|
Lake Tanganyika Sardine
The Lake Tanganyika sardine (''Limnothrissa miodon'') is a species of freshwater fish in the family Clupeidae which was endemic to Lake Tanganyika but which has now been introduced to other lakes in Africa as a food source. It is monotypic within the genus ''Limnothrissa''. It and the Lake Tanganyika sprat are known collectively as kapenta. Distribution As its name suggests the Lake Tanganyika sardine was endemic to Lake Tanganyika extending into the lower reaches of the Malagarasi River. It has been introduced to Lake Kivu in Rwanda and the man-made Lake Kariba in the Zambezi valley between Zambia and Zimbabwe and more recently into the Itezhi-Tezhi Dam in Zambia.The Life History of Limnothrissa miodon in Lake Kariba. Author: P.C. Chifamba. Lake Kariba Fisheries Research Institute 1992. Papers presented at the Symposium on Biology, Stock Assessment and Exploitation of Small Peleagic Fish Species in the African Great Lakes Region. It has colonised Cahora Bassa lake in Mozambi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Charles Tate Regan
Charles Tate Regan FRS (1 February 1878 – 12 January 1943) was a British ichthyologist, working mainly around the beginning of the 20th century. He did extensive work on fish classification schemes. Born in Sherborne, Dorset, he was educated at Derby School and Queens' College, Cambridge and in 1901 joined the staff of the Natural History Museum, where he became Keeper of Zoology, and later director of the entire museum, in which role he served from 1927 to 1938. Regan was elected Fellow of the Royal Society in 1917. Regan mentored a number of scientists, among them Ethelwynn Trewavas, who continued his work at the British Natural History Museum. Species Among the species he described is the Siamese fighting fish (''Betta splendens''). In turn, a number of fish species have been named ''regani'' in his honour: *A Thorny Catfish '' Anadoras regani'' (Steindachner, 1908) *The Dwarf Cichlid '' Apistogramma regani'' *'' Apogon regani'' *A Catfish '' Astroblepus regani'' * ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Itezhi-Tezhi Dam
The Itezhi-Tezhi Dam on the Kafue River in west-central Zambia was built between 1974 and 1977 at the Itezhi-Tezhi Gap, in a range of hills through which the river had eroded a narrow valley, leading to the broad expanse of the wetlands known as the Kafue Flats. The town of Itezhi-Tezhi is to the east side of the dam. Dimensions and purpose The dam has a height of , a crest length of and forms a reservoir of , flooding a section of the Kafue National Park. The initial purpose of the dam is to store water for the Kafue Gorge Upper Power Station more than downstream. The Kafue River, like most in south-central Africa, has a very high seasonal variation, flooding in the rainy season and slowing to perhaps a twentieth of the peak flow rate at the end of the dry season. Power generation however requires a steady flow, which can only be achieved by having a reservoir large enough to store the seasonal flood for use in the dry season. At the Kafue Gorge the topography does not allow ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Atyidae
Atyidae is a family of shrimp, present in all tropical and most temperate waters of the world. Adults of this family are almost always confined to fresh water. This is the only family in the superfamily Atyoidea. Genera and species The following classification follows De Grave ''et al.'' (2010), with subsequent additions. *'' Antecaridina'' Edmondson, 1954 *'' Archaeatya'' Villalobos, 1959 *''Atya'' Leach, 1816 *'' Atyaephyra'' de Brito Capello, 1867 *'' Atydina'' Cai, 2010 *'' Atyella'' Calman, 1906 *''Atyoida'' Randall, 1840 *''Atyopsis'' Chace, 1983 *'' Australatya'' Chace, 1983 *'' Caridella'' Calman, 1906 *''Caridina'' H. Milne-Edwards, 1837 *'' Caridinides'' Calman, 1926 *'' Caridinopsis'' Bouvier, 1912 *''Delclosia'' Rabadà, 1993 † *'' Dugastella'' Bouvier, 1912 *'' Edoneus'' Holthuis, 1978 *''Elephantis'' Castelin, Marquet & Klotz, 2013 *'' Gallocaris'' Sket & Zakšek, 2009 *''Halocaridina'' Holthuis, 1963 *'' Halocaridinides'' Fujino & Shokita, 1975 *'' Jolivetya'' ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Diaphanosoma
''Diaphanosoma'' is a genus of ''Sididae''. The genus was described in 1850 by Fischer. It has cosmopolitan distribution. Species: * ''Diaphanosoma amurensis'' Korovchinsky & Sheveleva, 2009 * ''Diaphanosoma australiensis'' Korovchinsky, 1981 * ''Diaphanosoma fluviatile ''Diaphanosoma fluviatile'' is a species of freshwater ctenopod in the family Sididae. Native to Central and South America, it has been found in lakes farther to the north. In 2008 it was reported to have been found in central Texas. In 2018 it ...'' Hansen, 1899 References {{Taxonbar, from=Q4561167 Cladocera ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ceriodaphnia
''Ceriodaphnia'' is a genus of the Daphniidae; the genus was described in 1853 by James Dwight Dana. It has cosmopolitan distribution In biogeography, cosmopolitan distribution is the term for the range of a taxon that extends across all or most of the world in appropriate habitats. Such a taxon, usually a species, is said to exhibit cosmopolitanism or cosmopolitism. The ext .... Species: * '' Ceriodaphnia dubia'' (Richard, 1894) * '' Ceriodaphnia quadrangula'' (O.F. Müller, 1785) * '' Ceriodaphnia reticulata'' (Jurine, 1820) References {{Taxonbar, from=Q6549092 Cladocera Branchiopoda genera ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Diaptomus
''Diaptomus'' is a genus of copepods with a single eye spot. It is superficially similar in size and appearance to ''Cyclops''. However it has characteristically very long first antennae that exceed the body length. In addition, the females carry the eggs in a single sac rather than the twin sacs seen in ''Cyclops''. It is a copepod of larger freshwater ponds, lakes and still waters. Species ''Diaptomus'' contains more than 60 species; many species formerly included in ''Diaptomus'' are now in separate genera such as ''Aglaodiaptomus'' and '' Notodiaptomus''. One species, the German endemic ''D. rostripes'', is included on the IUCN Red List as a Data Deficient species. *'' Diaptomus affinis'' Ulyanin, 1875 *'' Diaptomus africanus'' Daday, 1910 *'' Diaptomus alpestris'' (Vogt, 1845) *''Diaptomus angustaensis'' Turner, 1910 *'' Diaptomus armatus'' Herrick, 1882 *'' Diaptomus azureus'' Reid, 1985 *'' Diaptomus barabinensis'' Stepanova, 2008 *''Diaptomus bidens'' Brehm, 1924 *''Dia ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ceriodaphnia Dubia
''Ceriodaphnia dubia'' is a species of water flea in the class Branchiopoda, living in freshwater lakes, ponds, and marshes in most of the world. They are small, generally less than in length. Males are smaller than females. ''C. dubia'' moves using a powerful set of second antennae, and is used in toxicity testing of wastewater treatment plant effluent water in the United States. Climate change and particularly ultraviolet radiation B may seriously damage ''C. dubia'' populations, as they seems to be more sensitive than other cladocerans such as ''Daphnia pulex ''Daphnia pulex'' is the most common species of water flea. It has a cosmopolitan distribution: the species is found throughout the Americas, Europe, and Australia. It is a model species, and was the first crustacean to have its genome sequenced. ...'' or ''D. pulicaria''''.'' References Cladocera Crustaceans described in 1894 {{branchiopoda-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mesocyclops
''Mesocyclops'' is a genus of copepod crustaceans in the family Cyclopidae. Because the various species of ''Mesocyclops'' are known to prey on mosquito larvae, it is used as a nontoxic and inexpensive form of biological mosquito control. Biological control Individuals of ''Mesocyclops'' can be easily harvested, bred and released into freshwater containers where the ''Aedes aegypti'' mosquito larvae (the vector of Dengue fever) live. A big advantage of the ''Mesocyclops'' is that it is possible to teach schoolchildren how to recognize and collect them so that communities are able to perform sustainable mosquito control without much professional or governmental assistance. A field trial in Vietnam has shown that large-scale elimination of ''Aedes aegypti'' larvae is possible. Because ''Mesocyclops'' is a host for the parasitic round worm Guinea worm (''Dracunculus medinensis'', the causative agent of dracunculiasis), this method is potentially hazardous in the small number of co ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bosmina Longirostris
''Bosmina longirostris'' is a species of water flea found in the Great Lakes and Central Europe. It is found in the plankton Plankton are the diverse collection of organisms found in Hydrosphere, water (or atmosphere, air) that are unable to propel themselves against a Ocean current, current (or wind). The individual organisms constituting plankton are called plankt ... near the shoreline of lakes and ponds. Morphotypes ''Bosmina longirostris'' has multiple morphotypes. The most common morphotypes in freshwater are ''cornuta'', ''pellucida'', ''similis'', and ''typica''. The morphotypes refer to the size and curve of the antennules of the organism, as well as the size of the mucrones. References External links * Cladocera Freshwater crustaceans of North America Freshwater crustaceans of Europe Fauna of the Great Lakes region (North America) Crustaceans described in 1776 Taxa named by Otto Friedrich Müller {{Branchiopoda-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
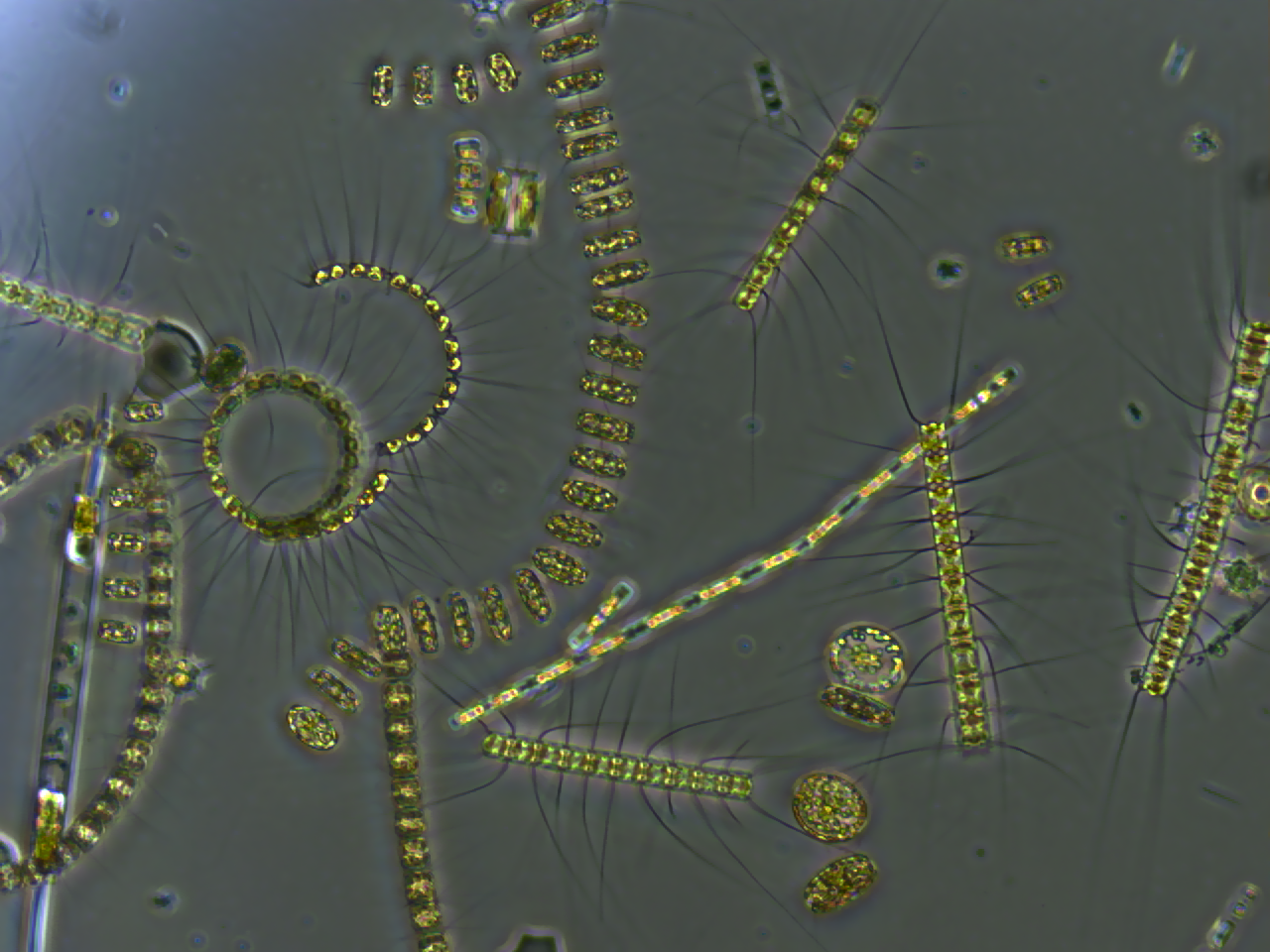
Phytoplankton
Phytoplankton () are the autotrophic (self-feeding) components of the plankton community and a key part of ocean and freshwater ecosystems. The name comes from the Greek words (), meaning 'plant', and (), meaning 'wanderer' or 'drifter'. Phytoplankton obtain their energy through photosynthesis, as do trees and other plants on land. This means phytoplankton must have light from the sun, so they live in the well-lit surface layers (euphotic zone) of oceans and lakes. In comparison with terrestrial plants, phytoplankton are distributed over a larger surface area, are exposed to less seasonal variation and have markedly faster turnover rates than trees (days versus decades). As a result, phytoplankton respond rapidly on a global scale to climate variations. Phytoplankton form the base of marine and freshwater food webs and are key players in the global carbon cycle. They account for about half of global photosynthetic activity and at least half of the oxygen production, despite ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Zooplankton
Zooplankton are the animal component of the planktonic community ("zoo" comes from the Greek word for ''animal''). Plankton are aquatic organisms that are unable to swim effectively against currents, and consequently drift or are carried along by currents in the ocean, or by currents in seas, lakes or rivers. Zooplankton can be contrasted with phytoplankton, which are the plant component of the plankton community ("phyto" comes from the Greek word for ''plant''). Zooplankton are heterotrophic (other-feeding), whereas phytoplankton are autotrophic (self-feeding). This means zooplankton cannot manufacture their own food but must eat other plants or animals instead — in particular they eat phytoplankton. Zooplankton are generally larger than phytoplankton, most are microscopic, but some (such as jellyfish) are macroscopic and can be seen with the naked eye. Many protozoans (single-celled protists that prey on other microscopic life) are zooplankton, including zooflagellates, fo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pelagic
The pelagic zone consists of the water column of the open ocean, and can be further divided into regions by depth (as illustrated on the right). The word ''pelagic'' is derived . The pelagic zone can be thought of as an imaginary cylinder or water column between the surface of the sea and the bottom. Conditions in the water column change with depth: pressure increases; temperature and light decrease; salinity, oxygen, micronutrients (such as iron, magnesium and calcium) all change. Marine life is affected by bathymetry (underwater topography) such as the seafloor, shoreline, or a submarine seamount, as well as by proximity to the boundary between the ocean and the atmosphere at the ocean surface, which brings light for photosynthesis, predation from above, and wind stirring up waves and setting currents in motion. The pelagic zone refers to the open, free waters away from the shore, where marine life can swim freely in any direction unhindered by topographical constraints. Th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |