|
Laser Drilling
Laser drilling is the process of creating thru-holes, referred to as “popped” holes or “percussion drilled” holes, by repeatedly pulsing focused laser energy on a material. The diameter of these holes can be as small as 0.002” (~50 μm). If larger holes are required, the laser is moved around the circumference of the “popped” hole until the desired diameter is created; this technique is called “trepanning”. Applications Laser drilling is one of the few techniques for producing high-aspect-ratio holes—holes with a depth-to-diameter ratio much greater than 10:1. Laser-drilled high-aspect-ratio holes are used in many applications, including the oil gallery of some engine blocks, aerospace turbine-engine cooling holes, laser fusion components, and printed circuit board micro-vias. Manufacturers of turbine engines for aircraft propulsion and for power generation have benefited from the productivity of lasers for drilling small (0.3–1 mm diameter typica ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Internal Combustion Engine
An internal combustion engine (ICE or IC engine) is a heat engine in which the combustion of a fuel occurs with an oxidizer (usually air) in a combustion chamber that is an integral part of the working fluid flow circuit. In an internal combustion engine, the expansion of the high-temperature and high-pressure gases produced by combustion applies direct force to some component of the engine. The force is typically applied to pistons ( piston engine), turbine blades (gas turbine), a rotor (Wankel engine), or a nozzle ( jet engine). This force moves the component over a distance, transforming chemical energy into kinetic energy which is used to propel, move or power whatever the engine is attached to. This replaced the external combustion engine for applications where the weight or size of an engine was more important. The first commercially successful internal combustion engine was created by Étienne Lenoir around 1860, and the first modern internal combustion engine, known ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nanosecond
A nanosecond (ns) is a unit of time in the International System of Units (SI) equal to one billionth of a second, that is, of a second, or 10 seconds. The term combines the SI prefix ''nano-'' indicating a 1 billionth submultiple of an SI unit (e.g. nanogram, nanometre, etc.) and ''second'', the primary unit of time in the SI. A nanosecond is equal to 1000 picoseconds or microsecond. Time units ranging between 10 and 10 seconds are typically expressed as tens or hundreds of nanoseconds. Time units of this granularity are commonly found in telecommunications, pulsed lasers, and related aspects of electronics. Common measurements * 0.001 nanoseconds – one picosecond * 0.5 nanoseconds – the half-life of beryllium-13. * 0.96 nanoseconds – 100 Gigabit Ethernet Interpacket gap * 1.0 nanosecond – cycle time of an electromagnetic wave with a frequency of 1 GHz (1 hertz). * 1.0 nanosecond – electromagnetic wavelength of 1 light-nanosecond. Equiv ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Titanium
Titanium is a chemical element with the symbol Ti and atomic number 22. Found in nature only as an oxide, it can be reduced to produce a lustrous transition metal with a silver color, low density, and high strength, resistant to corrosion in sea water, aqua regia, and chlorine. Titanium was discovered in Cornwall, Great Britain, by William Gregor in 1791 and was named by Martin Heinrich Klaproth after the Titans of Greek mythology. The element occurs within a number of minerals, principally rutile and ilmenite, which are widely distributed in the Earth's crust and lithosphere; it is found in almost all living things, as well as bodies of water, rocks, and soils. The metal is extracted from its principal mineral ores by the Kroll and Hunter processes. The most common compound, titanium dioxide, is a popular photocatalyst and is used in the manufacture of white pigments. Other compounds include titanium tetrachloride (TiCl4), a component of smoke screens and catalysts; and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Temperature
Temperature is a physical quantity that expresses quantitatively the perceptions of hotness and coldness. Temperature is measured with a thermometer. Thermometers are calibrated in various temperature scales that historically have relied on various reference points and thermometric substances for definition. The most common scales are the Celsius scale with the unit symbol °C (formerly called ''centigrade''), the Fahrenheit scale (°F), and the Kelvin scale (K), the latter being used predominantly for scientific purposes. The kelvin is one of the seven base units in the International System of Units (SI). Absolute zero, i.e., zero kelvin or −273.15 °C, is the lowest point in the thermodynamic temperature scale. Experimentally, it can be approached very closely but not actually reached, as recognized in the third law of thermodynamics. It would be impossible to extract energy as heat from a body at that temperature. Temperature is important in all fields of natur ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Trepanning
Trepanning, also known as trepanation, trephination, trephining or making a burr hole (the verb ''trepan'' derives from Old French from Medieval Latin from Greek , literally "borer, auger"), is a surgical intervention in which a hole is drilled or scraped into the human skull. The intentional perforation of the cranium exposes the ''dura mater'' to treat health problems related to intracranial diseases or release pressured blood buildup from an injury. It may also refer to any "burr" hole created through other body surfaces, including nail beds. A trephine is an instrument used for cutting out a round piece of skull bone to relieve pressure beneath a surface. In ancient times, holes were drilled into a person who was behaving in what was considered an abnormal way to let out what people believed were evil spirits. Evidence of trepanation has been found in prehistoric human remains from Neolithic times onward. The bone that was trepanned was kept by the prehistoric people and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Percussion Drill
A percussion instrument is a musical instrument that is sounded by being struck or scraped by a beater including attached or enclosed beaters or rattles struck, scraped or rubbed by hand or struck against another similar instrument. Excluding zoomusicological instruments and the human voice, the percussion family is believed to include the oldest musical instruments.''The Oxford Companion to Music'', 10th edition, p.775, In spite of being a very common term to designate instruments, and to relate them to their players, the percussionists, percussion is not a systematic classificatory category of instruments, as described by the scientific field of organology. It is shown below that percussion instruments may belong to the organological classes of ideophone, membranophone, aerophone and cordophone. The percussion section of an orchestra most commonly contains instruments such as the timpani, snare drum, bass drum, tambourine, belonging to the membranophones, and cymbal ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Heat-affected Zone
In fusion welding, the heat-affected zone (HAZ) is the area of base material, either a metal or a thermoplastic, which is not melted but has had its microstructure and properties altered by welding or heat intensive cutting operations. The heat from the welding process and subsequent re-cooling causes this change from the weld interface to the termination of the sensitizing temperature in the base metal. The extent and magnitude of property change depends primarily on the base material, the weld filler metal, and the amount and concentration of heat input by the welding process. The thermal diffusivity of the base material plays a large role—if the diffusivity is high, the material cooling rate is high and the HAZ is relatively small. Alternatively, a low diffusivity leads to slower cooling and a larger HAZ. The amount of heat input during the welding process also plays an important role as well, as processes like oxyfuel welding use high heat input and increase the size o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Surface Tension
Surface tension is the tendency of liquid surfaces at rest to shrink into the minimum surface area possible. Surface tension is what allows objects with a higher density than water such as razor blades and insects (e.g. water striders) to float on a water surface without becoming even partly submerged. At liquid–air interfaces, surface tension results from the greater attraction of liquid molecules to each other (due to cohesion) than to the molecules in the air (due to adhesion). There are two primary mechanisms in play. One is an inward force on the surface molecules causing the liquid to contract. Second is a tangential force parallel to the surface of the liquid. This ''tangential'' force is generally referred to as the surface tension. The net effect is the liquid behaves as if its surface were covered with a stretched elastic membrane. But this analogy must not be taken too far as the tension in an elastic membrane is dependent on the amount of deformation of the m ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pressure Gradient
In atmospheric science, the pressure gradient (typically of Earth's atmosphere, air but more generally of any fluid) is a physical quantity that describes in which direction and at what rate the pressure increases the most rapidly around a particular location. The pressure gradient is a dimensional quantity expressed in units of pascal (unit), pascals per metre (Pa/m). Mathematically, it is the gradient of pressure as a function of position. The negative gradient of pressure is known as the force density. In petroleum geology and the petrochemical sciences pertaining to oil wells, and more specifically within hydrostatics, pressure gradients refer to the gradient of vertical pressure in a column of fluid within a wellbore and are generally expressed in pounds per square inch per foot (unit), foot (psi/ft). This column of fluid is subject to the compound pressure gradient of the overlying fluids. The path and geometry of the column is totally irrelevant; only the vertical depth of t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Evaporation
Evaporation is a type of vaporization that occurs on the surface of a liquid as it changes into the gas phase. High concentration of the evaporating substance in the surrounding gas significantly slows down evaporation, such as when humidity affects rate of evaporation of water. When the molecules of the liquid collide, they transfer energy to each other based on how they collide. When a molecule near the surface absorbs enough energy to overcome the vapor pressure, it will escape and enter the surrounding air as a gas. When evaporation occurs, the energy removed from the vaporized liquid will reduce the temperature of the liquid, resulting in evaporative cooling. On average, only a fraction of the molecules in a liquid have enough heat energy to escape from the liquid. The evaporation will continue until an equilibrium is reached when the evaporation of the liquid is equal to its condensation. In an enclosed environment, a liquid will evaporate until the surrounding air is ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
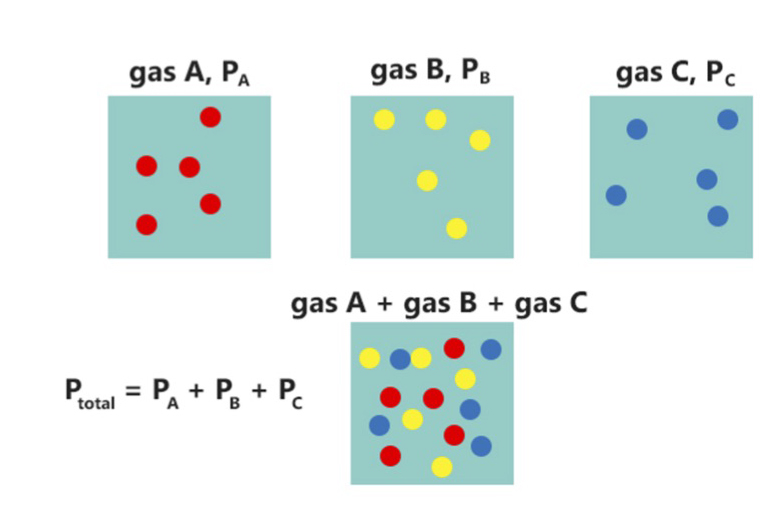
Gas Pressure
In a mixture of gases, each constituent gas has a partial pressure which is the notional pressure of that constituent gas as if it alone occupied the entire volume of the original mixture at the same temperature. The total pressure of an ideal gas mixture is the sum of the partial pressures of the gases in the mixture (Dalton's Law). The partial pressure of a gas is a measure of thermodynamic activity of the gas's molecules. Gases dissolve, diffuse, and react according to their partial pressures but not according to their concentrations in gas mixtures or liquids. This general property of gases is also true in chemical reactions of gases in biology. For example, the necessary amount of oxygen for human respiration, and the amount that is toxic, is set by the partial pressure of oxygen alone. This is true across a very wide range of different concentrations of oxygen present in various inhaled breathing gases or dissolved in blood; consequently, mixture ratios, like that of breathab ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Millisecond
A millisecond (from '' milli-'' and second; symbol: ms) is a unit of time in the International System of Units (SI) equal to one thousandth (0.001 or 10−3 or 1/1000) of a second and to 1000 microseconds. A unit of 10 milliseconds may be called a centisecond, and one of 100 milliseconds a decisecond, but these names are rarely used. To help compare orders of magnitude of different times, this page lists times between 10−3 seconds and 100 seconds (1 millisecond and one second). ''See also'' times of other orders of magnitude. Examples The Apollo Guidance Computer used metric units internally, with centiseconds used for time calculation and measurement. *1 millisecond (1 ms) – cycle time for frequency 1 kHz; duration of light for typical photo flash strobe; time taken for sound wave to travel about 34 cm; repetition interval of GPS C/A PN code *1 millisecond - time taken for light to travel 204.19 km in a single mode fiber optic cable for a wavelength o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |