|
La Victoria Del Viento
''La Victoria del Viento'' (Spanish language, Spanish: The Wind-Ridden Victory) is a monument in the city of Pachuca, Mexico, commemorating the Celebration of Mexican political anniversaries in 2010, bicentenary of the Mexican independence from Spain (1810–2010). Located on the Bicentennial Plaza, the monument was created by Mexican sculptor Bernardo Luis López Artasánchez and consists of 14 individual sculptures. The Victoria (mythology), personification of Victory refers to the Mexican legend about a young, open-hearted woman, who fell in love with the wind and who sacrificed herself to the earth in return of welfare of the land. The Victory raises her right hand with the torch of freedom, while leaving the north wind play with her hair. The eagle with a snake on a cactus at the Victory's feet, which also appears on the coat of arms of Mexico, refers to the legendary founding of Tenochtitlan. The figures surrounding the Victory are Miguel Hidalgo, José María Morelos, André ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pachuca
Pachuca (; ote, Nju̱nthe), formally known as Pachuca de Soto, is the capital and largest city of the Mexican state of Hidalgo. It is located in the south-central part of the state. Pachuca de Soto is also the name of the municipality of which the city serves as municipal seat. Pachuca is located about from Mexico City via Mexican Federal Highway 85. There is no consensus about the origin of the name ''Pachuca''. It has been traced to the word ''pachoa'' (strait; opening), ''Pachoacan'' (place of government; place of silver and gold), and ''patlachuican'' (place of factories; place of tears). The official name of Pachuca is Pachuca de Soto in honor of congressman Manuel Fernando Soto, who is given credit for the creation of Hidalgo state. Its nickname of "La bella airosa" (Beautiful Airy City) comes from the strong winds that blow into the valley through the canyons to the north of the city. In the indigenous Otomi language, Pachuca is known as . The area had been long inhabi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Andrés Quintana Roo
Andrés Eligio Quintana Roo (30 November 1787 – 15 April 1851) was a Mexican liberal politician, lawyer, and author. He was the husband of fellow independence activist Leona Vicario. Quintana Roo was one of the most influential men in the Mexican War of Independence and served as a member of the Congress of Chilpancingo where he presided over the National Constituent Congress, which drafted the Mexican Declaration of Independence in 1813. He served multiple terms in the Chamber of Deputies, serving as its president twice. Quintana Roo also served as a member of the Mexican Supreme Court. He edited and founded many newspapers including ''El Ilustrador Americano'' (The American Illustrator) ''El Semanario Patriótico Americano'' (The American Patriot Weekly), and ''El Federalista Mexicano'' (The Mexican Federalist). The Mexican state of Quintana Roo was named in his honor. Early life Quintana Roo was born to Don José Matías Quintana and Doña María Ana Roo de Quintana, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Buildings And Structures Completed In 2010
A building, or edifice, is an enclosed structure with a roof and walls standing more or less permanently in one place, such as a house or factory (although there's also portable buildings). Buildings come in a variety of sizes, shapes, and functions, and have been adapted throughout history for a wide number of factors, from building materials available, to weather conditions, land prices, ground conditions, specific uses, prestige, and aesthetic reasons. To better understand the term ''building'' compare the list of nonbuilding structures. Buildings serve several societal needs – primarily as shelter from weather, security, living space, privacy, to store belongings, and to comfortably live and work. A building as a shelter represents a physical division of the human habitat (a place of comfort and safety) and the ''outside'' (a place that at times may be harsh and harmful). Ever since the first cave paintings, buildings have also become objects or canvasses of much artistic ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Buildings And Structures In Hidalgo (state)
A building, or edifice, is an enclosed structure with a roof and walls standing more or less permanently in one place, such as a house or factory (although there's also portable buildings). Buildings come in a variety of sizes, shapes, and functions, and have been adapted throughout history for a wide number of factors, from building materials available, to weather conditions, land prices, ground conditions, specific uses, prestige, and aesthetic reasons. To better understand the term ''building'' compare the list of nonbuilding structures. Buildings serve several societal needs – primarily as shelter from weather, security, living space, privacy, to store belongings, and to comfortably live and work. A building as a shelter represents a physical division of the human habitat (a place of comfort and safety) and the ''outside'' (a place that at times may be harsh and harmful). Ever since the first cave paintings, buildings have also become objects or canvasses of much artis ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Angel Of Independence
The Angel of Independence, most commonly known by the shortened name ''El Ángel'' and officially known as ''Monumento a la Independencia'' ("Monument to Independence"), is a victory column on a roundabout on the major thoroughfare of Paseo de la Reforma in downtown Mexico City. ''El Ángel'' was built in 1910 during the presidency of Porfirio Díaz by architect Antonio Rivas Mercado, to commemorate the centennial of the beginning of Mexico's War of Independence. In later years it was made into a mausoleum for the most important heroes of that war. It is one of the most recognizable landmarks in Mexico City, and it has become a focal point for both celebration and protest. It resembles the July Column in Paris, the Berlin Victory Column in Berlin and Columbus Monument in New York City. Description The base of the column is quadrangular with each vertex featuring a bronze sculpture symbolizing law, war, justice and peace. Originally, nine steps led to the base, but due to the s ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hidalgo (state)
Hidalgo (), officially the Free and Sovereign State of Hidalgo ( es, Estado Libre y Soberano de Hidalgo) is one of the 31 states which, along with Mexico City, constitute the 32 federal entities of Mexico. It is divided into 84 municipalities and its capital city is Pachuca de Soto. Located in the eastern part of the country, Hidalgo is bordered by San Luis Potosí and Veracruz on the north, Puebla on the east, Tlaxcala and State of Mexico on the south and Querétaro on the west. In 1869, Benito Juárez created the State of Hidalgo and made Pachuca its capital city; Juárez would add the name ''"de Soto"'' in recognition of Manuel Fernando Soto, who is considered the most important driving force in creating the state. The state was named after Miguel Hidalgo y Costilla, the initiator of the Mexican War of Independence. The indigenous peoples of the state, such as the Otomi, retain much of their traditional culture. In addition to Mexicans of Spanish descent, there are also n ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pedestal
A pedestal (from French ''piédestal'', Italian ''piedistallo'' 'foot of a stall') or plinth is a support at the bottom of a statue, vase, column, or certain altars. Smaller pedestals, especially if round in shape, may be called socles. In civil engineering, it is also called ''basement''. The minimum height of the plinth is usually kept as 45 cm (for buildings). It transmits loads from superstructure to the substructure and acts as the retaining wall for the filling inside the plinth or raised floor. In sculpting, the terms base, plinth, and pedestal are defined according to their subtle differences. A base is defined as a large mass that supports the sculpture from below. A plinth is defined as a flat and planar support which separates the sculpture from the environment. A pedestal, on the other hand, is defined as a shaft-like form that raises the sculpture and separates it from the base. An elevated pedestal or plinth that bears a statue, and which is raised from th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ignacio López Rayón
Ignacio López Rayón (July 31, 1773 in Tlalpujahua, Intendancy of Valladolid (present-day Michoacán), New Spain – February 2, 1832 in Mexico City) was a general who led the insurgent forces of his country after Miguel Hidalgo's death, during the first years of the Mexican War of Independence. He subsequently established the first government, Zitacuaro Council, and first constitution of the proposed independent nation, called Constitutional Elements. First years López Rayón was born in Tlalpujahua, Intendancy of Valladolid, the first son of Andrés Mariano López-Rayón Piña (1742–1805) and María Josefa Rafaela López-Aguado y López-Bolaños (1754–1822). He went to the Colegio de San Nicolás in Valladolid (today's Morelia) and in Mexico City's Colegio de San Ildefonso where he became a lawyer in 1796. He lived in Mexico City but when his parent got sick he had to go back to Morelia to take control of the family business (agriculture and mining) and the post off ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
José María Morelos
José María Teclo Morelos Pérez y Pavón () (30 September 1765 – 22 December 1815) was a Mexican Catholic priest, statesman and military leader who led the Mexican War of Independence movement, assuming its leadership after the execution of Miguel Hidalgo y Costilla in 1811. Born in Valladolid, Michoacán, Morelos studied at Colegio de San Nicolás and was appointed priest of Carácuaro in 1799. He joined Miguel Hidalgo's Cry of Dolores, soon becoming an insurgency leader. Aided by local peoples, along with revolutionary leaders Mariano Matamoros and Ignacio López Rayón, Morelos occupied territories in southern and central New Spain, leading the Siege of Cuautla and capturing Acapulco, New Spain's main port in the Pacific Ocean. His campaigns galvanized regional insurgencies against Spanish rule, which made him the royalist army's main rival. :) In 1813, Morelos wrote ''Sentimientos de la Nación'', a document influenced by the Constitution of Cádiz where he outlined h ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mexico
Mexico (Spanish: México), officially the United Mexican States, is a country in the southern portion of North America. It is bordered to the north by the United States; to the south and west by the Pacific Ocean; to the southeast by Guatemala, Belize, and the Caribbean Sea; and to the east by the Gulf of Mexico. Mexico covers ,Mexico ''''. . making it the world's 13th-largest country by are ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Miguel Hidalgo
Don Miguel Gregorio Antonio Ignacio Hidalgo y Costilla y Gallaga Mandarte Villaseñor (8 May 1753 – 30 July 1811), more commonly known as Miguel Hidalgo y Costilla or Miguel Hidalgo (), was a Catholic priest, leader of the Mexican War of Independence and recognized as the Father of the Nation. A professor at the Colegio de San Nicolás Obispo in Valladolid, Hidalgo was influenced by Enlightenment ideas, which contributed to his ouster in 1792. He served in a church in Colima and then in Dolores. After his arrival, he was shocked by the rich soil he had found. He tried to help the poor by showing them how to grow olives and grapes, but in New Spain (modern Mexico) growing these crops was discouraged or prohibited by colonial authorities to prevent competition with imports from Spain. On 16 September 1810 he gave the Cry of Dolores, a speech calling upon the people to protect the interest of their King Ferdinand VII, held captive during the Peninsular War, by revoltin ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
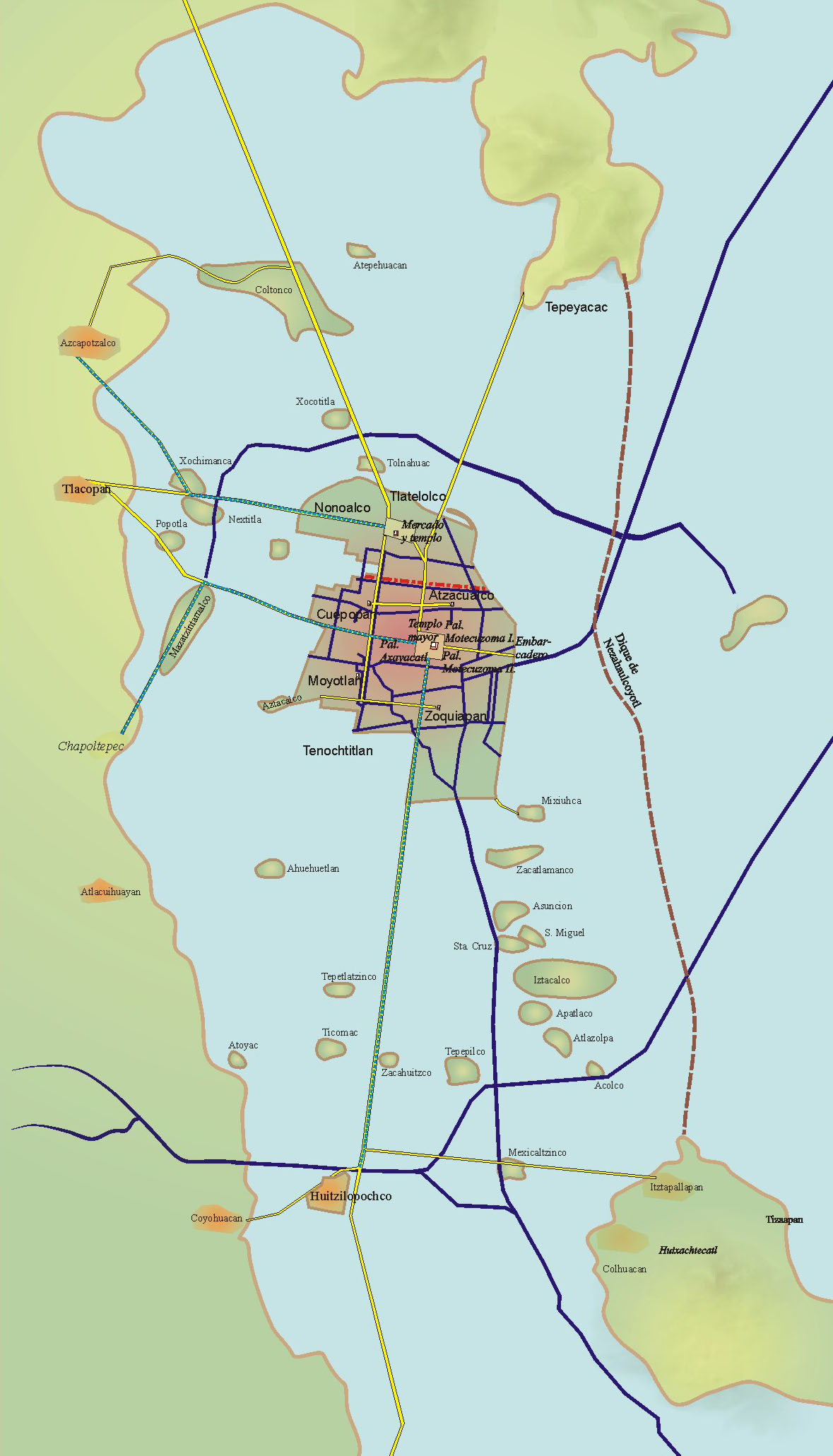
Tenochtitlan
, ; es, Tenochtitlan also known as Mexico-Tenochtitlan, ; es, México-Tenochtitlan was a large Mexican in what is now the historic center of Mexico City. The exact date of the founding of the city is unclear. The date 13 March 1325 was chosen in 1925 to celebrate the 600th anniversary of the city. The city was built on an island in what was then Lake Texcoco in the Valley of Mexico. The city was the capital of the expanding Aztec Empire in the 15th century until it was captured by the Spanish in 1521. At its peak, it was the largest city in the pre-Columbian Americas. It subsequently became a '' cabecera'' of the Viceroyalty of New Spain. Today, the ruins of are in the historic center of the Mexican capital. The World Heritage Site of contains what remains of the geography (water, boats, floating gardens) of the Mexica capital. was one of two Mexica (city-states or polities) on the island, the other being . The city is located in modern-day Mexico City. Etymolo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |





.jpg)