|
Laleng
The Laleng, also known as the Patra ( bn, পাত্র, Patro) are a small indigenous ethnolinguistic group primarily living deep in the forests of Sylhet District and Moulvibazar District in Bangladesh. They speak the endangered Laiunghtor language. There are diaspora communities in the Indian states of Assam and Meghalaya. Most people living in Sylhet are even unaware of the existence of this minority community, although their presence dates back centuries, as they choose to stay hidden in the deep forests. Etymology The endonym of the community is Laleng, which means "stone" in their native language and they also use the terms ''Lalong'' and ''Lalung''. They are known by a number of exonyms in the Bengali language such as Patra ( bn, পাত্র, Patro), Pathor ( bn, পাথর), Pator ( bn, পাতর) and Fattor ( syl, ফাত্তর). It is said that their ancestors were stone-collectors and coal merchants; hence the name. History They are said to have de ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sylhet Division
Sylhet Division ( bn, সিলেট বিভাগ) is the northeastern division of Bangladesh. It is bordered by the Indian states of Meghalaya, Assam and Tripura to the north, east and south respectively, and by the Bangladeshi divisions of Chittagong to the southwest and Dhaka and Mymensingh to the west. Prior to 1947, it included the subdivision of Karimganj (presently in Barak Valley, India). However, Karimganj (including the thanas of Badarpur, Patharkandi and Ratabari) was inexplicably severed from Sylhet by the Radcliffe Boundary Commission. According to Niharranjan Ray, it was partly due to a plea from a delegation led by Abdul Matlib Mazumdar. Etymology and names The name ''Sylhet'' is an anglicisation of ''Shilhot'' (শিলহট). Its origins seem to come from the Sanskrit words শিলা ''śilā'' (meaning 'stone') and হট্ট ''haṭṭa'' (meaning 'marketplace'). These words match the landscape and topography of the hilly region. The shila stones ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gour Kingdom
The Kingdom of Gour was one of the greater of the many petty kingdoms of the medieval Sylhet region. According to legend, it was founded by Gurak, off-shooting from Kamarupa's Jaintia Kingdom in 630. Much of its early history is considered legendary or mythological up until Navagirvana who is mentioned in the Bhatera copper-plate inscriptions. The Kings of Gour are described as patrons of Hindu revivalism in what was previously a predominantly Buddhist and animist populated land. The 11th century king Govinda-Rana Kesava Deva is recognised for introducing the ''navadinga'' (nine war boats) and heavily improving the kingdom's infantry, cavalry, and elephant power. Due to familial tensions, the kingdom split into two separate kingdoms in 1170; Gour (Northern Sylhet) and Brahmachal (Southern Sylhet), before being reunited by Raja Govardhan in the early years of his reign. However, this would be short-lasted as during Govardhan's reign, the kingdom would suffer attacks from neig ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
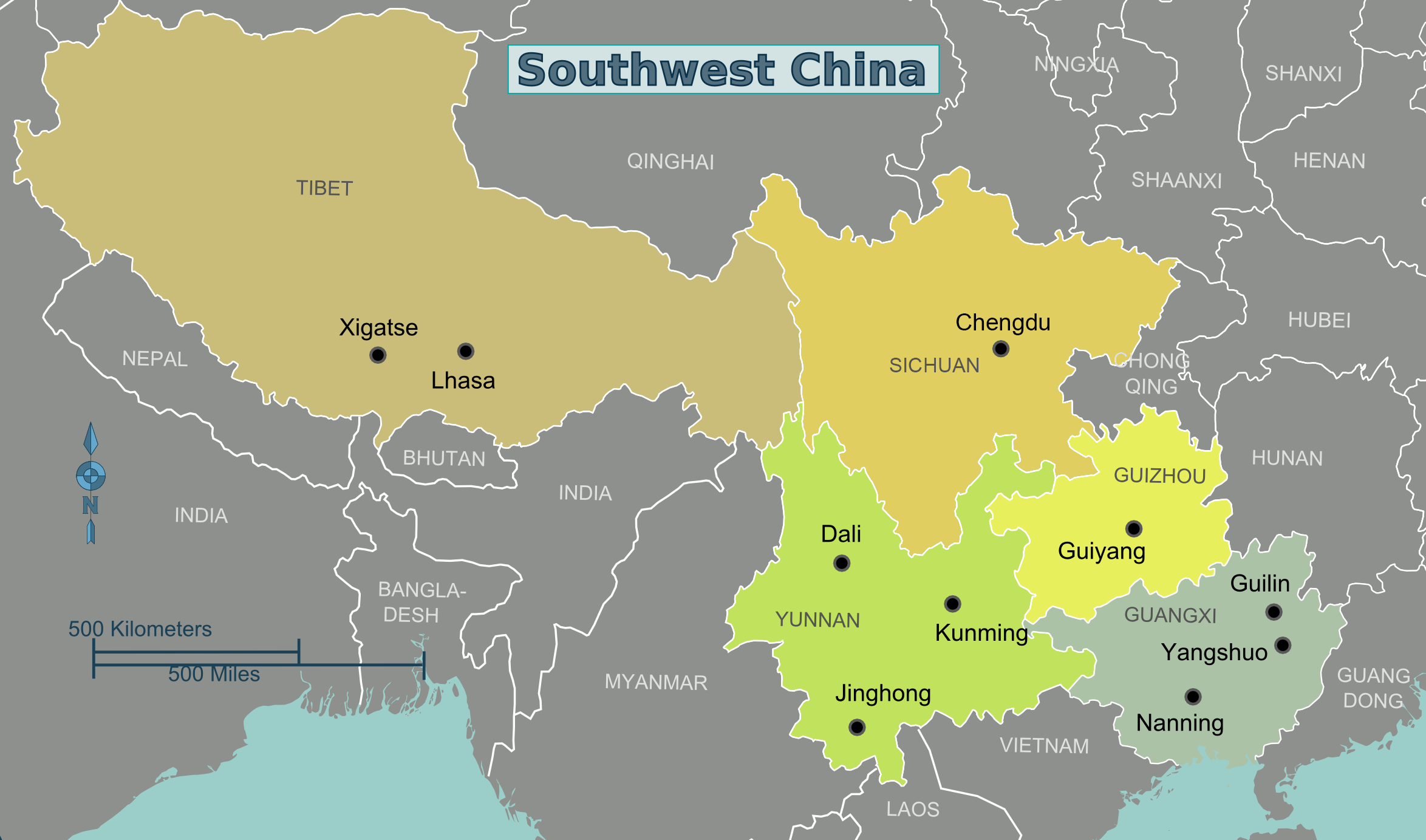
Southwest China
Southwest China () is a region in the south of the People's Republic of China. Geography Southwest China is a rugged and mountainous region, transitioning between the Tibetan Plateau to the west and the Chinese coastal hills (东南丘陵) and plains to the east. Key geographic features in the region include the Hengduan Mountains in the west, the Sichuan Basin in the northeast, and the karstic Yungui Plateau in the east. The majority of the region is drained by the Yangtze River which forms the Three Gorges in the northeast of the region. The narrowest concept of Southwest China consists of Sichuan, Chongqing, Yunnan, and Guizhou, while wider definitions often include Guangxi and western portions of Hunan. The official government definition of Southwest China includes the core provinces of Sichuan, Chongqing, Yunnan, and Guizhou, in addition to the Tibet Autonomous Region. History Portions of Southwest China were incorporated in the 3nd century BCE into the Qin dynast ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Government Of Bangladesh
The Government of the People's Republic of Bangladesh ( bn, গণপ্রজাতন্ত্রী বাংলাদেশ সরকার — ) is the central executive government of Bangladesh. The government was constituted by the Constitution of Bangladesh and represented by the president, the prime minister and the cabinet of Bangladesh. The legislature represented by the Jatiya Sangsad, and the judiciary, represented by the Supreme Court of Bangladesh. Bangladesh is a unitary state and the central government has the authority to govern over the entirety of the nation. The seat of the government is located in Dhaka, the capital of Bangladesh. The executive government is led by the prime minister, who selects all the remaining ministers. The prime minister and the other most senior ministers belong to the supreme decision-making committee, known as the Cabinet. The current prime minister is Sheikh Hasina, leader of the Bangladesh Awami League, who was sworn-in by the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bangladesh Liberation War
The Bangladesh Liberation War ( bn, মুক্তিযুদ্ধ, , also known as the Bangladesh War of Independence, or simply the Liberation War in Bangladesh) was a revolution and War, armed conflict sparked by the rise of the Bengali nationalism, Bengali nationalist and self-determination movement in East Pakistan, which resulted in the independence of Bangladesh. The war began when the Pakistani Military dictatorship, military junta based in West Pakistan—under the orders of Yahya Khan—launched Operation Searchlight against the people of East Pakistan on the night of 25 March 1971, initiating the 1971 Bangladesh genocide, Bangladesh genocide. In response to the violence, members of the Mukti Bahini—a guerrilla resistance movement formed by Bengali military, paramilitary and civilians—launched a mass Guerrilla warfare, guerrilla war against the Pakistani military, liberating numerous towns and cities in the initial months of the conflict. At first, the Pakis ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Partition Of India
The Partition of British India in 1947 was the Partition (politics), change of political borders and the division of other assets that accompanied the dissolution of the British Raj in South Asia and the creation of two independent dominions: Dominion of India, India and Dominion of Pakistan, Pakistan. The Dominion of India is today the India, Republic of India, and the Dominion of Pakistan—which at the time comprised two regions lying on either side of India—is now the Pakistan, Islamic Republic of Pakistan and the Bangladesh, People's Republic of Bangladesh. The partition was outlined in the Indian Independence Act 1947. The change of political borders notably included the division of two provinces of British India, Bengal Presidency, Bengal and Punjab Province (British India), Punjab. The majority Muslim districts in these provinces were awarded to Pakistan and the majority non-Muslim to India. The other assets that were divided included the British Indian Army, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sylhetis
The Sylheti () are an Indo-Aryan ethnocultural group that are associated with the Sylhet region in South Asia, specifically in northeast of Bengal presently divided between the Sylhet Division of Bangladesh, and the Barak Valley of Assam, India. There are sizeable Sylheti populations in Hojai district of Assam, the Indian areas of Meghalaya, North Tripura and Manipur's Jiribam district. They speak Sylheti, an Eastern Indo-Aryan language, which is ambiguously considered as an independent language, or as a dialect of Bengali."Along the linguistic continuum of eastern Indic languages, Sylheti occupies an ambiguous position, where it is considered a distinct language by many and also as a dialect of Bengali or Bangla by some others." Sylheti identity is associated mainly with a cultural, linguistic and a strong regional identity, while accompanied with a national (of either Bangladeshi or Indian) and a Bengali identity. History In September 1874, the British East India Company mad ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bengalis
Bengalis (singular Bengali bn, বাঙ্গালী/বাঙালি ), also rendered as Bangalee or the Bengali people, are an Indo-Aryan peoples, Indo-Aryan ethnolinguistic group originating from and culturally affiliated with the Bengal region of South Asia. The current population is divided between the independent country Bangladesh and the Indian states of West Bengal, Tripura and parts of Assam, Meghalaya and Manipur. Most of them speak Bengali language, Bengali, a language from the Indo-Aryan languages, Indo-Aryan language family. Bengalis are the List of contemporary ethnic groups, third-largest ethnic group in the world, after the Han Chinese and Arabs. Thus, they are the largest ethnic group within the Indo-Europeans and the largest ethnic group in South Asia. Apart from Bangladesh and the Indian states of West Bengal, Tripura, Manipur, and Assam's Barak Valley, Bengali-majority populations also reside in India's union territory of Andaman and Nicobar Islan ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
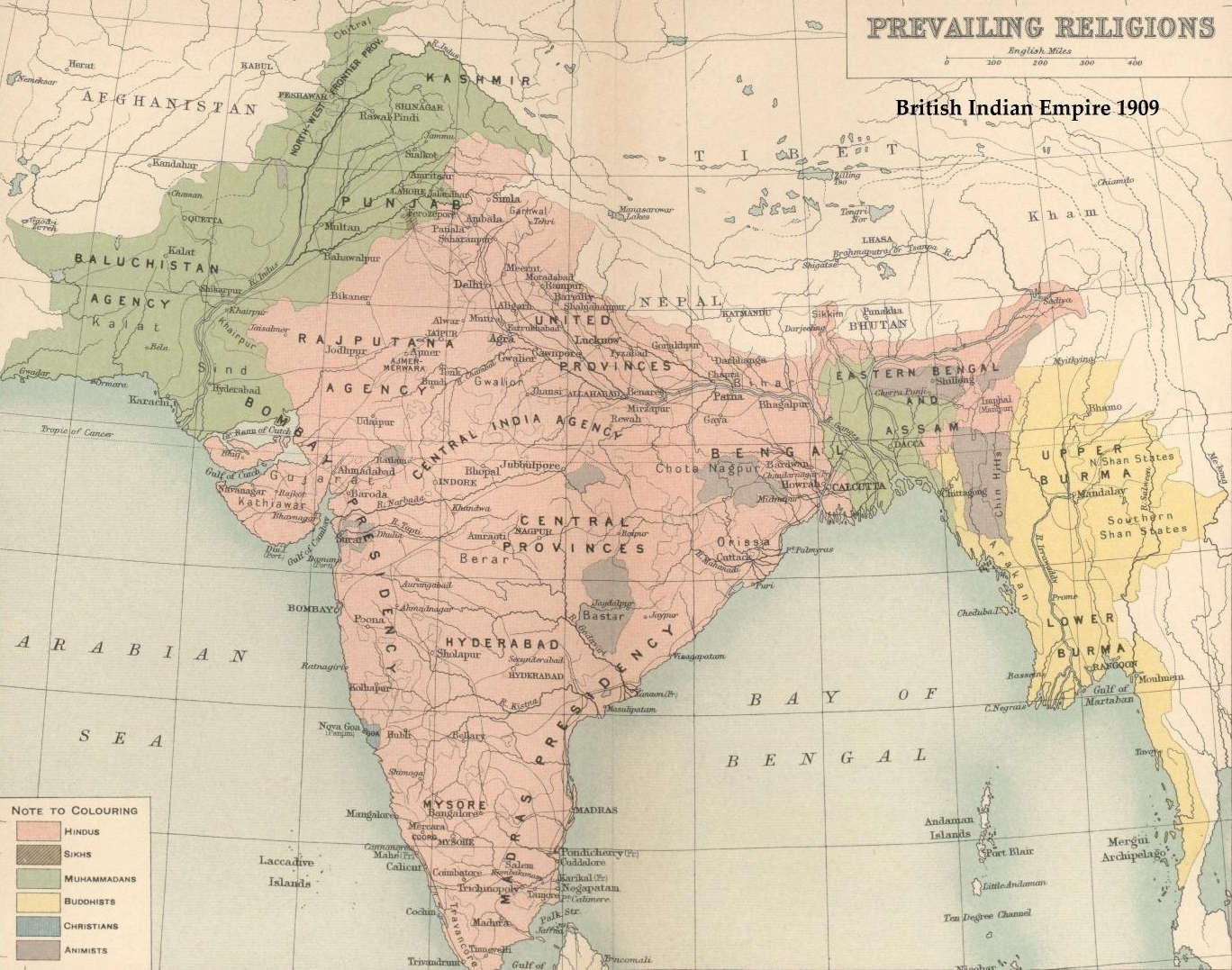
British Raj
The British Raj (; from Hindi ''rāj'': kingdom, realm, state, or empire) was the rule of the British Crown on the Indian subcontinent; * * it is also called Crown rule in India, * * * * or Direct rule in India, * Quote: "Mill, who was himself employed by the British East India company from the age of seventeen until the British government assumed direct rule over India in 1858." * * and lasted from 1858 to 1947. * * The region under British control was commonly called India in contemporaneous usage and included areas directly administered by the United Kingdom, which were collectively called British India, and areas ruled by indigenous rulers, but under British paramountcy, called the princely states. The region was sometimes called the Indian Empire, though not officially. As ''India'', it was a founding member of the League of Nations, a participating nation in the Summer Olympics in 1900, 1920, 1928, 1932, and 1936, and a founding member of the United Nations in San F ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sylhet Sadar Upazila
Sylhet Sadar ( bn, সিলেট সদর) is an upazila of Sylhet District in the Division of Sylhet, Bangladesh. Geography Sylhet Sadar is located at . It has 86,074 households and a total area of 323.17 km2. The city of Sylhet is located within central of Sylhet Sadar. Demographics At the 1991 Bangladesh census, Sylhet Sadar had a population of 554,412, of whom 287,304 were aged 18 or older. Males constituted 52.51% of the population, and females 47.49%. Sylhet Sadar had an average literacy rate of 87.6%, among them male 49.0%, female 51.0% (7+ years), and with the national average being 32.4% literate. Major religions are Muslim 81.26%, Hindu 17.43%, Buddhist, Christian and others 0.31%. Arts and culture The rich culture of Sylhet Sadar Upazila includes such major national festivals as Bangladesh Independence Day, Victory Day, Language Movement Day, Pohela Baishakh are widely celebrate in the upazila. Traditional and religious festivals like Eid-ul-Fitr, Eid-ul-Azh ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
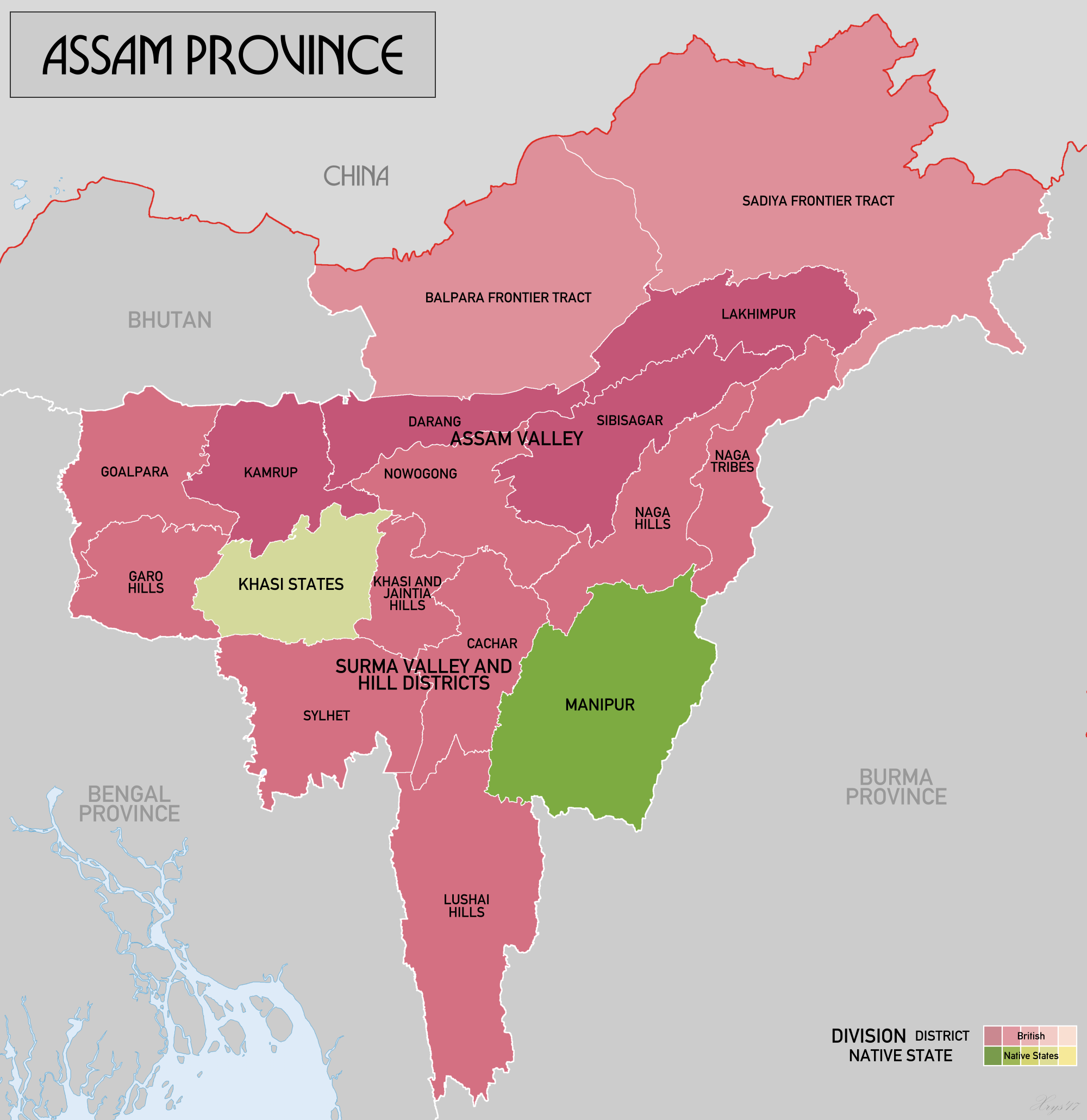
Sylhet Region
The 1947 Sylhet referendum was held in the Sylhet District of the Assam Province of British India to decide whether the district would remain in Undivided Assam and therefore within the post-independence Dominion of India, or leave Assam for East Bengal and consequently join the newly-created Dominion of Pakistan. The referendum's turnout was in favour of joining the Pakistani union; however, the district's Karimganj subdivision remained within the Indian state of Assam. History Prior to the British arrival in the region in 1765, the ''Sylhet Sarkar'' was a part of the Bengal Subah of the Mughal Empire. Initially, the Company Raj incorporated Sylhet into its Bengal Presidency; however, 109 years later on 16 February 1874, Sylhet was made a part of the non-regulation Chief Commissioner's Province of Assam (North-East Frontier) in order to facilitate Assam's commercial development. This transfer was implemented despite a memorandum of protests being submitted to the Viceroy, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Conquest Of Sylhet
The Conquest of Sylhet ( bn, শ্রীহট্টের বিজয়, Srīhôtter Bijôy, Conquest of Srihatta) predominantly refers to an Islamic conquest of Srihatta (present-day Sylhet, Bangladesh) led by Sikandar Khan Ghazi, the military general of Sultan Shamsuddin Firoz Shah of the Lakhnauti Sultanate, against the Hindu king Gour Govinda. The conquest was aided by a Muslim saint known as Shah Jalal, who later ordered his disciples to scatter throughout eastern Bengal and propagate the religion of Islam. The Conquest of Sylhet may also include other minor incidents taking place after Govinda's defeat, such as the capture of nearby Taraf. Background The Greater Sylhet region historically consisted of many Hindu petty kingdoms such as Srihatta (Gour), Laur and Jaintia. Govinda was a conservative Hindu ruler of the Gour Kingdom, intolerant and harsh towards other faiths such as Islam, Buddhism and even certain denominations of Hinduism. It was known by his people tha ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |