|
Lackawanna Old Road
The Lackawanna Old Road was part of the original mainline of the Delaware, Lackawanna & Western Railroad (DL&W). Opened in 1856, it was for a half-century a part of the line connecting the states of New Jersey and Pennsylvania. In 1911, the DL&W cut off the route by opening the Lackawanna Cut-Off, which branched off from existing track at the new Port Morris Junction and Slateford Junction. The stretch of existing track between these junctions was relegated to secondary status and became known as the "Old Road". History The Old Road involves one railroad tycoon ( John I. Blair) and four railroads: the DL&W, the Jersey Central (CNJ), the Morris & Essex Railroad (M&E), and the Warren Railroad. In 1853, construction began on the Warren Railroad, which would connect the CNJ at Hampton, New Jersey, and the DL&W's mainline at the Delaware River, in anticipation of an eventual merger between the two older railroads. Expensive to build, the Warren required three large bridges ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lackawanna Railroad
The Delaware, Lackawanna and Western Railroad (also known as the DL&W or Lackawanna Railroad) was a U.S. Class 1 railroad that connected Buffalo, New York, and Hoboken, New Jersey (and by ferry with New York City), a distance of . Incorporated in Pennsylvania in 1853 primarily for the purpose of providing a connection between the anthracite coal fields of Pennsylvania's Coal Region and the large markets for coal in New York City. The railroad gradually expanded both East and West, eventually linking Buffalo with New York City. Like most coal-focused railroads in Northeastern Pennsylvania (e.g., Lehigh Valley Railroad, New York, Ontario and Western Railroad and the Lehigh & New England Railroad), the DL&W was profitable during the first half of the twentieth century, but its margins were gradually hurt by declining Pennsylvania coal traffic, especially following the 1959 Knox Mine Disaster and competition from trucks following the expansion of the Interstate Highway System in the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gauntlet Track
Gauntlet track or interlaced track (also gantlet track) is an arrangement in which railway tracks run parallel on a single track bed and are interlaced (i.e., overlapped) in such a way that only one pair of rails can be used at any time. Since this requires only slightly more width than a single track, all rails can be carried on the same crossties/sleepers. Trains run on the discrete pair of rails appropriate to their direction, track gauge or loading gauge. The term ''gauntlet'' refers to the expression ''running the gauntlet'', which means running between two confining rows of adversaries. Configurations Frog gauntlet (double-gauntlet-double) Gauntlet tracks can be used to provide horizontal clearance to a fixed obstruction adjacent to a track such as a cutting, bridge, or tunnel. Frog gauntlets are also commonly used when a rail line's capacity is increased by the provision of an additional track, but cost or other factors prevent the widening of the bridges. They are ty ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Conrail
Conrail , formally the Consolidated Rail Corporation, was the primary Class I railroad in the Northeastern United States between 1976 and 1999. The trade name Conrail is a portmanteau based on the company's legal name. It continues to do business as an asset management and network services provider in three Shared Assets Areas that were excluded from the division of its operations during its acquisition by CSX Corporation and the Norfolk Southern Railway. The federal government created Conrail to take over the potentially-profitable lines of multiple bankrupt carriers, including the Penn Central Transportation Company and Erie Lackawanna Railway. After railroad regulations were lifted by the 4R Act and the Staggers Act, Conrail began to turn a profit in the 1980s and was privatized in 1987. The two remaining Class I railroads in the East, CSX Transportation and the Norfolk Southern Railway (NS), agreed in 1997 to acquire the system and split it into two roughly-equal parts (a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Erie Lackawanna Railway
The Erie Lackawanna Railway , known as the Erie Lackawanna Railroad until 1968, was formed from the 1960 merger of the Erie Railroad and the Delaware, Lackawanna & Western Railroad. The official motto of the line was "The Friendly Service Route". Like many railroads in the northeast already financially vulnerable from the expanding U.S. Interstate Highway System, the line was severely weakened fiscally by the extent, duration and record flood levels due to Hurricane Agnes in 1972. It would never recover. Most of the corporation's holdings became part of Conrail in 1976, ending its sixteen years as an independent operating railroad company. History Formation and early success The Interstate Commerce Commission approved the merger on Sept. 13, 1960, and on Oct. 17 the Erie Railroad and Delaware, Lackawanna and Western Railroad merged to form the Erie Lackawanna Railroad. The EL struggled for most of the 16 years it existed. The two railroads that created it were steadily losing ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Road Debris
Road debris, a form of road hazard, is debris on or off a road. Road debris includes substances, materials, and objects that are foreign to the normal roadway environment. Debris may be produced by vehicular or non-vehicular sources, but in all cases it is considered litter, a form of solid waste., AAA Foundation for Traffic Safety press release o"The Safety Impact of Vehicle-Related Road Debris" Gerry Forbes and John Robinson, June 2004 Debris may tend to collect in areas where vehicles do not drive, such as on the edges (shoulder), around traffic islands, and junctions. Road spray or tire kickup is road debris (usually liquid water) that has been kicked up, pushed out, or sprayed out from a tire. In 2004, a AAA Foundation for Traffic Safety study revealed that vehicle-related road debris caused 25,000 accidents and nearly 100 deaths a year. Causes Road debris can be caused by various factors, including objects falling off vehicles or natural disasters and weather, specifical ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hackettstown, NJ
Hackettstown is a town in Warren County, New Jersey. As of the 2020 United States census, the town's population was 10,248. Hackettstown was incorporated as a town by an act of the New Jersey Legislature on March 9, 1853, from portions of Independence Township. Portions of territory were exchanged with Mansfield Township in 1857, 1860, 1872 and 1875.Snyder, John P''The Story of New Jersey's Civil Boundaries: 1606-1968'' Bureau of Geology and Topography; Trenton, New Jersey; 1969. p. 246. Accessed July 6, 2012. History Founding William Johnson (1817–1891) was a prime contributor to the incorporation of the town in 1853. He and his brother George (1815–1889) were successful merchants in the town beginning in 1839 when they began operating the W.L. & G.W Johnson dry good store. The two men were very active in community affairs. George was a member of First Presbyterian Church, a director of the Hackettstown National Bank, and a member of the Hackettstown Water Board. Bot ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Port Morris, New Jersey
Port Morris is a historic unincorporated community located within Roxbury Township, in Morris County, New Jersey, United States. State of . Accessed June 9, 2016. Despite its name, Port Morris is in the hills of the , on the shores of Lake Musconetcong. In the 1820s, George P. Macculloch envisioned a canal that would transport Pennsylvania coal to . The plan was to construct a canal from |
East Stroudsburg, Pennsylvania
East Stroudsburg is a borough in Monroe County, Pennsylvania, United States. It is located in the Poconos region of the state. Originally known as "Dansbury", East Stroudsburg was renamed for geographic reasons when the Delaware, Lackawanna, and Western Railroad opened a station in town. Despite its name being derivative of its bordering borough, Stroudsburg, it has almost twice the population. East Stroudsburg is the largest municipality in Monroe County and in the East Stroudsburg, Pennsylvania, Metropolitan Statistical Area as designated by the Office of Management and Budget based on data from the 2010 US Census. The population was 9,847 at the 2020 census. East Stroudsburg is located northeast of Allentown, north of Philadelphia, and west of New York City. Geography East Stroudsburg is located at (41.001442, -75.180111). According to the United States Census Bureau, the borough has a total area of , all land. When traveling west on Interstate 80, East Stroudsburg is ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Trenton, New Jersey
Trenton is the capital city of the U.S. state of New Jersey and the county seat of Mercer County. It was the capital of the United States from November 1 to December 24, 1784.New Jersey County Map New Jersey Department of State. Accessed July 10, 2017. The city's metropolitan area, including all of Mercer County, is grouped with the New York combined statistical area by the |
Belvidere, New Jersey
Belvidere is a town in Warren County, in the U.S. state of New Jersey. As of the 2010 U.S. census, the town's population was 2,681,DP-1 - Profile of General Population and Housing Characteristics: 2010 for Belvidere town, Warren County, New Jersey . Accessed May 31, 2013. [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bel-Del
Trenton Transit Center, The Belvidere-Delaware Railroad (Bel-Del, 1851–1871) was a railroad running along the eastern shore of the Delaware River from Trenton, New Jersey north via Phillipsburg, New Jersey to the small village of Manunka Chunk, New Jersey. It became an important feeder line for the Lehigh Valley Railroad's join to the Central Railroad of New Jersey,Robert H. Sayre, Sayre, Robert H., 1889, Chief engineer, Lehigh, Schuylkill, & Susquehanna Railroad Company, later renamed Lehigh Valley Railroad in 1853 re-printed from the collections at the University of California Libraries. Personal papers of this seminal individual starts with Engineering Survey of 1846, then various annual reports in early years of railways operations: Aug 1852, '1st' 31 Dec 1855, 30 Nov 1856; & Annual reports of 30 November: 1857, 1858, 1859, 1860, 1861, 29 Nov 1862 (Lengthy multi-part 7th annual rpt.), reports of 4 July 1859, and lastly, 30 Nov 1863. which was constructed into Phillipsburg, N ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
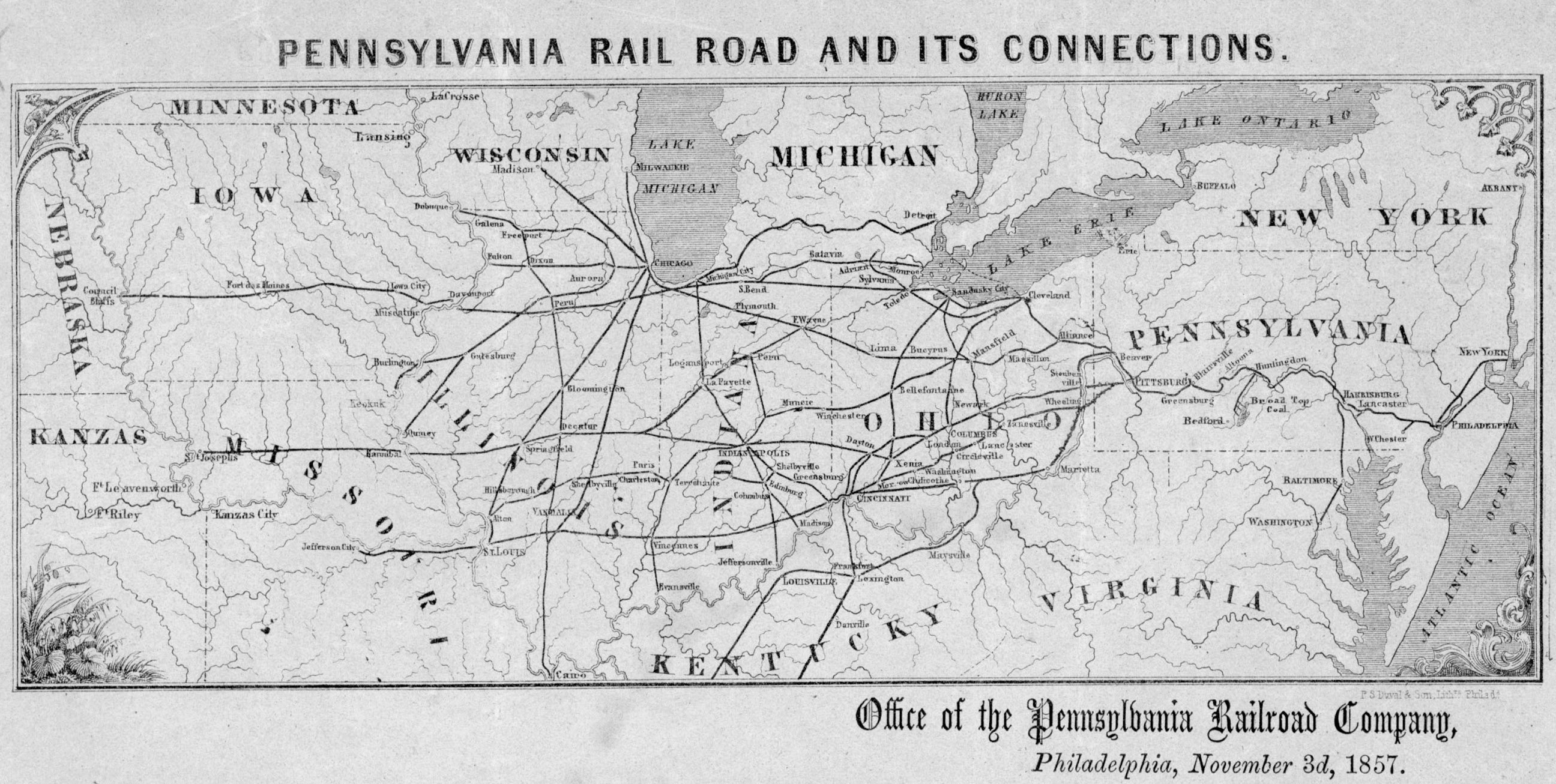
Pennsylvania Railroad
The Pennsylvania Railroad (reporting mark PRR), legal name The Pennsylvania Railroad Company also known as the "Pennsy", was an American Class I railroad that was established in 1846 and headquartered in Philadelphia, Pennsylvania. It was named for the commonwealth in which it was established. By 1882, Pennsylvania Railroad had become the largest railroad (by traffic and revenue), the largest transportation enterprise, and the largest corporation in the world. Its budget was second only to the U.S. government. Over the years, it acquired, merged with, or owned part of at least 800 other rail lines and companies. At the end of 1926, it operated of rail line;This mileage includes companies independently operated. PRR miles of all tracks, which includes first (or main), second, third, fourth, and sidings, totalled 28,040.49 at the end of 1926. in the 1920s, it carried nearly three times the traffic as other railroads of comparable length, such as the Union Pacific and Atchison, T ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |