945) is a Dutch-born archaeological architect who currently lives and works in Wales, after having spent 22 years (1967–89) in Jerusalem. Career Ritmeyer holds an M.A. in Conservation Studies from the Institute of Advanced Architectural Studies, University of York, England, and a Ph.D. from the University of Manchester, England. Beginning in 1973, Ritmeyer served for 4 years as official architect of the archaeological dig at the Western Wall and Southern Wall of the Temple Mount directed by Benjamin Mazar,"How We Lost the Temple Mount," Hershel Shanks, Moment (magazine), June 2002. and 10 years in the Jewish Quarter Excavations of the Old City of Jerusalem, directed by Nahman Avigad. In Gershom Gorenberg's words, " en archeologists speak today of solid scientific research on the Temple's location, they’re most likely to refer to Leen Ritmeyer", referring to his work on the Temple Mount in Jerusalem. He presented solid arguments based on archaeological ev ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Rowman & Littlefield
Rowman & Littlefield Publishing Group is an independent publishing house founded in 1949. Under several imprints, the company offers scholarly books for the academic market, as well as trade books. The company also owns the book distributing company National Book Network based in Lanham, Maryland. History The current company took shape when University Press of America acquired Rowman & Littlefield in 1988 and took the Rowman & Littlefield name for the parent company. Since 2013, there has also been an affiliated company based in London called Rowman & Littlefield International. It is editorially independent and publishes only academic books in Philosophy, Politics & International Relations and Cultural Studies. The company sponsors the Rowman & Littlefield Award in Innovative Teaching, the only national teaching award in political science given in the United States. It is awarded annually by the American Political Science Association for people whose innovations have advanced ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Foundation Stone
The cornerstone (or foundation stone or setting stone) is the first stone set in the construction of a masonry foundation. All other stones will be set in reference to this stone, thus determining the position of the entire structure. Over time a cornerstone became a ceremonial masonry stone, or replica, set in a prominent location on the outside of a building, with an inscription on the stone indicating the construction dates of the building and the names of architect, builder, and other significant individuals. The rite of laying a cornerstone is an important cultural component of eastern architecture and metaphorically in sacred architecture generally. Some cornerstones include time capsules from, or engravings commemorating, the time a particular building was built. History The ceremony typically involved the placing of offerings of grain, wine and oil on or under the stone. These were symbolic of the produce and the people of the land and the means of their subsistence. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Eric H
The given name Eric, Erich, Erikk, Erik, Erick, or Eirik is derived from the Old Norse name ''Eiríkr'' (or ''Eríkr'' in Old East Norse due to monophthongization). The first element, ''ei-'' may be derived from the older Proto-Norse language, Proto-Norse ''*wikt:Reconstruction:Proto-Germanic/ainaz, aina(z)'', meaning "one, alone, unique", ''as in the form'' ''Æ∆inrikr'' explicitly, but it could also be from ''*wikt:Reconstruction:Proto-Germanic/aiwaz, aiwa(z)'' "everlasting, eternity", as in the Gothic form ''Euric''. The second element ''-wikt:ríkr, ríkr'' stems either from Proto-Germanic language, Proto-Germanic ''*wikt:Reconstruction:Proto-Germanic/rīks, ríks'' "king, ruler" (cf. Gothic ''wikt:𐍂𐌴𐌹𐌺𐍃, reiks'') or the therefrom derived ''*wikt:Reconstruction:Proto-Germanic/rīkijaz, ríkijaz'' "kingly, powerful, rich, prince"; from the common Proto-Indo-European language, Proto-Indo-European root *wikt:Reconstruction:Proto-Indo-European/h₃rḗǵs, h� ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Andrews University
Andrews University is a private Seventh-day Adventist university in Berrien Springs, Michigan. Founded in 1874 as Battle Creek College, it was the first higher education facility started by Seventh-day Adventists and is the flagship university of the Seventh-day Adventist school system, the world's second largest Christian school system. The university consists of eight schools or colleges, offering 130 undergraduate majors and 70 graduate majors. In addition, post-baccalaureate degrees are offered by all. It is accredited by the Higher Learning Commission, and the Adventist Accrediting Association (AAA). History 1874–1901: Battle Creek College Andrews University was founded as a small Seventh-day Adventist school called Battle Creek College in 1874 named for the nearby city of Battle Creek, Michigan. 1901–1959: Emmanuel Missionary College In 1901, the school moved from Battle Creek, Michigan to its current location in Berrien Springs.Review and Herald, July 30, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Siegfried H
Siegfried is a German-language male given name, composed from the Germanic elements ''sig'' "victory" and ''frithu'' "protection, peace". The German name has the Old Norse cognate ''Sigfriðr, Sigfrøðr'', which gives rise to Swedish ''Sigfrid'' (hypocorisms ''Sigge, Siffer''), Danish/Norwegian ''Sigfred''. In Norway, ''Sigfrid'' is given as a feminine name. official statistics at Statistisk Sentralbyrå, National statistics office of Norway, http://www.ssb.no; Statistiska Centralbyrån, National statistics office of Sweden, http://www.scb.se/ The name is medieval and was borne by the legendary dragon-slayer also known as . It did survive in marginal use into the modern period, but after 1876 it enjoyed renewed popularity ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Yeshiva University Museum
The Yeshiva University Museum is a teaching museum and the cultural arm of Yeshiva University. Along with the American Jewish Historical Society, the American Sephardi Federation, the Leo Baeck Institute, New York and the YIVO Institute for Jewish Research, it is a member organization of the Center for Jewish History, a Smithsonian Institution affiliate located in New York’s Chelsea neighborhood. History and mission The museum was founded in 1973. Its mission is to celebrate the culturally diverse intellectual and artistic achievements of 3,000 years of Jewish experience. The museum aims to provide a window into Jewish culture around the world and throughout history through multi-disciplinary exhibitions and publications. Following the retirement of Sylvia A. Herskowitz, Dr. Jacob Wisse was appointed the museum’s director on February 26, 2009. Collection The museum’s collection of more than 8,000 artifacts includes fine and folk art, ethnographic and archaeological artifa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Replicas Of The Jewish Temple
Replicas of the Jewish Temple are scale models or authentic buildings that attempt to replicate the Temple of Solomon, Second Temple and Herod's Temple in Jerusalem. Scale models In the seventeenth century, Rabbi Jacob Judah Leon of Amsterdam (1602–1675) built a widely exhibited model of the Temple based on his understanding of the biblical specifications. Another notable model was constructed by Gerhard Schott (1641–1702), follows an interpretation made by the Spanish Jesuit Juan Bautista Villalpando. Schott's model, known as the Hamburg temple model, is still displayed in the Hamburg Museum in Hamburg. Conrad Schick constructed a series of replicas of the Jewish Temple. His replica of the Biblical Tabernacle was visited in Jerusalem by several crowned heads of state, toured the United Kingdom, and was exhibited at the 1873 Vienna World's Fair. It was purchased by the King of Württemberg, who awarded Schick a knighthood in recognition of his work. Schick built a repli ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Herodian Dynasty
The Herodian dynasty was a royal dynasty of Idumaean (Edomite) descent, ruling the Herodian Kingdom of Judea and later the Herodian Tetrarchy as a vassal state of the Roman Empire. The Herodian dynasty began with Herod the Great, who assumed the throne of Judea, with Roman support, bringing down the century-old Hasmonean Kingdom. His kingdom lasted until his death in 4 BCE, when it was divided among his sons as a tetrarchy, which lasted for about 10 years. Most of those tetrarchies, including Judea proper, were incorporated into Judaea Province from 6 CE, though limited Herodian ''de facto'' kingship continued until Agrippa I's death in 44 CE and nominal title of kingship continued until 92 CE, when the last Herodian monarch, Agrippa II, died and Rome assumed full power over his ''de jure'' domain. History Origin During the time of the Hasmonean ruler John Hyrcanus (134–104 BCE), Judea conquered Edom (Idumea) and forced the Edomites to convert to Judaism. The Edo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
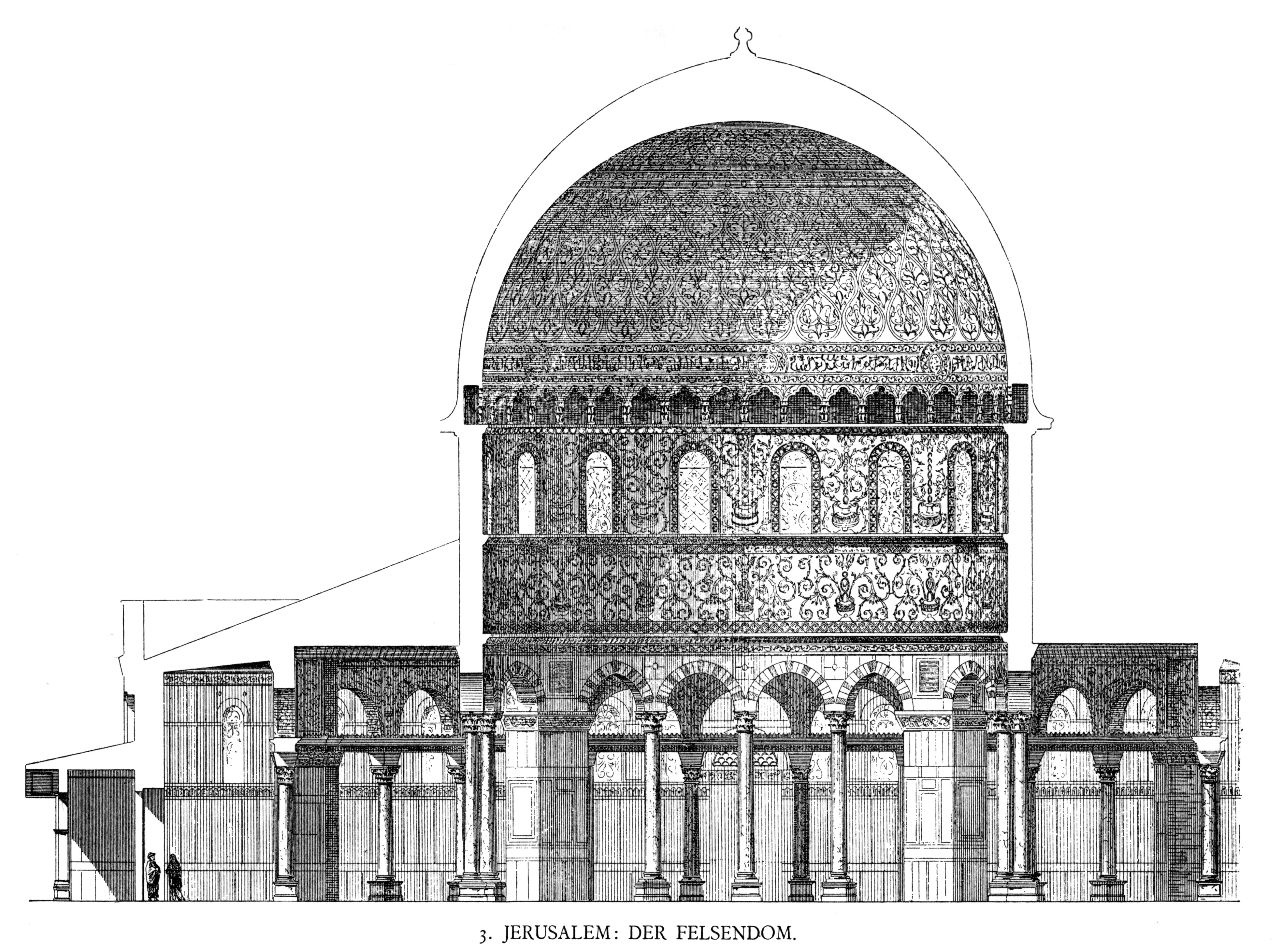
Dome Of The Rock
The Dome of the Rock ( ar, قبة الصخرة, Qubbat aṣ-Ṣakhra) is an Islamic shrine located on the Temple Mount in the Old City of Jerusalem, a site also known to Muslims as the ''al-Haram al-Sharif'' or the Al-Aqsa Compound. Its initial construction was undertaken by the Umayyad Caliphate on the orders of Abd al-Malik during the Second Fitna in 691–692 CE, and it has since been situated on top of the site of the Second Jewish Temple (built in to replace the destroyed Solomon's Temple), which was destroyed by the Romans in 70 CE. The original dome collapsed in 1015 and was rebuilt in 1022–23. The Dome of the Rock is the world's oldest surviving work of Islamic architecture. Its architecture and mosaics were patterned after nearby Byzantine churches and palaces, although its outside appearance was significantly changed during the Ottoman period and again in the modern period, notably with the addition of the gold-plated roof, in 1959–61 and again in 1993. The oc ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Middot (Talmud)
Tractate Middot ( he, מִדּוֹת, lit. "Measurements") is the tenth tractate of '' Seder Kodashim'' ("Order of Holies") of the Mishnah and of the Talmud. This tractate describes the dimensions and the arrangement of the Temple Mount in Jerusalem, and the Second Temple buildings and courtyards, various gates, the altar of sacrifice and its surroundings, and the places where the Priests and Levites kept watch in the Temple. The tractate is divided into five chapters and has no Gemara either in the Jerusalem Talmud or the Babylonian Talmud, nor a Tosefta. Subject matter This tractate describes the details and measurements of a hill in the city of Jerusalem known as the Temple Mount (''Har Ha'bayit''), and the Second Temple buildings, courtyards, gates and elements of the site as well as the places where the ''Kohanim'' (priests) and Levites kept watch in the Temple. The tractate gives the measurements of the Temple Mount and its various divisions. It states that the Temple Cour ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mishnah
The Mishnah or the Mishna (; he, מִשְׁנָה, "study by repetition", from the verb ''shanah'' , or "to study and review", also "secondary") is the first major written collection of the Jewish oral traditions which is known as the Oral Torah. It is also the first major work of rabbinic literature. The Mishnah was redacted by Judah ha-Nasi probably in Beit Shearim or Sepphoris at the beginning of the 3rd century CE in a time when, according to the Talmud, the persecution of the Jews and the passage of time raised the possibility that the details of the oral traditions of the Pharisees from the Second Temple period (516 BCE – 70 CE) would be forgotten. Most of the Mishnah is written in Mishnaic Hebrew, but some parts are in Aramaic. The Mishnah consists of six orders (', singular ' ), each containing 7–12 tractates (', singular ' ; lit. "web"), 63 in total, and further subdivided into chapters and paragraphs. The word ''Mishnah'' can also indicate a single paragraph of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cubit
The cubit is an ancient unit of length based on the distance from the elbow to the tip of the middle finger. It was primarily associated with the Sumerians, Egyptians, and Israelites. The term ''cubit'' is found in the Bible regarding Noah's Ark, Ark of the Covenant, Tabernacle, Solomon's Temple Solomon's Temple, also known as the First Temple (, , ), was the Temple in Jerusalem between the 10th century BC and . According to the Hebrew Bible, it was commissioned by Solomon in the United Kingdom of Israel before being inherited by th .... The ''common cubit'' was divided into 6 palms × 4 Finger (unit), fingers = 24 digit (unit), digits. ''Royal cubits'' added a palm for 7 palms × 4 fingers = 28 digits. These lengths typically ranged from , with an ancient Roman cubit being as long as . Cubits of various lengths were employed in many parts of the world in ancient history, antiquity, during the Middle Ages and as recently as Early modern Europe, early modern time ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |