|
Lambda (letter)
Lambda (}, ''lám(b)da'') is the 11th letter of the Greek alphabet, representing the voiced alveolar lateral approximant . In the system of Greek numerals, lambda has a value of 30. Lambda is derived from the Phoenician Lamed . Lambda gave rise to the Latin L and the Cyrillic El (Л). The ancient grammarians and dramatists give evidence to the pronunciation as () in Classical Greek times. In Modern Greek, the name of the letter, Λάμδα, is pronounced . In early Greek alphabets, the shape and orientation of lambda varied. Most variants consisted of two straight strokes, one longer than the other, connected at their ends. The angle might be in the upper-left, lower-left ("Western" alphabets) or top ("Eastern" alphabets). Other variants had a vertical line with a horizontal or sloped stroke running to the right. With the general adoption of the Ionic alphabet, Greek settled on an angle at the top; the Romans put the angle at the lower-left. The HTML 4 character entity re ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Greek Alphabet
The Greek alphabet has been used to write the Greek language since the late 9th or early 8th century BCE. It is derived from the earlier Phoenician alphabet, and was the earliest known alphabetic script to have distinct letters for vowels as well as consonants. In Archaic Greece, Archaic and early Classical Greece, Classical times, the Greek alphabet existed in Archaic Greek alphabets, many local variants, but, by the end of the 4th century BCE, the Euclidean alphabet, with 24 letters, ordered from alpha to omega, had become standard and it is this version that is still used for Greek writing today. The letter case, uppercase and lowercase forms of the 24 letters are: : , , , , , , , , , , , , , , , , , /ς, , , , , , . The Greek alphabet is the ancestor of the Latin script, Latin and Cyrillic scripts. Like Latin and Cyrillic, Greek originally had only a single form of each letter; it developed the letter case distinction between uppercase and lowercase in parallel with Latin ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Subatomic Particle
In physical sciences, a subatomic particle is a particle that composes an atom. According to the Standard Model of particle physics, a subatomic particle can be either a composite particle, which is composed of other particles (for example, a proton, neutron, or meson), or an elementary particle, which is not composed of other particles (for example, an electron, photon, or muon). Particle physics and nuclear physics study these particles and how they interact. Experiments show that light could behave like a stream of particles (called photons) as well as exhibiting wave-like properties. This led to the concept of wave–particle duality to reflect that quantum-scale behave like both particles and waves; they are sometimes called wavicles to reflect this. Another concept, the uncertainty principle, states that some of their properties taken together, such as their simultaneous position and momentum, cannot be measured exactly. The wave–particle duality has been shown to app ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
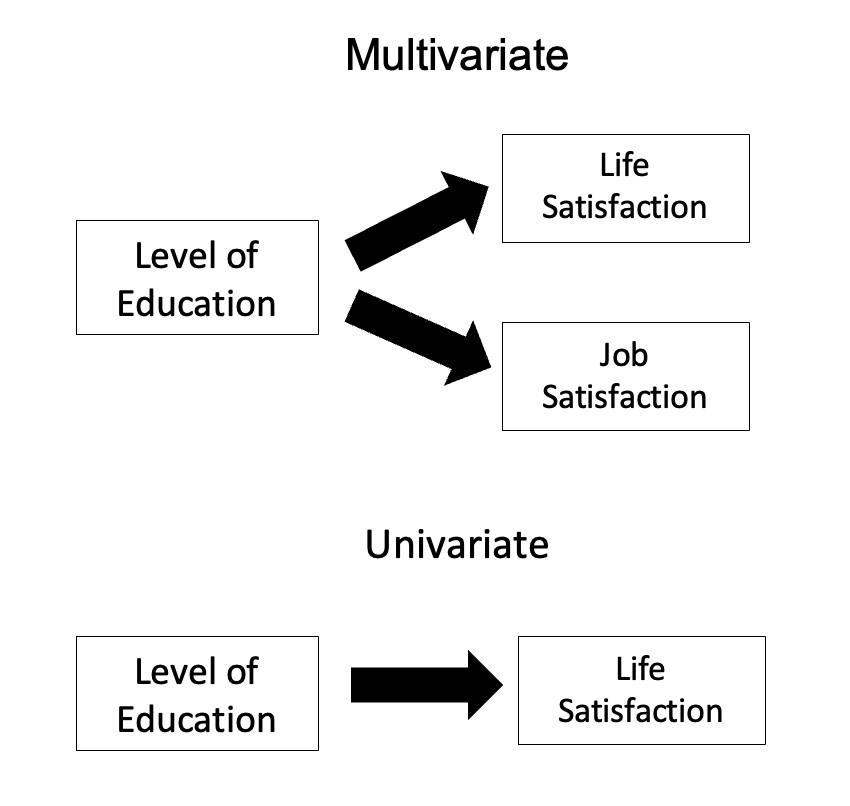
MANOVA
In statistics, multivariate analysis of variance (MANOVA) is a procedure for comparing multivariate sample means. As a multivariate procedure, it is used when there are two or more dependent variables, and is often followed by significance tests involving individual dependent variables separately. Without relation to the image, the dependent variables may be k life satisfactions scores measured at sequential time points and p job satisfaction scores measured at sequential time points. In this case there are k+p dependent variables whose linear combination follows a multivariate normal distribution, multivariate variance-covariance matrix homogeneity, and linear relationship, no multicollinearity, and each without outliers. Relationship with ANOVA MANOVA is a generalized form of univariate analysis of variance (ANOVA), although, unlike univariate ANOVA, it uses the covariance between outcome variables in testing the statistical significance of the mean differences. Where sums o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Samuel Stanley Wilks
Samuel Stanley Wilks (June 17, 1906 – March 7, 1964) was an American mathematician and academic who played an important role in the development of mathematical statistics, especially in regard to practical applications. Early life and education Wilks was born in Little Elm, Texas and raised on a farm. He studied Industrial Arts at the North Texas State Teachers College in Denton, Texas, obtaining his bachelor's degree in 1926. He received his master's degree in mathematics in 1928 from the University of Texas. He obtained his Ph.D. at the University of Iowa under Everett F. Lindquist; his thesis dealt with a problem of statistical measurement in education, and was published in the ''Journal of Educational Psychology''. Career Wilks became an instructor in mathematics at Princeton University in 1933; in 1938 he assumed the editorship of the journal ''Annals of Mathematical Statistics'' in place of Harry C. Carver. Wilks assembled an advisory board for the journal that ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |