|
Lappmark
Lappmarken was an earlier Swedish name for the northern part of the old Kingdom of Sweden inhabited by the Sami people. In addition to the present-day Swedish Lapland, it also covered Västerbotten, Jämtland and Härjedalen, as well as the Finnish Lapland. As a name, it is related to Finnmark, an old Norwegian name for the Sami area. "Finn" and "Lapp" are mutually exchangeable old names for the Sami people, although the latter is sometimes deemed offensive. Already in the Middle Ages, Lappmarken consisted of "lappmarks" whose Sami people were loosely governed either by the crown or birkarls. The purpose of lappmarks was largely colonial in nature. Originally, each consisted of a river valley with its surrounding areas from the Gulf of Bothnia up to the fjelds. The first lappmarks were: * Lycksele lappmark (Ume River valley) * Åsele lappmark (Ångerman River valley) * Tornio lappmark (Tornio River valley) * Piteå lappmark (Pite River valley) * Luleå lappmark (Lule River valley) ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Swedish Lapland
Lapland, also known by its Swedish name Lappland (, fi, Lappi, la, Lapponia), is a province in northernmost Sweden. It borders Jämtland, Ångermanland, Västerbotten, Norrbotten, Norway and Finland. Nearly a quarter of Sweden's land area is in Lappland. Lapland originally extended eastward. However, in 1809 the Russian Empire annexed the eastern part of Sweden, and created the Grand Duchy of Finland, which in effect split Lapland into a Swedish part and a Finnish part, both of which still exist today. It primarily consists of Västerbotten County in the south and Norrbotten County in the north, forming the further inland areas of the two counties. Lapland has the coldest climates of Sweden with vast seasonal differences caused by the high latitudes and the interior location. History The history of Lapland is in many ways connected to the history of Norrbotten County and Västerbotten County, since Lapland is a historic region connected to these counties. During the Mi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Birkarls
The Birkarls (''birkarlar'' in Swedish, unhistorical ''pirkkamiehet'' or ''pirkkalaiset'' in Finnish; ''bircharlaboa'', ''bergcharl'' etc. in historical sources) were a small, unofficially organized group that controlled taxation and commerce in central Lappmarken in Sweden from the 13th to the 17th century.Vahtola, Jouko. ''Tornionlaakson historia I''. Birkarlit, 'pirkkalaiset'. Malungs boktryckeri AB. Malung, Sweden. 1991. The article draws heavily from the material available in the book. Background Birkarls (bircharlaboa) are first mentioned in 1328, when they are listed as one of the settler groups in northern Hälsingland, a designation that covered the western coast of Gulf of Bothnia all the way up and around the gulf to Oulu River. The name ''birkarl'' probably originates from an ancient Scandinavian word '' birk'' that has been used in reference to commerce in various contexts. In the late 16th century, claims about birkarls coming from Great Pirkkala (a parish in Up ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sápmi
(, smj, Sábme / Sámeednam, sma, Saepmie, sju, Sábmie, , , sjd, Са̄мь е̄ммьне, Saam' jiemm'n'e) is the cultural region traditionally inhabited by the Sámi people. Sápmi is in Northern and Eastern Europe and includes the northern parts of Fennoscandia, also known as the "Cap of the North". The region stretches over four countries: Norway, Sweden, Finland, and Russia. On the north it is bounded by the Barents Sea, on the west by the Norwegian Sea, and on the east by the White Sea."Lapland." Encyclopædia Britannica. ''Encyclopædia Britannica Online. Encyclopædia Britannica'', 2009. Web. 24 November 2009 http://search.eb.com/eb/article-9047170. The area is historically referred to as Lapland () in English, although the term "Lapp" for its inhabitants is now considered pejorative.; ; Norwegian Sápmi was historically called ''Finnmǫrk'', a name used for the former county Finnmark, now Troms og Finnmark. Sápmi refers to the areas where the Sámi people ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Laponia (historical Province)
{{refimprove, date=December 2007 Laponia ( sv, Lappland) was a historical Swedish province, or ''landscape'', in the north of Sweden which evolved from Lappmarken. In 1809, Sweden ceded the eastern part, along with Finland, to the Russian Empire, which in effect created a Swedish Lapland and Finnish Lapland. Today, the Swedish part serves no administrative purpose. On the Finnish side, there was a Province of Lapland (much larger to the south, especially by population, and where there were no Sami for many centuries) from 1938 until 2010, when Finnish provinces were discontinued, and the province was replaced by the Region of Lapland. Lapland is considered in some nations — notably the United Kingdom, Ireland, Serbia, Sweden, Finland, Latvia, Romania and France — to be the home of Father Christmas (more widely known as Santa Claus). Population The current population of Swedish Lapland plus the municipalities Enontekiö (Eanodat), Inari (Ánar), Utsjoki (Ohcejohka ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Finnish Lapland
Lapland ( fi, Lappi ; se, Lappi; smn, Laapi; sv, Lappland; la, Lapponia, links=no) is the largest and northernmost region of Finland. The 21 municipalities in the region cooperate in a Regional Council. Lapland borders the region of North Ostrobothnia in the south. It also borders the Gulf of Bothnia, Norrbotten County in Sweden, Troms and Finnmark County in Norway, and Murmansk Oblast and the Republic of Karelia The Republic of Karelia (russian: Респу́блика Каре́лия, Respublika Kareliya; ; krl, Karjalan tašavalta; ; fi, Karjalan tasavalta; vep, Karjalan Tazovaldkund, Ludic: ''Kard’alan tazavald''), also known as just Karelia (rus ... in Russia. Topography varies from vast mires and forests of the South to Fell, fells in the North. The Arctic Circle crosses Lapland, so polar phenomena such as the midnight sun and polar night can be viewed in Lapland. Lapland's cold and wintry climate, coupled with its relative abundance of conifer trees such as p ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ångerman River
__NOTOC__ The Ångerman or Angerman ( sv, Ångermanälven) is one of Sweden's longest rivers with a total length of . It also has the third largest flow rate, after the Göta and Lule. Name The name was formerly written Ångermann or Angermann. The name is derived from the Old Norse ''anger'', which means "deep fjord" and appear as such in placenames in Norway and as "ånger" in placenames along the coast of Norrland. Course It starts in the Scandinavian mountain range in the southern parts of the Swedish province of Lapland. It then trails through Jämtland, increasing in power in the province of Ångermanland, whose name derives from it. The Vojmån, Fjällsjö, and Fax are its main tributaries. It contains an internal bifurcation Vängelälven. It is navigable for about from the sea. Over the last (after the town of Sollefteå noted on the map), it flows through a scenic valley known as Ådalen. The Ångerman then empties into the Baltic Sea's Gulf of Bothnia near the tow ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Norrland
Norrland (, "Northland", originally ''Norrlanden'' or "the Northlands") is the northernmost, largest and least populated of the three traditional lands of Sweden, consisting of nine provinces. Although Norrland does not serve any administrative purposes, it continues to exist as a historical, cultural, and geographic region; it is often referred to in everyday language, e.g., in weather forecasts. Several related Norrland dialects form a distinct subset of dialects of the Swedish language separate from those to its south. Norrland consists of the majority of the Swedish landmass at about 60% of the land area, but only has about 12% of the country's population. Its largest city is Umeå, while the other four county seats are Gävle, Sundsvall, Östersund and Luleå. The largest non-capitals are Skellefteå and Örnsköldsvik while Kiruna is the largest town of the vast Lapland province in the far north. Sweden's highest mountain Kebnekaise and deepest lake of Hornavan are ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
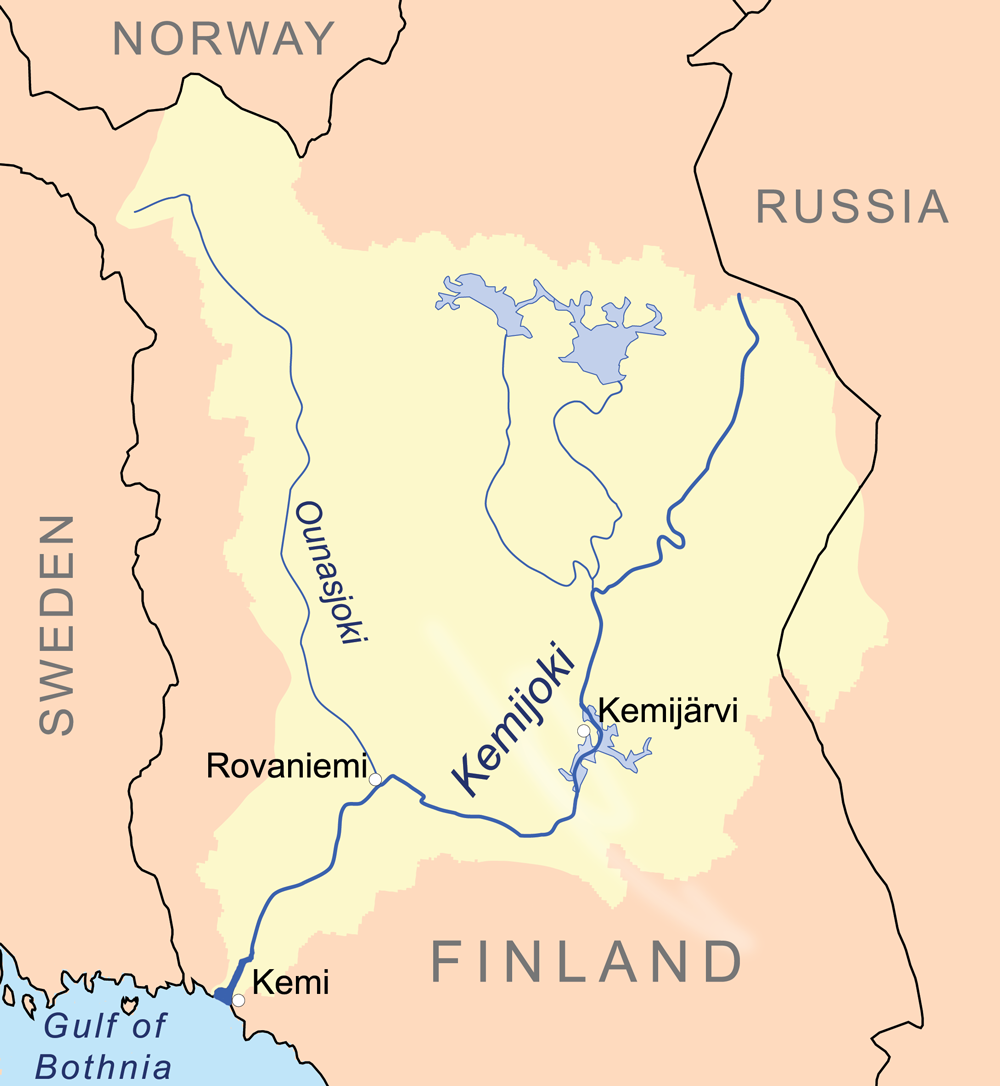
Kemi River
Kemijoki ( sv, Kemi älv, se, Giemajohka), with its length, is the longest river in Finland. It runs through Kemijärvi and Rovaniemi before reaching the Gulf of Bothnia at Kemi.Facta (encyclopedia), Facta 2001, part 8, ''finnish'' At Rovaniemi the Ounasjoki river merges with Kemijoki. The first hydroelectric plant on Kemijoki was constructed in 1949 at Isohaara. A total of 15 power plants have been constructed so far. The plants are owned by Kemijoki Oy and Pohjolan Voima Oy. In 2003 the plants produced a total of 4.3 TWh, which was about 34.5% of Finland's total hydroelectric production. See also * List of rivers of the Baltic Sea * Rivers of Finland References External links Hydroelectric power stations in Finland Tervola Kemijoki basin Rivers of Rovaniemi {{Finland-river-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kemi
Kemi (; sme, Giepma ; smn, Kiemâ; sms, Ǩeeʹmm; Swedish (historically): ''Kiemi'') is a town and municipality of Finland. It is located very near the city of Tornio and the Swedish border. The distance to Oulu is to the south and to Rovaniemi is to the northeast. It was founded in 1869 by a decree of the Emperor Alexander II of Russia because of its proximity to a deepwater port. The town has a population of () and covers an area of of which are water. The population density is . History World War II hostage crisis During World War II, after Finland signed the Moscow Armistice and found itself involved in the Lapland War against its former German ally, German forces at the beginning of October 1944 captured 132 Finnish civilian hostages in Kemi (as well as 130 in Rovaniemi) and threatened to kill them unless the Finnish army released the German POWs captured in the Battle of Tornio. However, Finland refused to comply and threatened to retaliate by killing the German P ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lule River
Lule River ( smj, Julevädno, sv, Lule älv, ''Luleälven'') is a major river in Sweden, rising in northern Sweden and flowing southeast for before reaching the Gulf of Bothnia at Luleå. It is the second longest river by watershed area or length in Norrbotten County (after the Torne River and very slightly ahead of the Kalix River, which is 460.65 km long), but is the largest by average discharge. It has a watershed of 25,240.5 km² of which 24,545.6 km² is in Sweden and 694.9 km² in Norway. The river is an important source of hydroelectric energy, with major hydroelectric plants at e.g. Porjus and the 977 MW Harsprånget, commissioned in 1952 and expanded in 1983 to become Sweden's largest hydro power station.Mellgren, Erik"Third time counted for Harsprånget" ''Ny Teknik'' 28 July 2012. Retrieved: 7 August 2012. The river was used extensively for the transportation of timber, with logs floated downstream for processing at Luleå, but this stopped in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Luleå
Luleå ( , , locally ; smj, Luleju; fi, Luulaja) is a city on the coast of northern Sweden, and the capital of Norrbotten County, the northernmost county in Sweden. Luleå has 48,728 inhabitants in its urban core (2018) and is the seat of Luleå Municipality (with a total population of 77,832). Luleå is Sweden's 25th largest city and Norrbotten County's largest city. Luleå has the seventh biggest harbour in Sweden for shipping goods. It has a large steel industry and is a centre for extensive research. It is also home to the Swedish Air Force Wing Norrbotten Wing (F 21) based in Luleå Airport. Luleå University of Technology is one of Sweden's three technology universities (the other two are KTH and Chalmers) and the northernmost university in Sweden. The university has approximately 15,000 students. History The town's Royal charter was granted in 1621 by King Gustavus Adolphus of Sweden. The original town was situated where Gammelstad (Old Town) is situated today ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pite River
The Pite River (''Bidumedno'' in Pite Sami. ''Piteälven'', ''Pite älv'' or ''Piteå älv'' in Swedish.) is a river in northern Sweden, flowing through the Norrbotten County. It is one of the four major rivers in Norrland that have been left mostly untouched by water power plants, the river has a single dam at Sikfors approximately 15 km upstream from the sea. It starts in the large lakes in eastern Sweden, such as Tjeggelvas, Vuolvojaure and Labbas, in Jokkmokk Municipality, and flows to the east coast, discharging in the Gulf of Bothnia, in the Piteå Municipality. It has a length of 400 kilometers, covering an area of 11,200 km². Its largest waterfall is Storforsen, which has also become the most popular place to visit in Norrbotten. It is located in Älvsbyn Municipality. See also Some of the other large Norrland rivers: * Kalix River * Torne River * Lule River * Ume River * Skellefte River The Skellefte River ( sv, Skellefteälven or ; sje, Seldutiedno; sj ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |