|
Lead Paint
Lead paint or lead-based paint is paint containing lead. As pigment, lead(II) chromate (, "chrome yellow"), lead(II,IV) oxide, (, "red lead"), and lead(II) carbonate (, "white lead") are the most common forms.. Lead is added to paint to accelerate drying, increase durability, maintain a fresh appearance, and resist moisture that causes corrosion. It is one of the main health and environmental hazards associated with paint. Lead paint has been generally phased out of use due to the toxic nature of lead. Alternatives such as water-based, lead-free traffic paint are readily available. In some countries, lead continues to be added to paint intended for domestic use, whereas countries such as the United States and the United Kingdom have regulations prohibiting its use. However, lead paint may still be found in older properties painted prior to the introduction of such regulations. Although lead has been banned from household paints in the United States since 1978, it may still be f ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Vitruvius
Vitruvius (; c. 80–70 BC – after c. 15 BC) was a Roman architect and engineer during the 1st century BC, known for his multi-volume work entitled ''De architectura''. He originated the idea that all buildings should have three attributes: , , and ("strength", "utility", and "beauty"). These principles were later widely adopted in Roman architecture. His discussion of perfect proportion in architecture and the human body led to the famous Renaissance drawing of the ''Vitruvian Man'' by Leonardo da Vinci. Little is known about Vitruvius' life, but by his own descriptionDe Arch. Book 1, preface. section 2. he served as an artilleryman, the third class of arms in the Roman military offices. He probably served as a senior officer of artillery in charge of ''doctores ballistarum'' (artillery experts) and ''libratores'' who actually operated the machines. As an army engineer he specialized in the construction of ''ballista'' and '' scorpio'' artillery war machines for sieges. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
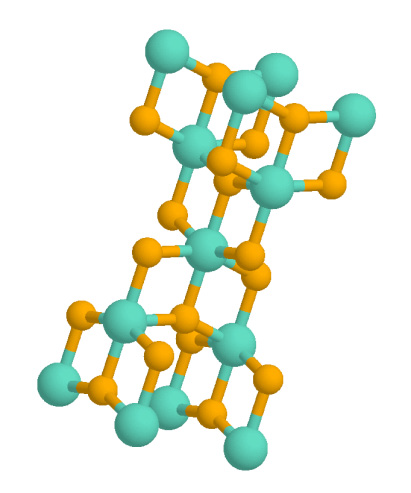
Lead Sugar
Lead(II) acetate (Pb(CH3COO)2), also known as lead acetate, lead diacetate, plumbous acetate, sugar of lead, lead sugar, salt of Saturn, or Goulard's powder, is a white crystalline chemical compound with a slightly sweet taste. Like many other lead compounds, it is toxic. Lead acetate is soluble in water and glycerin. With water it forms the trihydrate, Pb(CH3COO)2·3H2O, a colourless or white efflorescent monoclinic crystalline substance. The substance is used as a reagent to make other lead compounds and as a fixative for some dyes. In low concentrations, it is the principal active ingredient in progressive types of hair colouring dyes. Lead(II) acetate is also used as a mordant in textile printing and dyeing, and as a drier in paints and varnishes. It was historically used as a sweetener and preservative in wines and in other foods and for cosmetics. Production Lead acetate can be made by boiling elemental lead in acetic acid and hydrogen peroxide. This method will also work ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hathitrust
HathiTrust Digital Library is a large-scale collaborative repository of digital content from research libraries including content digitized via Google Books and the Internet Archive digitization initiatives, as well as content digitized locally by libraries. History HathiTrust was founded in October 2008 by the twelve universities of the Committee on Institutional Cooperation and the eleven libraries of the University of California. The partnership includes over 60 research libraries across the United States, Canada, and Europe, and is based on a shared governance structure. Costs are shared by the participating libraries and library consortia. The repository is administered by the University of Michigan , mottoeng = "Arts, Knowledge, Truth" , former_names = Catholepistemiad, or University of Michigania (1817–1821) , budget = $10.3 billion (2021) , endowment = $17 billion (2021)As o .... The executive director of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sherwin-Williams
Sherwin-Williams Company is an American Cleveland, Ohio–based company in the paint and coating manufacturing industry. The company primarily engages in the manufacture, distribution, and sale of paints, coatings, floorcoverings, and related products to professional, industrial, commercial, and retail customers primarily in North and South America and Europe. At the end of 2020, Sherwin-Willams had operations in over 120 countries. History Sherwin-Williams dates from 1866, when Cleveland bookkeeper Henry Sherwin invested in Truman Dunham & Co., a paint distributorship. After the partnership dissolved in 1870, he formed Sherwin, Williams, & Co. with Edward Williams and A.T. Osborn. For its first factory, in 1873 the company acquired a cooperage in Cleveland from Standard Oil. Sherwin-Williams was incorporated in Ohio on July 16, 1884, two years after Osborn sold his interest in the company while retaining the retail operations. The company grew through acquisitions and expans ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Titanium White
Titanium dioxide, also known as titanium(IV) oxide or titania , is the inorganic compound with the chemical formula . When used as a pigment, it is called titanium white, Pigment White 6 (PW6), or CI 77891. It is a white solid that is insoluble to water, although mineral forms can appear black. As a pigment, it has a wide range of applications, including paint, sunscreen, and food coloring. When used as a food coloring, it has E number E171. World production in 2014 exceeded 9 million tonnes. It has been estimated that titanium dioxide is used in two-thirds of all pigments, and pigments based on the oxide have been valued at a price of $13.2 billion. Structure In all three of its main dioxides, titanium exhibits octahedral geometry, being bonded to six oxide anions. The oxides in turn are bonded to three Ti centers. The overall crystal structure of rutile is tetragonal in symmetry whereas anatase and brookite are orthorhombic. The oxygen substructures are all slight distorti ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Zinc White
Zinc oxide is an inorganic compound with the formula . It is a white powder that is insoluble in water. ZnO is used as an additive in numerous materials and products including cosmetics, food supplements, rubbers, plastics, ceramics, glass, cement, lubricants, paints, ointments, adhesives, sealants, pigments, foods, batteries, ferrites, fire retardants, and first-aid tapes. Although it occurs naturally as the mineral zincite, most zinc oxide is produced synthetically. ZnO is a wide-band gap semiconductor of the II-VI semiconductor group. The native doping of the semiconductor due to oxygen vacancies or zinc interstitials is n-type. Other favorable properties include good transparency, high electron mobility, wide band gap, and strong room-temperature luminescence. Those properties make ZnO valuable for a variety of emerging applications: transparent electrodes in liquid crystal displays, energy-saving or heat-protecting windows, and electronics as thin-film transistors and light- ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Benjamin Franklin
Benjamin Franklin ( April 17, 1790) was an American polymath who was active as a writer, scientist, inventor, statesman, diplomat, printer, publisher, and political philosopher. Encyclopædia Britannica, Wood, 2021 Among the leading intellectuals of his time, Franklin was one of the Founding Fathers of the United States, a drafter and signer of the United States Declaration of Independence, and the first United States Postmaster General. As a scientist, he was a major figure in the American Enlightenment and the history of physics for his studies of electricity, and for charting and naming the current still known as the Gulf Stream. As an inventor, he is known for the lightning rod, bifocals, and the Franklin stove, among others. He founded many civic organizations, including the Library Company, Philadelphia's first fire department, and the University of Pennsylvania. Isaacson, 2004, p. Franklin earned the title of "The First American" for his early and indefa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Epilepsy
Epilepsy is a group of non-communicable neurological disorders characterized by recurrent epileptic seizures. Epileptic seizures can vary from brief and nearly undetectable periods to long periods of vigorous shaking due to abnormal electrical activity in the brain. These episodes can result in physical injuries, either directly such as broken bones or through causing accidents. In epilepsy, seizures tend to recur and may have no immediate underlying cause. Isolated seizures that are provoked by a specific cause such as poisoning are not deemed to represent epilepsy. People with epilepsy may be treated differently in various areas of the world and experience varying degrees of social stigma due to the alarming nature of their symptoms. The underlying mechanism of epileptic seizures is excessive and abnormal neuronal activity in the cortex of the brain which can be observed in the electroencephalogram (EEG) of an individual. The reason this occurs in most cases of epilepsy is u ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Apoplexy
Apoplexy () is rupture of an internal organ and the accompanying symptoms. The term formerly referred to what is now called a stroke. Nowadays, health care professionals do not use the term, but instead specify the anatomic location of the bleeding, such as cerebral, ovarian or pituitary. Informally or metaphorically, the term ''apoplexy'' is associated with being furious, especially as "apoplectic". Historical meaning From the late 14th to the late 19th century,''OED Online'', 2010, Oxford University Press. 7 February 2011 ''apoplexy'' referred to any sudden death that began with a sudden loss of consciousness, especially one in which the victim died within a matter of seconds after losing consciousness. The word ''apoplexy'' was sometimes used to refer to the symptom of sudden loss of consciousness immediately preceding death. Ruptured aortic aneurysms, and even heart attacks and strokes were referred to as apoplexy in the past, because before the advent of medical science, the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Acetic Acid
Acetic acid , systematically named ethanoic acid , is an acidic, colourless liquid and organic compound with the chemical formula (also written as , , or ). Vinegar is at least 4% acetic acid by volume, making acetic acid the main component of vinegar apart from water and other trace elements. Acetic acid is the second simplest carboxylic acid (after formic acid). It is an important Reagent, chemical reagent and industrial chemical, used primarily in the production of cellulose acetate for photographic film, polyvinyl acetate for wood Adhesive, glue, and synthetic fibres and fabrics. In households, diluted acetic acid is often used in descaling agents. In the food industry, acetic acid is controlled by the E number, food additive code E260 as an acidity regulator and as a condiment. In biochemistry, the acetyl group, derived from acetic acid, is fundamental to all forms of life. When bound to coenzyme A, it is central to the metabolism of carbohydrates and fats. The global ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fermentation
Fermentation is a metabolic process that produces chemical changes in organic substrates through the action of enzymes. In biochemistry, it is narrowly defined as the extraction of energy from carbohydrates in the absence of oxygen. In food production, it may more broadly refer to any process in which the activity of microorganisms brings about a desirable change to a foodstuff or beverage. The science of fermentation is known as zymology. In microorganisms, fermentation is the primary means of producing adenosine triphosphate (ATP) by the degradation of organic nutrients anaerobically. Humans have used fermentation to produce foodstuffs and beverages since the Neolithic age. For example, fermentation is used for preservation in a process that produces lactic acid found in such sour foods as pickled cucumbers, kombucha, kimchi, and yogurt, as well as for producing alcoholic beverages such as wine and beer. Fermentation also occurs within the gastrointestinal tracts of all a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |

-acetate-xtal-Pb-coordination-3D-bs-17.png)