|
Lagrange Reversion Theorem
In mathematics, the Lagrange reversion theorem gives series or formal power series expansions of certain implicitly defined functions; indeed, of compositions with such functions. Let ''v'' be a function of ''x'' and ''y'' in terms of another function ''f'' such that :v=x+yf(v) Then for any function ''g'', for small enough ''y'': :g(v)=g(x)+\sum_^\infty\frac\left(\frac\partial\right)^\left(f(x)^kg'(x)\right). If ''g'' is the identity, this becomes :v=x+\sum_^\infty\frac\left(\frac\partial\right)^\left(f(x)^k\right) In which case the equation can be derived using perturbation theory. In 1770, Joseph Louis Lagrange (1736–1813) published his power series solution of the implicit equation for ''v'' mentioned above. However, his solution used cumbersome series expansions of logarithms. In 1780, Pierre-Simon Laplace (1749–1827) published a simpler proof of the theorem, which was based on relations between partial derivatives with respect to the variable x and the parameter y. Cha ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mathematics
Mathematics is an area of knowledge that includes the topics of numbers, formulas and related structures, shapes and the spaces in which they are contained, and quantities and their changes. These topics are represented in modern mathematics with the major subdisciplines of number theory, algebra, geometry, and analysis, respectively. There is no general consensus among mathematicians about a common definition for their academic discipline. Most mathematical activity involves the discovery of properties of abstract objects and the use of pure reason to prove them. These objects consist of either abstractions from nature orin modern mathematicsentities that are stipulated to have certain properties, called axioms. A ''proof'' consists of a succession of applications of deductive rules to already established results. These results include previously proved theorems, axioms, andin case of abstraction from naturesome basic properties that are considered true starting poin ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Series (mathematics)
In mathematics, a series is, roughly speaking, a description of the operation of adding infinitely many quantities, one after the other, to a given starting quantity. The study of series is a major part of calculus and its generalization, mathematical analysis. Series are used in most areas of mathematics, even for studying finite structures (such as in combinatorics) through generating functions. In addition to their ubiquity in mathematics, infinite series are also widely used in other quantitative disciplines such as physics, computer science, statistics and finance. For a long time, the idea that such a potentially infinite summation could produce a finite result was considered paradoxical. This paradox was resolved using the concept of a limit during the 17th century. Zeno's paradox of Achilles and the tortoise illustrates this counterintuitive property of infinite sums: Achilles runs after a tortoise, but when he reaches the position of the tortoise at the beginn ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Formal Power Series
In mathematics, a formal series is an infinite sum that is considered independently from any notion of convergence, and can be manipulated with the usual algebraic operations on series (addition, subtraction, multiplication, division, partial sums, etc.). A formal power series is a special kind of formal series, whose terms are of the form a x^n where x^n is the nth power of a variable x (n is a non-negative integer), and a is called the coefficient. Hence, power series can be viewed as a generalization of polynomials, where the number of terms is allowed to be infinite, with no requirements of convergence. Thus, the series may no longer represent a function of its variable, merely a formal sequence of coefficients, in contrast to a power series, which defines a function by taking numerical values for the variable within a radius of convergence. In a formal power series, the x^n are used only as position-holders for the coefficients, so that the coefficient of x^5 is the fift ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Implicitly Defined Function
In mathematics, an implicit equation is a relation of the form R(x_1, \dots, x_n) = 0, where is a function of several variables (often a polynomial). For example, the implicit equation of the unit circle is x^2 + y^2 - 1 = 0. An implicit function is a function that is defined by an implicit equation, that relates one of the variables, considered as the value of the function, with the others considered as the arguments. For example, the equation x^2 + y^2 - 1 = 0 of the unit circle defines as an implicit function of if , and is restricted to nonnegative values. The implicit function theorem provides conditions under which some kinds of implicit equations define implicit functions, namely those that are obtained by equating to zero multivariable functions that are continuously differentiable. Examples Inverse functions A common type of implicit function is an inverse function. Not all functions have a unique inverse function. If is a function of that has a unique invers ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Perturbation Theory
In mathematics and applied mathematics, perturbation theory comprises methods for finding an approximate solution to a problem, by starting from the exact solution of a related, simpler problem. A critical feature of the technique is a middle step that breaks the problem into "solvable" and "perturbative" parts. In perturbation theory, the solution is expressed as a power series in a small parameter The first term is the known solution to the solvable problem. Successive terms in the series at higher powers of \varepsilon usually become smaller. An approximate 'perturbation solution' is obtained by truncating the series, usually by keeping only the first two terms, the solution to the known problem and the 'first order' perturbation correction. Perturbation theory is used in a wide range of fields, and reaches its most sophisticated and advanced forms in quantum field theory. Perturbation theory (quantum mechanics) describes the use of this method in quantum mechanics. Th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Joseph Louis Lagrange
Joseph-Louis Lagrange (born Giuseppe Luigi LagrangiaJoseph-Louis Lagrange, comte de l’Empire ''Encyclopædia Britannica'' or Giuseppe Ludovico De la Grange Tournier; 25 January 1736 – 10 April 1813), also reported as Giuseppe Luigi Lagrange or Lagrangia, was an Italian and , later naturalized |
Pierre-Simon Laplace
Pierre-Simon, marquis de Laplace (; ; 23 March 1749 – 5 March 1827) was a French scholar and polymath whose work was important to the development of engineering, mathematics, statistics, physics, astronomy, and philosophy. He summarized and extended the work of his predecessors in his five-volume Traité de mécanique céleste, ''Mécanique céleste'' (''Celestial Mechanics'') (1799–1825). This work translated the geometric study of classical mechanics to one based on calculus, opening up a broader range of problems. In statistics, the Bayesian probability, Bayesian interpretation of probability was developed mainly by Laplace. Laplace formulated Laplace's equation, and pioneered the Laplace transform which appears in many branches of mathematical physics, a field that he took a leading role in forming. The Laplace operator, Laplacian differential operator, widely used in mathematics, is also named after him. He restated and developed the nebular hypothesis of the origi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Charles Hermite
Charles Hermite () FRS FRSE MIAS (24 December 1822 – 14 January 1901) was a French mathematician who did research concerning number theory, quadratic forms, invariant theory, orthogonal polynomials, elliptic functions, and algebra. Hermite polynomials, Hermite interpolation, Hermite normal form, Hermitian operators, and cubic Hermite splines are named in his honor. One of his students was Henri Poincaré. He was the first to prove that '' e'', the base of natural logarithms, is a transcendental number. His methods were used later by Ferdinand von Lindemann to prove that π is transcendental. Life Hermite was born in Dieuze, Moselle, on 24 December 1822, with a deformity in his right foot that would impair his gait throughout his life. He was the sixth of seven children of Ferdinand Hermite and his wife, Madeleine née Lallemand. Ferdinand worked in the drapery business of Madeleine's family while also pursuing a career as an artist. The drapery business reloca ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
A Course Of Modern Analysis
''A Course of Modern Analysis: an introduction to the general theory of infinite processes and of analytic functions; with an account of the principal transcendental functions'' (colloquially known as Whittaker and Watson) is a landmark textbook on mathematical analysis written by Edmund T. Whittaker and George N. Watson, first published by Cambridge University Press in 1902. The first edition was Whittaker's alone, but later editions were co-authored with Watson. History Its first, second, third, and the fourth edition were published in 1902, 1915, 1920, and 1927, respectively. Since then, it has continuously been reprinted and is still in print today. A revised, expanded and digitally reset (typesetting), digitally reset fifth edition, edited by Victor H. Moll, was published in 2021. The book is notable for being the standard reference and textbook for a generation of Cambridge mathematicians including John Edensor Littlewood, Littlewood and Godfrey H. Hardy. Mary L. Cartwr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kepler's Equation
In orbital mechanics, Kepler's equation relates various geometric properties of the orbit of a body subject to a central force. It was first derived by Johannes Kepler in 1609 in Chapter 60 of his ''Astronomia nova'', and in book V of his ''Epitome of Copernican Astronomy'' (1621) Kepler proposed an iterative solution to the equation. The equation has played an important role in the history of both physics and mathematics, particularly classical celestial mechanics. Equation Kepler's equation is where M is the mean anomaly, E is the eccentric anomaly, and e is the eccentricity. The 'eccentric anomaly' E is useful to compute the position of a point moving in a Keplerian orbit. As for instance, if the body passes the periastron at coordinates x = a(1 - e), y = 0, at time t = t_0, then to find out the position of the body at any time, you first calculate the mean anomaly M from the time and the mean motion n by the formula M = n(t - t_0), then solve the Kepler equation abov ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
MathWorld
''MathWorld'' is an online mathematics reference work, created and largely written by Eric W. Weisstein. It is sponsored by and licensed to Wolfram Research, Inc. and was partially funded by the National Science Foundation's National Science Digital Library grant to the University of Illinois at Urbana–Champaign. History Eric W. Weisstein, the creator of the site, was a physics and astronomy student who got into the habit of writing notes on his mathematical readings. In 1995 he put his notes online and called it "Eric's Treasure Trove of Mathematics." It contained hundreds of pages/articles, covering a wide range of mathematical topics. The site became popular as an extensive single resource on mathematics on the web. Weisstein continuously improved the notes and accepted corrections and comments from online readers. In 1998, he made a contract with CRC Press and the contents of the site were published in print and CD-ROM form, titled "CRC Concise Encyclopedia of Mathem ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Equation Of Time
In mathematics, an equation is a formula that expresses the equality of two expressions, by connecting them with the equals sign . The word ''equation'' and its cognates in other languages may have subtly different meanings; for example, in French an ''équation'' is defined as containing one or more variables, while in English, any well-formed formula consisting of two expressions related with an equals sign is an equation. ''Solving'' an equation containing variables consists of determining which values of the variables make the equality true. The variables for which the equation has to be solved are also called unknowns, and the values of the unknowns that satisfy the equality are called solutions of the equation. There are two kinds of equations: identities and conditional equations. An identity is true for all values of the variables. A conditional equation is only true for particular values of the variables. An equation is written as two expressions, connected b ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |

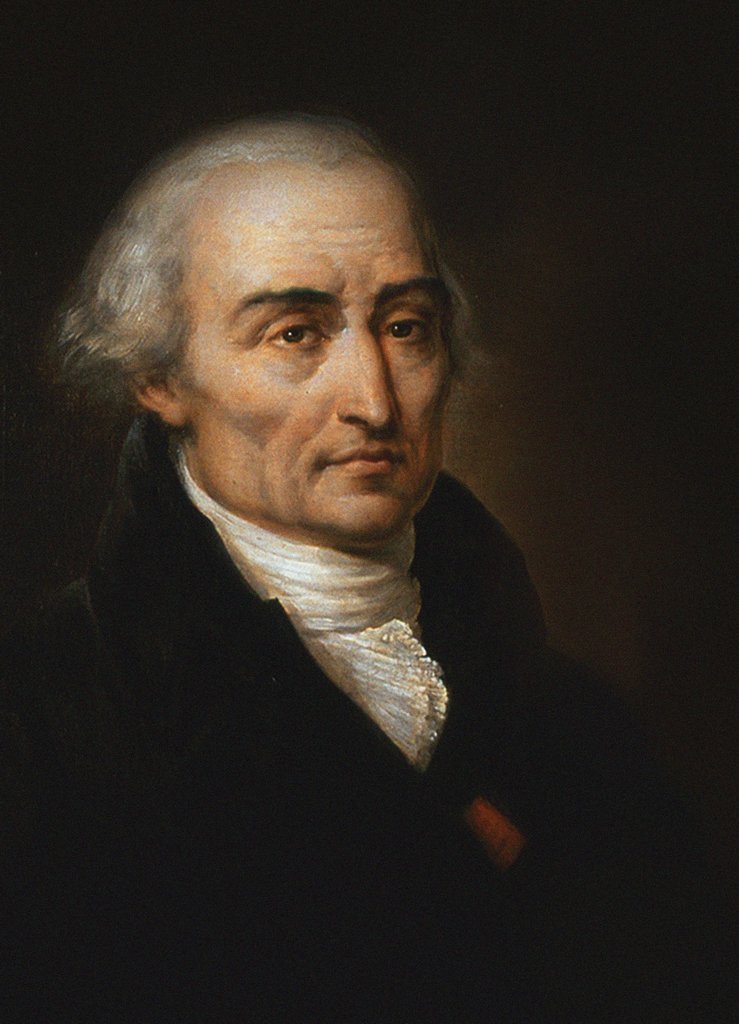
.jpg)


