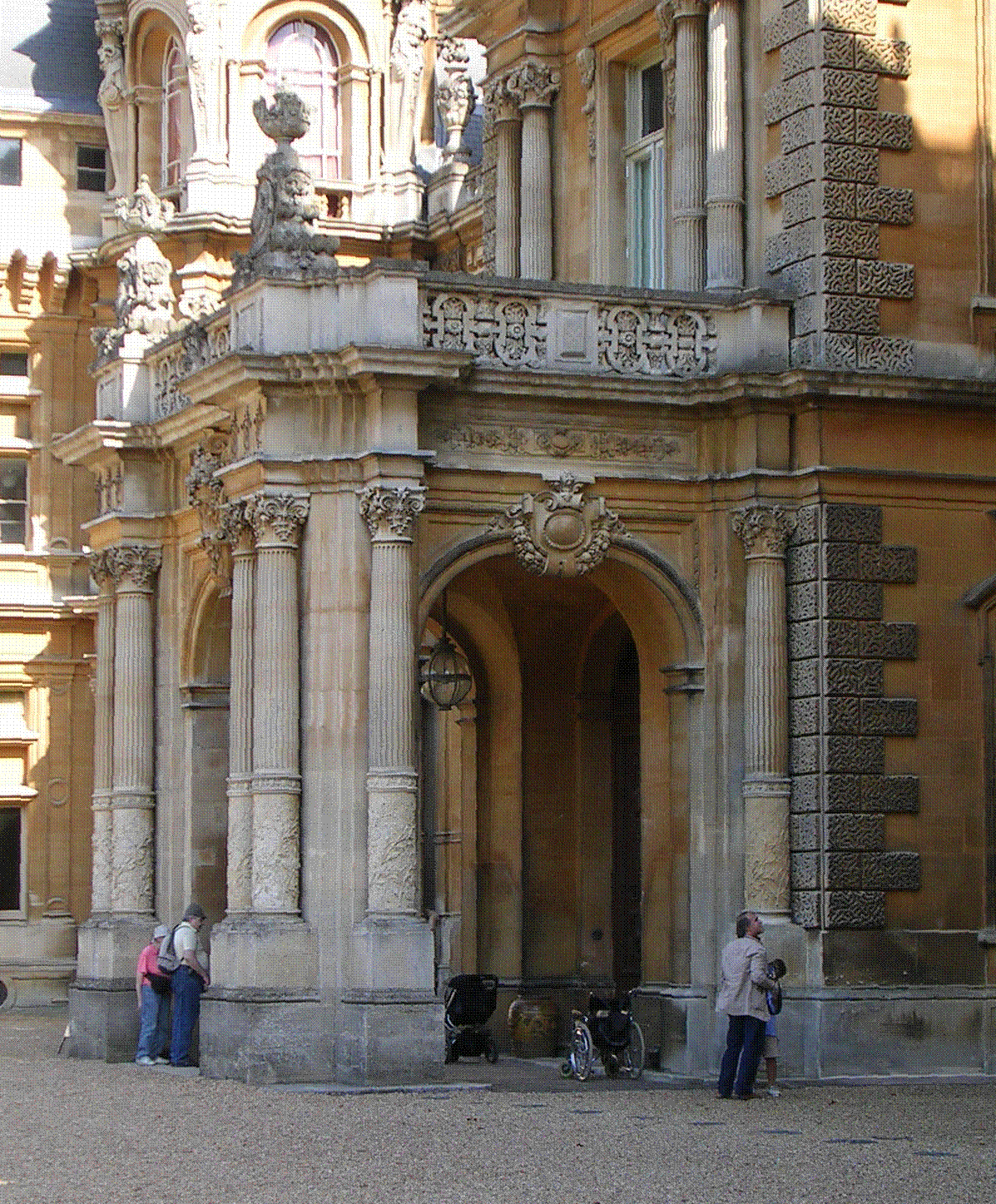|
Lartington Hall
Lartington Hall is a 17th-century country house, at Lartington, Teesdale, County Durham, England. It is a listed building, Grade II* listed building. Architecture The earliest part of the house, built for the Appleby family, is the three-storey four-bayed central block and projecting three-storey porch, which dates from about 1635. The west wing and chapel dedicated to St Lawrence were added in about 1800, and an east wing in the early 19th century, to which was added a ballroom in 1836 possibly to a design by Ignatius Bonomi. A curved porte-cochère on the north side, and adjoining vestibule and corridor, were added in 1861-5 by Joseph Hansom. History The Roman Catholic family of Maire acquired the manor of Lartington by marriage in 1654. It passed to the Lawson family when Lawson Baronets, Sir Henry Lawson Bt (d. 1834) of Brough Hall married Anna Anastasia, the Maire heiress. Their grandson Henry Thomas Maire Silvertop, who inherited the estate, married Eliza Witham and changed ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lartington
Lartington is a village and civil parish about west of the town of Barnard Castle, in Teesdale, in the Pennines of England. The United Kingdom Census 2011, 2011 Census recorded the parish's population as 135. Lartington is Historic counties of England, historically in the North Riding of Yorkshire but along with the rest of the former Startforth Rural District it was transferred to County Durham for metropolitan and non-metropolitan counties of England, administrative and ceremonial counties of England, ceremonial purposes on 1 April 1974 under the Local Government Act 1972. The parish is notable for Lartington Hall, the seat of the Catholic church, Roman Catholic Maire family. Lartington railway station was on the South Durham and Lancashire Union Railway, which is now abandoned. It opened in 1861 and closed in 1962. References External links Civil parishes in County Durham Villages in County Durham {{Durham-geo-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Teesdale
Teesdale is a dale, or valley, in Northern England. The dale is in the River Tees’s drainage basin, most water flows stem from or converge into said river, including the Skerne and Leven. Upper Teesdale, more commonly just Teesdale, falls between the Durham and Yorkshire Dales. Large parts of Upper Teesdale are in the North Pennines AONB (Area of Outstanding Natural Beauty) - the second largest AONB in England and Wales. The River Tees rises below Cross Fell, the highest hill in the Pennines at , and its uppermost valley is remote and high. The local climate was scientifically classified as "Sub-Arctic" and snow has sometimes lain on Cross Fell into June (there is an alpine ski area Yad Moss). Lower Teesdale has mixed urban (Tees Valley or Teesside) and rural (Cleveland) parts. Roseberry Topping is a notable hill on the south eastern side, of which this and other adjoining hills form the northern end of the North York Moors. Newer terms have gained stronger associations w ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
County Durham
County Durham ( ), officially simply Durham,UK General Acts 1997 c. 23Lieutenancies Act 1997 Schedule 1(3). From legislation.gov.uk, retrieved 6 April 2022. is a ceremonial county in North East England.North East Assembly �About North East England. Retrieved 30 November 2007. The ceremonial county spawned from the historic County Palatine of Durham in 1853. In 1996, the county gained part of the abolished ceremonial county of Cleveland.Lieutenancies Act 1997 . Retrieved 27 October 2014. The county town is the of |
England
England is a country that is part of the United Kingdom. It shares land borders with Wales to its west and Scotland to its north. The Irish Sea lies northwest and the Celtic Sea to the southwest. It is separated from continental Europe by the North Sea to the east and the English Channel to the south. The country covers five-eighths of the island of Great Britain, which lies in the North Atlantic, and includes over 100 smaller islands, such as the Isles of Scilly and the Isle of Wight. The area now called England was first inhabited by modern humans during the Upper Paleolithic period, but takes its name from the Angles, a Germanic tribe deriving its name from the Anglia peninsula, who settled during the 5th and 6th centuries. England became a unified state in the 10th century and has had a significant cultural and legal impact on the wider world since the Age of Discovery, which began during the 15th century. The English language, the Anglican Church, and Engli ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Listed Building
In the United Kingdom, a listed building or listed structure is one that has been placed on one of the four statutory lists maintained by Historic England in England, Historic Environment Scotland in Scotland, in Wales, and the Northern Ireland Environment Agency in Northern Ireland. The term has also been used in the Republic of Ireland, where buildings are protected under the Planning and Development Act 2000. The statutory term in Ireland is " protected structure". A listed building may not be demolished, extended, or altered without special permission from the local planning authority, which typically consults the relevant central government agency, particularly for significant alterations to the more notable listed buildings. In England and Wales, a national amenity society must be notified of any work to a listed building which involves any element of demolition. Exemption from secular listed building control is provided for some buildings in current use for worship, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ignatius Bonomi
Ignatius Bonomi (1787–1870) was an English architect and surveyor, with Italian origins by his father, strongly associated with Durham in north-east England. Life He was the son of an architect and draughtsman, Joseph Bonomi (1739–1808), who had worked with Robert and James Adam, while his brother Joseph Bonomi the Younger was a noted artist, sculptor and Egyptologist. Bonomi was Surveyor of Bridges for the County of Durham, and his works included the Skerne Bridge; one of the first railway bridges in Britain, over the River Skerne, near Darlington, for the Stockton and Darlington Railway, in 1824 (hence he is sometimes referred to as 'the first railway architect'). He was also responsible for a number of church buildings (including commissions at Durham Cathedral). Other historic buildings, in Gothic and neo-classical styles, included Durham Castle, Lambton Castle (continuing the work started by his father), Durham Prison, Elvet Hill House (1820), Burn Hall, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Porte-cochère
A porte-cochère (; , late 17th century, literally 'coach gateway'; plural: porte-cochères, portes-cochères) is a doorway to a building or courtyard, "often very grand," through which vehicles can enter from the street or a covered porch-like structure at a main or secondary entrance to a building through which originally a horse and carriage and today a motor vehicle can pass to provide arriving and departing occupants protection from the elements. Portes-cochères are still found on such structures as major public buildings and hotels, providing covered access for visitors and guests arriving by motorized transport. A porte-cochère, a structure for vehicle passage, is to be distinguished from a portico, a columned porch or entry for human, rather than vehicular, traffic. History The porte-cochère was a feature of many late 18th- and 19th-century mansions and public buildings. A well-known example is at Buckingham Palace in London. A portico at the White House in Wa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Joseph Hansom
Joseph Aloysius Hansom (26 October 1803 – 29 June 1882) was a British architect working principally in the Gothic Revival style. He invented the Hansom cab and founded the eminent architectural journal, ''The Builder'', in 1843. Career Hansom was born in the parish of St Martin's (possibly on St Martin's Lane), York to a large Roman Catholic family and baptised as Josephus Aloysius Handsom(e). He was the brother of the architect Charles Francis Hansom and the uncle of Edward J. Hansom. He was apprenticed to his father, Henry, as a joiner, but showing an early aptitude for draughtsmanship and construction, he transferred his apprenticeship to a York architect named Matthew Philips, without informing the City of York. By around 1823 he had completed his apprenticeship and became a clerk in Philips' office. About 1825 he settled in Halifax, Yorkshire, and in the same year he married Hannah Glover, the elder sister of the architect George Glover (1812-1890), at St Michael le ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Roman Catholic
Roman or Romans most often refers to: *Rome, the capital city of Italy *Ancient Rome, Roman civilization from 8th century BC to 5th century AD *Roman people, the people of ancient Rome *'' Epistle to the Romans'', shortened to ''Romans'', a letter in the New Testament of the Christian Bible Roman or Romans may also refer to: Arts and entertainment Music * Romans (band), a Japanese pop group * ''Roman'' (album), by Sound Horizon, 2006 * ''Roman'' (EP), by Teen Top, 2011 *" Roman (My Dear Boy)", a 2004 single by Morning Musume Film and television * Film Roman, an American animation studio * ''Roman'' (film), a 2006 American suspense-horror film * ''Romans'' (2013 film), an Indian Malayalam comedy film * ''Romans'' (2017 film), a British drama film * ''The Romans'' (''Doctor Who''), a serial in British TV series People *Roman (given name), a given name, including a list of people and fictional characters *Roman (surname), including a list of people named Roman or Romans *Ῥωμ� ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Brough Hall
Brough () may mean or refer to an ''area'', ''enclosure'', ''round tower'' or ''outer wall of a feudal castle''. Places England * Brough, Cumbria, a village in Cumbria **Brough Castle *Brough-on-Noe, a hamlet in Derbyshire *Brough, East Riding of Yorkshire, a town **Brough Aerodrome, an aerodrome and former motor racing circuit nearby *Brough with St Giles, a village and civil parish in North Yorkshire **Brough Hall *Brough, Nottinghamshire, a village on the Fosse Way *Middlesbrough, a town in North Yorkshire Scotland * Brough, Caithness, near Dunnet Head *Brough, Shetland * Brough, Yell, Shetland *Brough of Birsay, a tidal island and lighthouse, Orkney Islands Other uses *Brough (surname) *Brough Motorcycles, made in England from 1908 to 1926 *Brough Superior Brough Superior ( ) motorcycles, sidecars, and motor cars were made by George Brough in his Brough Superior works on Haydn Road in Nottingham, England, from 1919 to 1940. The motorcycles were dubbed the "Rolls-Ro ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Henry Witham
Henry Thomas Maire Witham FRSE FGS (1779–1844) was a British landowner remembered as an amateur palaeontologist and mineralogist. He was an early researcher into the internal structure of fossil plants. Life He was born Henry Silvertop the son of John Silvertop of Minsteracres in Northumberland. His mother was Catherine Lawson of Brough. He was a compulsive gambler and ran up debts of £105,000 (a truly huge sum in the 1820s) and was forced to sell off much of his property to settle his debts. From 1826 to 1832 he lived in Edinburgh at 14 Great King Street. During his time in Edinburgh (in 1827) he was elected a Fellow of the Royal Society of Edinburgh, his proposer being Thomas Allan. Though having no botanical training, he applied William Nicol's method of examining fossils and rocks under the microscope by slicing them into thin sections. Nicol's first published account of this process is contained in Witham's 1831 publication, ''Observations of Fossil Vegetables'' ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |