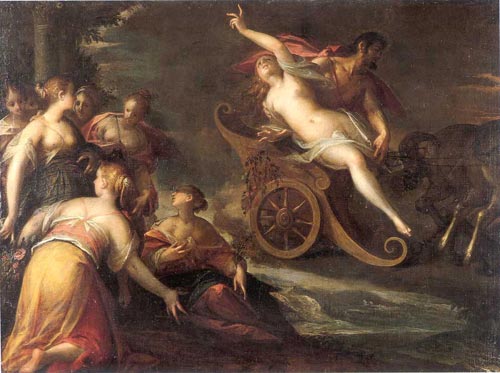|
Laetitia (goddess)
Laetitia, deriving from the root word ''laeta'', meaning "happy", "glad", "lucky", "successful", "prosperous", "luxurious", "lush", or "abounding", was a minor Roman mythology, Roman goddess of Gaiety (mood), gaiety. Her name was used to mean happiness with prosperity and abundance. She is usually shown with greenery to depict the abundance of seasonal decorations that many sites would include. Wreaths of flowers or leaves are commonly worn at festivals or holy rituals, similarly Laetitia would be shown wearing a garland to mean celebration. She was sometimes depicted on Roman coinage with an anchor, as a representation of stability, or, like Fortuna, a ship's rudder symbolizing her guiding one to good fortune or prosperity. Laetitia, engraved Felicitas Temporum, ''the happiness of the times'', has children playing across the four seasons on different coins, the ''limes'' denarus holds Laetitia at an altar sacrificing near lit candles while the back features a half-moon and seven st ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cuirass
A cuirass (; french: cuirasse, la, coriaceus) is a piece of armour that covers the torso, formed of one or more pieces of metal or other rigid material. The word probably originates from the original material, leather, from the French '' cuirace'' and Latin word '' coriacea''. The use of the term "cuirass" generally refers to both the chest plate (or breastplate) and the back piece together; whereas a breastplate only protects the front, a cuirass protects both the front and the back. Description In Hellenistic and Roman times, the musculature of the male torso was idealized in the form of the muscle cuirass or "heroic cuirass" (in French the ''cuirasse esthétique'') sometimes further embellished with symbolic representation in relief, familiar in the Augustus of Prima Porta and other heroic representations in official Roman sculpture. As parts of the actual military equipment of classical antiquity, cuirasses and corsets of bronze, iron, or some other rigid substance were us ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Septimius Severus
Lucius Septimius Severus (; 11 April 145 – 4 February 211) was Roman emperor from 193 to 211. He was born in Leptis Magna (present-day Al-Khums, Libya) in the Roman province of Africa (Roman province), Africa. As a young man he advanced through cursus honorum, the customary succession of offices under the reigns of Marcus Aurelius and Commodus. Severus seized power after the death of the emperor Pertinax in 193 during the Year of the Five Emperors. After deposing and killing the incumbent emperor Didius Julianus, Severus fought his rival claimants, the Roman generals Pescennius Niger and Clodius Albinus. Niger was defeated in 194 at the Battle of Issus (194), Battle of Issus in Roman Cilicia, Cilicia. Later that year Severus waged a short punitive campaign beyond the eastern frontier, annexing the Osroene, Kingdom of Osroene as a new province. Severus defeated Albinus three years later at the Battle of Lugdunum in Roman Gaul, Gaul. Following the consolidation of his rule over ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Providentia
In ancient Roman religion, Providentia is a divine personification of the ability to foresee and make provision. She was among the embodiments of virtues that were part of the Imperial cult of ancient Rome. Providentia thus figures in art, cult, and literature, but has little or no mythology as such. ''Providentia'' was an important moral and philosophical abstraction in Roman discourse. Cicero says it is one of the three main components of ''prudentia'', "the knowledge of things that are good or bad or neither," along with ''memoria'', "memory," and ''intellegentia'', "understanding." The Latin word is the origin of the Christian concept of divine providence. Imperial cult Upon the death of Augustus, the emperor Tiberius established an altar to Providentia Augusta in recognition of "the godhead manifested in his father's provisions for the Roman state." The cult title Augusta was attached also to such goddesses as Pax, Justitia, and Concordia during the Imperial era. Traditiona ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pax (goddess)
Pax (Latin for ''Peace''), more commonly known in English as Peace, was the Roman goddess of peace derived and adopted from the ancient Greek equivalent Eirene. Pax was seen as the daughter of the Roman king god Jupiter and the goddess Justice. Worship of Peace was organized and made popular during the rule of the emperor Augustus who used her imagery to help stabilise the empire after the years of turmoil and civil war of the late republic. Augustus commissioned an altar of peace in her honour on the Campus Martius called Ara Pacis, and the emperor Vespasian built a temple for her on called the Templum Pacis. Pax had a festival held for her on January 3. In art she is commonly depicted holding out olive branches as a peace offering, as well as a caduceus, cornucopia, corn and a sceptre. Pax is also often associated with spring. History of Worship Early depictions and Greek influence Early Roman worship and mythology was very much based on and adopted from the Greek pan ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Persephone
In ancient Greek mythology and religion, Persephone ( ; gr, Περσεφόνη, Persephónē), also called Kore or Cora ( ; gr, Κόρη, Kórē, the maiden), is the daughter of Zeus and Demeter. She became the queen of the underworld after her abduction by and marriage to her uncle Hades, the king of the underworld.Martin Nilsson (1967). ''Die Geschichte der Griechische Religion'' Vol I pp 462–463, 479–480 The myth of her abduction, her sojourn in the underworld, and her temporary return to the surface represents her functions as the embodiment of spring and the personification of vegetation, especially grain crops, which disappear into the earth when sown, sprout from the earth in spring, and are harvested when fully grown. In Classical Greek art, Persephone is invariably portrayed robed, often carrying a sheaf of grain. She may appear as a mystical divinity with a sceptre and a little box, but she was mostly represented in the process of being carried off by Hades. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Demeter
In ancient Greek religion and mythology, Demeter (; Attic: ''Dēmḗtēr'' ; Doric: ''Dāmā́tēr'') is the Olympian goddess of the harvest and agriculture, presiding over crops, grains, food, and the fertility of the earth. Although she is mostly known as a grain goddess, she also appeared as a goddess of health, birth, and marriage, and had connections to the Greek Underworld, Underworld. She is also called Deo (). In Greek tradition, Demeter is the second child of the Titans Rhea (mythology), Rhea and Cronus, and sister to Hestia, Hera, Hades, Poseidon, and Zeus. Like her other siblings but Zeus, she was swallowed by her father as an infant and rescued by Zeus. Through her brother Zeus, she became the mother of Persephone, a fertility goddess. One of the most notable Homeric Hymns, the ''Homeric Hymn to Demeter'', tells the story of Persephone's abduction by Hades and Demeter's search for her. When Hades, the King of the Underworld, wished to make Persephone his wife ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Proserpina
Proserpina ( , ) or Proserpine ( ) is an ancient Roman goddess whose iconography, functions and myths are virtually identical to those of Greek Persephone. Proserpina replaced or was combined with the ancient Roman fertility goddess Libera, whose principal cult was housed in the Aventine temple of the grain-goddess Ceres, along with the wine god Liber. Each of these three deities occupied their own ''cella'' at the temple. Their cults were served or supervised by a male public priesthood. Ceres was by far the senior of the three, one of the dii consentes, Rome's approximate equivalent to the Greek Twelve Olympians. She was identified with Greek Demeter and Liber was identified with Bacchus and Dionysus. Libera is sometimes described as a female version of Liber Pater, concerned with female fertility. Otherwise she is given no clear identity or mythology by Roman sources, and no Greek equivalent. Nothing is known of her native iconography: her name translates as a feminine form ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ceres (mythology)
In ancient Roman religion, Ceres ( , ) was a goddess of agriculture, grain crops, fertility and motherly relationships.Room, Adrian, ''Who's Who in Classical Mythology'', p. 89-90. NTC Publishing 1990. . She was originally the central deity in Rome's so-called plebeian or Aventine Triad, then was paired with her daughter Proserpina in what Romans described as "the Greek rites of Ceres". Her seven-day April festival of Cerealia included the popular ''Ludi Ceriales'' (Ceres' games). She was also honoured in the May ''lustratio'' of the fields at the Ambarvalia festival, at harvest-time, and during Roman marriages and funeral rites. She is usually depicted as a mature woman. Ceres is the only one of Rome's many agricultural deities to be listed among the Dii Consentes, Rome's equivalent to the Twelve Olympians of Greek mythology. The Romans saw her as the counterpart of the Greek goddess Demeter,''Larousse Desk Reference Encyclopedia'', The Book People, Haydock, 1995, p. 215. whos ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dominate
The Dominate, also known as the late Roman Empire, is the name sometimes given to the "despotic" later phase of imperial government in the ancient Roman Empire. It followed the earlier period known as the "Principate". Until the empire was reunited in 313, this phase is more often called the Tetrarchy.Menne, I., ''Power and Status in the Roman Empire, AD 193–284'' (2011) p. 21 It may begin with the commencement of the reign of Diocletian in AD 284, following the Third Century Crisis of AD 235–284, and to end in the west with the fall of the Western Roman Empire in AD 476, while in the east its end is disputed, as either occurring at the close of the reign of Justinian I (AD 565) or of Heraclius (AD 641). In form, the Dominate is considered to have been more authoritarian, less collegial and more bureaucratic than the Principate from which it emerged. Etymology The modern term ''dominate'' is derived from the Latin ''dominus'', which translates into English as ''lord'' or ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Publius Vellaeus
Publius may refer to: Roman name * Publius (praenomen) * Ancient Romans with the name: ** Publius Valerius Publicola (died 503 BC), Roman consul, co-founder of the Republic **Publius Clodius Pulcher (c. 93 BC – 52 BC), Republican politician **Publius Cornelius Scipio (consul 218 BC), Publius Cornelius Scipio (died 211 BC), Roman consul **Publius Quinctilius Varus (46 BC – 9 AD), Roman general and politician, who commanded the legions in Battle of the Teutoburg Forest **Publius Clodius Thrasea Paetus (died 66 AD), senator during Nero's reign **Publius Aelius Fortunatus, Roman painter in the 2nd century AD **Publius Servilius Casca Longus, better known as Servilius Casca (died 42 BC), Roman tribune and one of the assassins of Julius Caesar **Publius Aelius Hadrianus, the Emperor Hadrian (76–138 AD) **Publius Cornelius Lentulus Spinther, Roman patrician contemporary with Julius Caesar **Publius Cornelius Tacitus (56 AD – after 117), better known as Tacitus, a senator and a h ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Plutus
In ancient Greek religion and mythology, Plutus (; grc-gre, Πλοῦτος, Ploûtos, wealth) is the god and the personification of wealth, and the son of the goddess of agriculture Demeter and the mortal Iasion. Family Plutus is most commonly the son of Demeter and Iasion, with whom she lay in a thrice-ploughed field. He is alternatively the son of the fortune goddess Tyche.Aesop, ''Fables'413 Phaedrus 4.12">Phaedrus_(fabulist).html" ;"title="Phaedrus (fabulist)">Phaedrus 4.12 Two ancient depictions of Plutus, one of him as a little boy standing with a cornucopia before Demeter, and another inside the cornucopia being handed to Demeter by a goddess rising out of the earth, perhaps implying that he had been born in the Underworld, were interpreted by Karl Kerenyi to mean that Plutus was supposed to be the son of Hades and Persephone, the king and the queen of the Greek Underworld, Underworld, though no such version is attested in any primary source. In the arts In the phil ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Globus Cruciger
The ''globus cruciger'' ( for, , Latin, cross-bearing orb), also known as "the orb and cross", is an orb surmounted by a cross. It has been a Christian symbol of authority since the Middle Ages, used on coins, in iconography, and with a sceptre as royal regalia. The cross represents Christ's dominion over the orb of the world, literally held in the hand of an earthly ruler. In the iconography of Western art, when Christ himself holds the globe, he is called ''Salvator Mundi'' (Latin for 'Saviour of the World'). For instance, the 16th-century Infant Jesus of Prague statue holds a ''globus cruciger'' in this manner. History Holding the world in one's hand, or, more ominously, under one's foot, has been a symbol since antiquity. To citizens of the Roman Empire, the plain spherical globe held by the god Jupiter represented the world or the universe, as the dominion held by the Emperor. A 2nd-century coin from the reign of Emperor Hadrian shows the Roman goddess Salus with her ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |