|
Leake Mounds
Leake Mounds ( 9BR2) is an important archaeological site in Bartow County, Georgia built and used by peoples of the Swift Creek Culture. The site is west of the well-known Etowah Mounds on the Etowah River. It predates that site by hundreds of years. Excavation of nearly on the site showed that Leake Mounds was one of the most important Middle Woodland period site in this area from around 300 BCE to 650 CE. It was a center with ties throughout the Southeast and Midwest. It was abandoned about 650 CE. It was not occupied again for nearly nine hundred years, until about 1500, by different peoples near the end of the Mississippian culture period. The site includes at least three major platform mounds and a large semi-circular moat/ditch. While much of the mounds were razed to be used as road fill for the expansion of the Georgia State Route 113 and Georgia State Route 61 in the 1940s, significant portions of the site remain. Several sites on nearby Ladds Mountain were integrally ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cartersville, Georgia
Cartersville is a city in Bartow County, Georgia, United States; it is located within the northwest edge of the Atlanta metropolitan area. As of the 2020 census, the city had a population of 23,187. Cartersville is the county seat of Bartow County. History Cartersville, originally known as Birmingham, was founded by English-Americans in 1832. The town was incorporated as Cartersville in 1854. The present name is for Col. Farish Carter of Milledgeville, the owner of a large plantation. Cartersville was the long-time home of Amos Akerman, U.S. Attorney General under President Ulysses S. Grant; in that office he spearheaded the federal prosecution of members of the Ku Klux Klan and was one of the most important public servants of the Reconstruction era. Cartersville was designated the seat of Bartow County in 1867 following the destruction of Cassville by Sherman in the American Civil War. Cartersville was incorporated as a city in 1872. On February 26, 1916 a group of one hundr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mann Site
The Mann site ( 12 Po 2) is a Crab Orchard culture site located off Indian Mound Road in Mount Vernon, Posey County, Indiana. It was placed on the National Historic Register on October 1, 1974. Exotic ceramics and other artifacts found at the site reflect contact with Ohio Hopewell people, in addition to more distant peoples in the Southeast of the Swift Creek culture of the Georgia Piedmont and Gulf Coastal Plain. In addition, the scale and complexity of works here suggests that the population was larger than at comparable Ohio sites. It may have been the largest Hopewell site in the Midwest. Description The site is a large late Middle Woodland period multicomponent complex of mounds, geometric earthworks, and habitation sites near the confluence of the Wabash and Ohio rivers in extreme southwestern Indiana, dating between about 100 and 500 CE. It is located on a high river terrace. The scale and complexity of mounds and other earthworks at the Mann site is rivaled in the Mid ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Archaeological Sites In Georgia (U
Archaeology or archeology is the scientific study of human activity through the recovery and analysis of material culture. The archaeological record consists of Artifact (archaeology), artifacts, architecture, biofact (archaeology), biofacts or ecofacts, archaeological site, sites, and cultural landscapes. Archaeology can be considered both a social science and a branch of the humanities. It is usually considered an independent academic discipline, but may also be classified as part of anthropology (in North America – the four-field approach), history or geography. Archaeologists study human prehistory and history, from the development of the first stone tools at Lomekwi in East Africa 3.3 million years ago up until recent decades. Archaeology is distinct from palaeontology, which is the study of fossil remains. Archaeology is particularly important for learning about prehistoric societies, for which, by definition, there are no written records. Prehistory includes ove ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
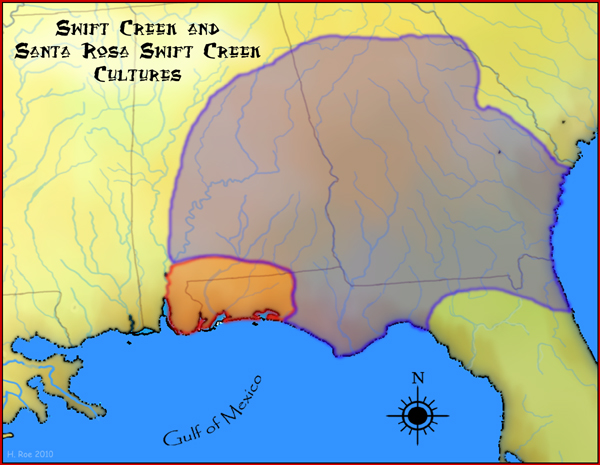
Swift Creek Culture
The Swift Creek culture was a Middle Woodland period archaeological culture in the Southeastern Woodlands of North America, dating to around 100-800 CE. It occupied the areas now part of Georgia, Alabama, Florida, South Carolina, and Tennessee. In Florida, Swift Creek ceremonial practices and burial complexes are referred to technically as the Yent-Green Point complex. The Swift Creek culture was contemporaneous with and interacted with the Hopewell culture; Swift Creek is often described as "Hopewellian." The type site for the Swift Creek culture was the Swift Creek mound site, which was located in Bibb County, Georgia. The Leake Mounds are another significant Swift Creek Culture site in Georgia. Swift Creek peoples practiced mound-building but were generally non-sedentary. Their sustenance resulted from hunting, gathering/collecting, and fishing. Swift Creek are characterized by earthenware pottery with complicated stamped designs, involving mostly curvilinear elements. Examples ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
List Of Hopewell Sites
This is a list of Hopewell sites. The Hopewell tradition (also incorrectly called the "Hopewell culture") refers to the common aspects of the Native American culture that flourished along rivers in the northeastern and midwestern United States from 200 BCE to 500 CE. The Hopewell tradition was not a single culture or society, but a widely dispersed set of related populations that were connected by a common network of trade routes, known as the Hopewell Exchange System. See also * Hopewell tradition * National Register of Historic Places listings in Ross County, Ohio * National Register of Historic Places listings in Warren County, Ohio __NOTOC__ This is a list of the National Register of Historic Places listings in Warren County, Ohio. This is intended to be a complete list of the properties and districts on the National Register of Historic Places in Warren County, Ohio, Uni ... References External links {{Pre-Columbian North America +Sites Hopewell sites +H ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
List Of Burial Mounds In The United States
This is a list of notable burial mounds in the United States built by Native Americans. Burial mounds were built by many different cultural groups over a span of many thousands of years, beginning in the Late Archaic period and continuing through the Woodland period up to the time of European contact. Adena and Hopewell culture burial mounds Mississippian culture burial mounds See also * List of Adena culture sites * List of Hopewell sites * List of Mississippian sites * List of the oldest buildings in the United States References External links International Architecture: database website {{Prehistoric technology Burial mounds in the United States Burial mounds in the United States Burial mounds Burial mounds in the United States Burial mounds Burial mounds Historic preservation in the United States Mound builders (people) Burial mounds United States The United States of America (U.S.A. or USA), commonly known as the United States (U.S. or U ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
King Archaeological Site
The King Archaeological Site ( 9FL5) is a protohistoric Native American archaeological site located on the Coosa River in Floyd County, Georgia. It is one of 5 large contemporaneous village sites located in a section of the river. The site was a satellite village associated with the Coosa chiefdom centered on the Little Egypt Site located upstream. Site description The site is a village located on the eastern bank of the Coosa River at Foster Bend and dating from the mid-sixteenth century. The village is basically square in layout ( in length on each side) and surrounded by a ditch and palisade on three sides and the Coosa River to the north. At the center of the town was a large plaza, at the center of which was a post measuring almost in diameter at its base and probably to high. In between the plaza and the encircling palisade was a village area, with approximately 47 houses and a number of elevated maize storage facilities. The house structures were rectangular with roun ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Etowah Indian Mounds
Etowah Indian Mounds ( 9BR1) are a archaeological site in Bartow County, Georgia, south of Cartersville. Built and occupied in three phases, from 1000–1550 CE, the prehistoric site is located on the north shore of the Etowah River. Etowah Indian Mounds Historic Site is a designated National Historic Landmark, managed by the Georgia Department of Natural Resources. It is considered "the most intact Mississippian culture site in the Southeast", according to Georgia State Parks and Historic Sites. Both the historic Muscogee Creek and the Cherokee peoples, who each occupied this area at varying times, hold the site to be sacred. History This site was professionally excavated beginning in the early 20th century. Additional studies have been undertaken as more evidence and knowledge has accumulated about the succession of cultures in this area, aided by modern technology such as radio carbon dating and magnetometers. Late 20th-century studies showed the mounds were built and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tennessee
Tennessee ( , ), officially the State of Tennessee, is a landlocked state in the Southeastern region of the United States. Tennessee is the 36th-largest by area and the 15th-most populous of the 50 states. It is bordered by Kentucky to the north, Virginia to the northeast, North Carolina to the east, Georgia, Alabama, and Mississippi to the south, Arkansas to the southwest, and Missouri to the northwest. Tennessee is geographically, culturally, and legally divided into three Grand Divisions of East, Middle, and West Tennessee. Nashville is the state's capital and largest city, and anchors its largest metropolitan area. Other major cities include Memphis, Knoxville, Chattanooga, and Clarksville. Tennessee's population as of the 2020 United States census is approximately 6.9 million. Tennessee is rooted in the Watauga Association, a 1772 frontier pact generally regarded as the first constitutional government west of the Appalachian Mountains. Its name derives from "Tanas ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Yearwood Site
Yearwood is a surname. Notable people with the surname include: * Barrington Yearwood (born 1986), Barbadian cricketer *Gilberto Yearwood (born 1956), retired Honduran football player * Kathleen Yearwood (born 1958), Canadian experimental singer-songwriter and author *Lennox Yearwood, minister, community activist, influential in Hip Hop political life *Richard Yearwood (born 1970), English-Canadian voice-over artist, director, producer, and character actor *Robin Yearwood, Antiguan politician and member of the Antigua Labour Party (ALP) *Trisha Yearwood (born 1964), American country music artist *Wayne Yearwood (born 1964), former professional and Olympic basketball player from Canada See also *Earthwood, a brand of acoustic bass guitars *Erwood, a village in Powys, Wales *Harewood (surname) Harewood is a surname. Notable persons with that surname include: * Adrian Harewood, Canadian broadcaster * David Harewood (born 1965), British actor * Dorian Harewood (born 1950), American ac ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mandeville Site
The Mandeville site ( 9CY1) is an archaeological site in Clay County in southwest Georgia in the United States. The site now lies under the Walter F. George Reservoir, which is a part of the Chattahoochee River basin. History The first occupations of the site were a village settlement during the Deptford period. Occupation of the site and the construction of two mounds continue into the Middle Woodland period. Ceramic evidence also dates occupation to the Early Swift Creek culture. The final layer of Mound A indicates it was converted to a platform mound typical of the Mississippian period. Excavations The site was first visited by Clarence B. Moore at the turn of the century. He tested the site but did not conduct any excavations due to negative results. The site was visited by a field party from the University of Georgia in 1950. Some minor surface excavations were conducted. Thorough excavations on the site were conducted during 1959-1960 by Arthur Kelly, James H. Kellar a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |


.jpg)