|
Lawa Language
Lawa (La'wa, L'wa) is a Mon–Khmer language of Thailand. There are two distinct varieties or dialects of Lawa, considered to be separate languages; their names in the ''Ethnologue'' are Eastern Lawa and Western Lawa. They are spoken in Lawa villages in the provinces of Mae Hong Son and Chiang Mai in Northern Thailand. Linguistically, Lawa belongs to the Palaungic branch of the Mon-Khmer family of languages, which is part of the Austro-Asiatic super-family. Eastern Lawa is distinct from Western Lawa despite being highly cognate because the two languages are not mutually understandable based on consistent testimonies of Eastern and Western Lawa speakers and testing by SIL.Nahhas, Dr. Ramzi W. 2007Sociolinguistic survey of Lawa in Thailand Chiang Mai: Payap University. There are two distinct dialects spoken among the Eastern Lawa. These dialects have differences in pronunciation and some lexeme differences. The differences, however, do not present any difficulty in comprehension ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Thailand
Thailand ( ), historically known as Siam () and officially the Kingdom of Thailand, is a country in Southeast Asia, located at the centre of the Indochinese Peninsula, spanning , with a population of almost 70 million. The country is bordered to the north by Myanmar and Laos, to the east by Laos and Cambodia, to the south by the Gulf of Thailand and Malaysia, and to the west by the Andaman Sea and the extremity of Myanmar. Thailand also shares maritime borders with Vietnam to the southeast, and Indonesia and India to the southwest. Bangkok is the nation's capital and largest city. Tai peoples migrated from southwestern China to mainland Southeast Asia from the 11th century. Indianised kingdoms such as the Mon, Khmer Empire and Malay states ruled the region, competing with Thai states such as the Kingdoms of Ngoenyang, Sukhothai, Lan Na and Ayutthaya, which also rivalled each other. European contact began in 1511 with a Portuguese diplomatic mission to Ayutthaya, w ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mon-Khmer
The Austroasiatic languages , , are a large language family in Mainland Southeast Asia and South Asia. These languages are scattered throughout parts of Thailand, Laos, India, Myanmar, Malaysia, Bangladesh, Nepal, and southern China and are the majority languages of Vietnam and Cambodia. There are around 117 million speakers of Austroasiatic languages. Of these languages, only Vietnamese, Khmer, and Mon have a long-established recorded history. Only two have official status as modern national languages: Vietnamese in Vietnam and Khmer in Cambodia. The Mon language is a recognized indigenous language in Myanmar and Thailand. In Myanmar, the Wa language is the de facto official language of Wa State. Santali is one of the 22 scheduled languages of India. The rest of the languages are spoken by minority groups and have no official status. ''Ethnologue'' identifies 168 Austroasiatic languages. These form thirteen established families (plus perhaps Shompen, which is poorly attest ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Northern Thai People
The Northern Thai people or Tai Yuan ( th, ไทยวน, ), self-designation ''khon mu(e)ang'' ( nod, , คนเมือง meaning "people of the (cultivated) land" or "people of our community") are a Tai ethnic group, native to eight provinces in Northern Thailand, principally in the area of the former kingdom of Lan Na. As a Tai group, they are closely related to Tai Lü and Tai Khün with regards to common culture, language and history as well as to Thailand's dominant Thai ethnic group (in contrast referred to as ''Siamese'' or ''Central Thai''). There are approximately 6 million Tai Yuan. Most of them live in Northern Thailand, with a small minority 29,442 (2005 census) living across the border in Bokeo Province and Sainyabuli Province and Luang Namtha Province of Laos. Their language is called Northern Thai, Lanna or ''Kham Mueang''. Exonym and endonym Central Thai may call northern Thai people and their language Thai Yuan, probably derived from Sanskrit ''yav ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Northern Thai Language
Kam Mueang ( nod, , กำเมือง) or Northern Thai language ( th, ภาษาไทยถิ่นเหนือ) is the language of the Northern Thai people of Lanna, Thailand. It is a Southwestern Tai language that is closely related to Lao. Kam Mueang has approximately six million speakers, most of whom live in the native Northern Thailand, with a smaller community of Lanna speakers in northwestern Laos. Speakers of this language generally consider the name "Tai Yuan" to be pejorative. They refer to themselves as ' (, คน เมือง, – literally "people of Mueang" meaning "city dwellers"), Lanna, or Northern Thai. The language is also sometimes referred to as ' (พายัพ, ), "Northwestern (speech)". The term Yuan is still sometimes used for Northern Thai's distinctive Tai Tham alphabet, which is closely related to the old Tai Lue alphabet and the Lao religious alphabets. The use of the ', as the traditional alphabet is known, is now largely lim ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hot District
Hot ( th, ฮอด, ) is a district (''amphoe'') in the southern part of Chiang Mai province in northern Thailand. Geography Neighboring districts are (from the north clockwise) Mae Chaem, Chom Thong of Chiang Mai Province, Ban Hong, Li of Lamphun province, Doi Tao, Omkoi of Chiang Mai Province, Sop Moei and Mae Sariang of Mae Hong Son province. The canyon of Op Luang National Park is in Hot District. History In 1905 the district Muet Ka was abolished and split into the district Mueang Hot and the minor district Mueang Hot. In 1917 the district was renamed Hot. Administration The district is divided into six sub-districts (''tambon''), which are further subdivided into 60 villages (''muban''). There are two sub-district municipalities (''thesaban tambon''), Tha Kham and Hang Dong, both covering parts of ''tambon'' Hang Don. There are a further six tambon administrative organizations (TAO). Gallery File:Pine cones and pine (Unsplash).jpg, Pine forests of Hot Refer ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bo Sali
Bo Sali ( th, บ่อสลี) is a ''tambon'' (subdistrict) of Hot District, in Chiang Mai Province, Thailand. In 2019, it had a total population of 8,026 people. History The subdistrict was created effective July 20, 1971 by splitting off 7 administrative villages from Bo Luang. Administration Central administration The ''tambon'' is subdivided into 10 administrative villages (''muban Muban ( th, หมู่บ้าน; , ) is the lowest administrative sub-division of Thailand. Usually translated as 'village' and sometimes as 'hamlet', they are a subdivision of a tambon (subdistrict). , there were 74,944 administrative mu ...''). Local administration The whole area of the subdistrict is covered by the subdistrict administrative organization (SAO) Bo Sali (องค์การบริหารส่วนตำบลบ่อสลี). References External linksThaitambon.com on Bo Sali Tambon of Chiang Mai province Populated places in Chiang Mai province ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bo Luang
Bo Luang ( th, บ่อหลวง) is a ''tambon'' (subdistrict) of Hot District, in Chiang Mai Province, Thailand. In 2019 it had a total population of 12,143 people. Administration Central administration The ''tambon'' is subdivided into 13 administrative villages (''muban''). Local administration The whole area of the subdistrict is covered by the subdistrict municipality (''Thesaban Tambon Thesaban ( th, เทศบาล, , ) are the municipalities of Thailand. There are three levels of municipalities: city, town, and sub-district. Bangkok and Pattaya are special municipal entities not included in the ''thesaban'' system. The mu ...'') Bo Luang (เทศบาลตำบลบ่อหลวง). References External linksThaitambon.com on Bo Luang Tambon of Chiang Mai province Populated places in Chiang Mai province {{coord, 18.2833, N, 98.6333, E, source:wikidata-and-enwiki-cat-tree_region:TH, display=title ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Austro-Asiatic
The Austroasiatic languages , , are a large language family in Mainland Southeast Asia and South Asia. These languages are scattered throughout parts of Thailand, Laos, India, Myanmar, Malaysia, Bangladesh, Nepal, and southern China and are the majority languages of Vietnam and Cambodia. There are around 117 million speakers of Austroasiatic languages. Of these languages, only Vietnamese, Khmer, and Mon have a long-established recorded history. Only two have official status as modern national languages: Vietnamese in Vietnam and Khmer in Cambodia. The Mon language is a recognized indigenous language in Myanmar and Thailand. In Myanmar, the Wa language is the de facto official language of Wa State. Santali is one of the 22 scheduled languages of India. The rest of the languages are spoken by minority groups and have no official status. ''Ethnologue'' identifies 168 Austroasiatic languages. These form thirteen established families (plus perhaps Shompen, which is poorly atteste ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Palaungic
The nearly thirty Palaungic or Palaung–Wa languages form a branch of the Austroasiatic languages. Phonological developments Most of the Palaungic languages lost the contrastive voicing of the ancestral Austroasiatic consonants, with the distinction often shifting to the following vowel. In the Wa branch, this is generally realized as breathy voice vowel phonation; in Palaung–Riang, as a two-way register tone system. The Angkuic languages have contour tone — the U language, for example, has four tones, ''high, low, rising, falling,'' — but these developed from vowel length and the nature of final consonants, not from the voicing of initial consonants. Homeland Paul Sidwell (2015) suggests that the Palaungic Urheimat (homeland) was in what is now the border region of Laos and Sipsongpanna in Yunnan, China. The Khmuic homeland was adjacent to the Palaungic homeland, resulting in many lexical borrowings among the two branches due to intense contact. Sidwell (2014) suggests t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lawa People
Lawa ( th, ลัวะ or ; ) are an ethnic group in northern Thailand. The Lawa language is related to the Blang and the Wa language found in China and Burma, and belongs to the Palaungic languages, a branch of the Austroasiatic languages. Their population is estimated to be some 17,000. The Western Lawa are found in the vicinity of Mae Sariang in the south of Mae Hong Son Province, the Eastern Lawa are centred on Bo Luang in Chiang Mai Province.http://www.sil.org/system/files/reapdata/33/89/43/33894368593744268318445295670982885176/silesr2011_044.pdf Overview The Lawa are sometimes mistaken for being the same people as the Lua of northern Laos and of Nan Province, Thailand, who are speakers of the more distantly related Khmuic languages. This problem is compounded by the Eastern Lawa of Chiang Mai Province preferring to be called Lua by outsiders, and by the Thai people generally referring to speakers of these different Palaungic languages as Lua. Today, those Lawa who have ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
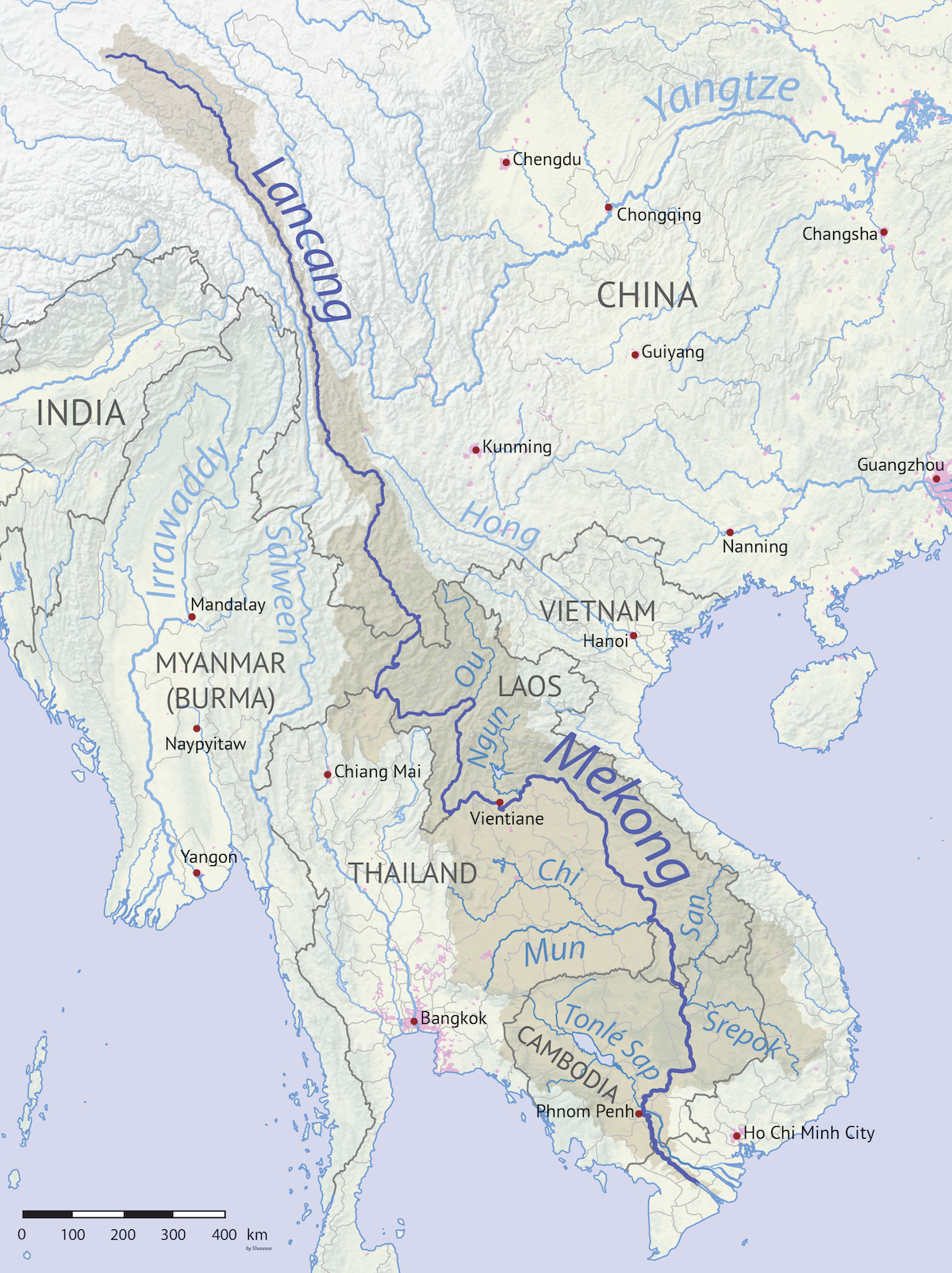
Northern Thailand
Northern Thailand, or more specifically Lanna, is geographically characterised by several mountain ranges, which continue from the Shan Hills in bordering Myanmar to Laos, and the river valleys which cut through them. Though like most of Thailand, it has a tropical savanna climate, its relatively high elevation and latitude contribute to more pronounced seasonal temperature variation, with cooler winters than the other regions. Historically it is related to the Lanna Kingdom and its culture. Geography North Thailand is bound by the Salween River in the west and the Mekong in the east. The basins of rivers Ping, Wang, Yom, and Nan, all tributaries of the Chao Phraya River, in the central part run from north to south and are mostly very wide. The basins cut across the mountains of two great ranges, the Thanon Range in the western part and the Phi Pan Nam in the eastern. Their elevations are generally moderate, a little above for the highest summits. Although formerly forested, m ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |