|
Lake Balangida
Lake Balangida is a shallow alkaline lake in Hanang District of west Manyara Region in the Natron-Manyara-Balangida branch of the East African Rift The East African Rift (EAR) or East African Rift System (EARS) is an active continental rift zone in East Africa. The EAR began developing around the onset of the Miocene, 22–25 million years ago. In the past it was considered to be part of a ... in north-central Tanzania. The area surrounding Lake Balangida is used for agriculture and grazing. References Balangida Balangida Southern Eastern Rift {{Tanzania-geo-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Alkaline
In chemistry, an alkali (; from ar, القلوي, al-qaly, lit=ashes of the saltwort) is a base (chemistry), basic, ionic compound, ionic salt (chemistry), salt of an alkali metal or an alkaline earth metal. An alkali can also be defined as a base that dissolves in water. A solution of a soluble base has a pH greater than 7.0. The adjective alkaline, and less often, alkalescent, is commonly used in English language, English as a synonym for basic, especially for bases soluble in water. This broad use of the term is likely to have come about because alkalis were the first bases known to obey the acid-base reaction theories#Arrhenius theory, Arrhenius definition of a base, and they are still among the most common bases. Etymology The word "alkali" is derived from Arabic ''al qalīy'' (or ''alkali''), meaning ''the calcined ashes'' (see calcination), referring to the original source of alkaline substances. A water-extract of burned plant ashes, called potash and composed mostly ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Salt Lake
A salt lake or saline lake is a landlocked body of water that has a concentration of salts (typically sodium chloride) and other dissolved minerals significantly higher than most lakes (often defined as at least three grams of salt per litre). In some cases, salt lakes have a higher concentration of salt than sea water; such lakes can also be termed hypersaline lakes, and may also be pink lakes on account of their colour. An alkalic salt lake that has a high content of carbonate is sometimes termed a soda lake. One saline lake classification differentiates between: *subsaline: 0.5–3‰ (0.05-0.3%) *hyposaline: 3–20‰ (0.3-2%) *mesosaline: 20–50‰ (2-5%) *hypersaline: greater than 50‰ (5%) Properties Salt lakes form when the water flowing into the lake, containing salt or minerals, cannot leave because the lake is endorheic (terminal). The water then evaporates, leaving behind any dissolved salts and thus increasing its salinity, making a salt lake an excellent place ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Soda Lake
A soda lake or alkaline lake is a lake on the strongly alkaline side of neutrality, typically with a pH value between 9 and 12. They are characterized by high concentrations of carbonate salts, typically sodium carbonate (and related salt complexes), giving rise to their alkalinity. In addition, many soda lakes also contain high concentrations of sodium chloride and other dissolved salts, making them saline or hypersaline lakes as well. High pH and salinity often coincide, because of how soda lakes develop. The resulting hypersaline and highly alkalic soda lakes are considered some of the most extreme aquatic environments on Earth.Grant, W. D. (2006). ''Alkaline environments and biodiversity.'' in ''Extremophiles'', 2006, UNESCO / Eolss Publishers, Oxford, UK In spite of their apparent inhospitability, soda lakes are often highly productive ecosystems, compared to their (pH-neutral) freshwater counterparts. Gross primary production (photosynthesis) rates above (grams of carbon p ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hanang District
Hanang District is one of the six districts of the Manyara Region of Tanzania. It is bordered to the north by the Mbulu District and Babati Rural District, to the southeast by the Dodoma Region and to the southwest by the Singida Region. Mount Hanang is located within the boundaries of the district. According to the 2002 Tanzania National Census, the population of the Hanang District was 205,133. According to the 2012 Tanzania National Census, the population of Hanang District was 275,990. The District Commissioner of the Hanang District is Moses B. Sanga. Transport Paved trunk road T14 from Singida to Babati Babati, United States National Geospatial-Intelligence Agency is a town in Babati Urban District of Manyara Region of Tanzania. It is the administrative capital of Babati Urban District and Babati Rural District and also the administrative cap ... town passes through the district. Administrative subdivisions As of 2012, Hanang District was administratively divided i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Manyara Region
Manyara Region (''Mkoa wa Manyara'' in Swahili) is one of Tanzania's 31 administrative regions. The regional capital is the town of Babati. According to the 2012 national census, the region had a population of 1,425,131, which was lower than the pre-census projection of 1,497,555.Population Distribution by Administrative Units, United Republic of Tanzania, 2013 For 2002-2012, the region's 3.2 percent average annual population growth rate was tied for the third highest in the country. It was also the 22nd most densely populated region with 32 people per square kilometre. |
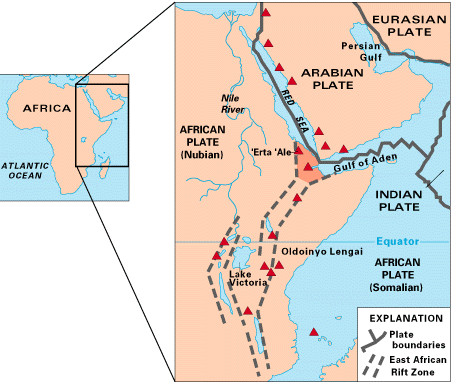
East African Rift
The East African Rift (EAR) or East African Rift System (EARS) is an active continental rift zone in East Africa. The EAR began developing around the onset of the Miocene, 22–25 million years ago. In the past it was considered to be part of a larger Great Rift Valley that extended north to Asia Minor. A narrow zone, the rift is a developing divergent tectonic plate boundary where the African Plate is in the process of splitting into two tectonic plates, called the Somali Plate and the Nubian Plate, at a rate of 6-7 mm per year. The rift system consists of three microplates, the Victoria Microplate to the north, and the Rovuma and Lwandle microplates to the south. The Victoria Microplate is rotating anti-clockwise with respect to the African plate. Its rotation is caused by the configuration of mechanically weaker and stronger lithospheric regions in the EARS. Extent A series of distinct rift basins, the East African Rift System extends over thousands of kilometers. The ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tanzania
Tanzania (; ), officially the United Republic of Tanzania ( sw, Jamhuri ya Muungano wa Tanzania), is a country in East Africa within the African Great Lakes region. It borders Uganda to the north; Kenya to the northeast; Comoro Islands and the Indian Ocean to the east; Mozambique and Malawi to the south; Zambia to the southwest; and Rwanda, Burundi, and the Democratic Republic of the Congo to the west. Mount Kilimanjaro, Africa's highest mountain, is in northeastern Tanzania. According to the United Nations, Tanzania has a population of million, making it the most populous country located entirely south of the equator. Many important hominid fossils have been found in Tanzania, such as 6-million-year-old Pliocene hominid fossils. The genus Australopithecus ranged across Africa between 4 and 2 million years ago, and the oldest remains of the genus ''Homo'' are found near Lake Olduvai. Following the rise of '' Homo erectus'' 1.8 million years ago, humanity spread ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Endorheic Basins Of Africa
An endorheic basin (; also spelled endoreic basin or endorreic basin) is a drainage basin that normally retains water and allows no outflow to other external bodies of water, such as rivers or oceans, but drainage converges instead into lakes or swamps, permanent or seasonal, that equilibrate through evaporation. They are also called closed or terminal basins, internal drainage systems, or simply basins. Endorheic regions contrast with exorheic regions. Endorheic water bodies include some of the largest lakes in the world, such as the Caspian Sea, the world's largest inland body of water. Basins with subsurface outflows which eventually lead to the ocean are generally not considered endorheic; they are cryptorheic. Endorheic basins constitute local base levels, defining a limit of erosion and deposition processes of nearby areas. Etymology The term was borrowed from French ''endor(rh)éisme'', coined from the combining form ''endo-'' (from grc, ἔνδον ''éndon'' 'withi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lakes Of Tanzania
Tanzania lies in the African Great Lakes region and boasts over of surface area that is covered by lakes. This makes up 6% of the national surface area and 88% of this area is covered by the three major lakes. Lake Victoria and Lake Tanganyika are part of the two great lakes in that nation, with Lake Victoria being the largest freshwater lake in Africa and Lake Tanganyika being the second-deepest lake in the world. List of lakes The table lists information about each lake:and can be sorted by size or alphabetically by name. For a more comprehensive list, see: :sw:Orodha ya maziwa ya Tanzania : Name: as listed by the World Heritage Committee : Surface Area: Surface area of lake (note: several lakes change their surface area continually based on weather) : Bordering Nations: Nations whose border goes through the lake : Description: Brief description of the lake : See also *Geography of Tanzania *Tanzania Ports Authority * Marine Services Company Limited References E ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |