|
LAG3
Lymphocyte-activation gene 3, also known as LAG-3, is a protein which in humans is encoded by the ''LAG3'' gene. LAG3, which was discovered in 1990 and was designated CD223 (cluster of differentiation 223) after the Seventh Human Leucocyte Differentiation Antigen Workshop in 2000, is a cell surface molecule with diverse biologic effects on T cell function. It is an immune checkpoint receptor and as such is the target of various drug development programs by pharmaceutical companies seeking to develop new treatments for cancer and autoimmune disorders. In soluble form it is also being developed as a cancer drug in its own right. Gene The LAG3 gene contains 8 exons. The sequence data, exon/ intron organization, and chromosomal localization all indicate a close relationship of LAG3 to CD4. The gene for LAG-3 lies adjacent to the gene for CD4 on human chromosome 12 (12p13) and is approximately 20% identical to the CD4 gene. Protein The LAG3 protein, which belongs to immunoglob ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Frédéric Triebel
Frédéric Triebel (born 20 November 1954) is a French immunologist who is best known for his 1990 discovery of the LAG3 immune control mechanism. Triebel worked through the 1990s in a collaboration between Institut Gustave Roussy and Merck Serono to establish LAG-3's mechanism of action in T cells and dendritic cells. In 2001 he founded Immutep SA, a biotech company, to develop the therapeutic potential of LAG3. In 2014 this company was acquired by Prima BioMed, where Triebel remains Chief Scientific and Medical Officer. Early life and education He completed his Doctor of Medicine degree at Poitiers University in 1981 and then a four-year clinical hematology fellowship in Paris hospitals. In 1983, Frédéric Triebel received the Gold Medal of the Paris Medicine University. In parallel, Triebel gained a PhD in Immunology at the University of Paris VI in 1985. His PhD thesis was in the field of immunogenetics, focused on the mechanisms that activate human antigen-specific T-cel ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Immutep
Immutep Ltd (formerly Prima Biomed) is a biotechnology company working primarily in the field of cancer immunotherapy using the LAG3 immune control mechanism. The company was originally built on CVac, a therapeutic cancer vaccine. In late 2014 the privately held French immunotherapy company Immutep SA was purchased by Prima Biotech. Prima currently has three main products in its pipeline, all acquired with Immutep: Eftilagimod alpha, (lab name: IMP321) which is recombinant soluble LAG-3, used as an activator of antigen presenting cells. This product has completed a Phase IIa clinical study, where it doubled the expected response rate in HER2-negative metastatic breast cancer. IMP731, a depleting monoclonal antibody for autoimmune diseases, targeting LAG-3+ activated T cells. This antibody has been licensed to GlaxoSmithKline. IMP701, an antagonist monoclonal antibody to LAG3 for use in cancer. This product has been licensed to Novartis History Immutep (formerly Prima B ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
T Cell Activation
A T cell is a type of lymphocyte. T cells are one of the important white blood cells of the immune system and play a central role in the adaptive immune response. T cells can be distinguished from other lymphocytes by the presence of a T-cell receptor (TCR) on their cell surface. T cells are born from hematopoietic stem cells, found in the bone marrow. Developing T cells then migrate to the thymus gland to develop (or mature). T cells derive their name from the thymus. After migration to the thymus, the precursor cells mature into several distinct types of T cells. T cell differentiation also continues after they have left the thymus. Groups of specific, differentiated T cell subtypes have a variety of important functions in controlling and shaping the immune response. One of these functions is immune-mediated cell death, and it is carried out by two major subtypes: CD8+ "killer" and CD4+ "helper" T cells. (These are named for the presence of the cell surface proteins CD8 or C ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
T Cell
A T cell is a type of lymphocyte. T cells are one of the important white blood cells of the immune system and play a central role in the adaptive immune response. T cells can be distinguished from other lymphocytes by the presence of a T-cell receptor (TCR) on their cell surface. T cells are born from hematopoietic stem cells, found in the bone marrow. Developing T cells then migrate to the thymus gland to develop (or mature). T cells derive their name from the thymus. After migration to the thymus, the precursor cells mature into several distinct types of T cells. T cell differentiation also continues after they have left the thymus. Groups of specific, differentiated T cell subtypes have a variety of important functions in controlling and shaping the immune response. One of these functions is immune-mediated cell death, and it is carried out by two major subtypes: CD8+ "killer" and CD4+ "helper" T cells. (These are named for the presence of the cell surface proteins CD8 or ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Immune Checkpoint
Immune checkpoints are regulators of the immune system. These pathways are crucial for self-tolerance, which prevents the immune system from attacking cells indiscriminately. However, some cancers can protect themselves from attack by stimulating immune checkpoint targets. Inhibitory checkpoint molecules are targets for cancer immunotherapy due to their potential for use in multiple types of cancers. Currently approved checkpoint inhibitors block CTLA4 and PD-1 and PD-L1. For the related basic science discoveries, James P. Allison and Tasuku Honjo won the Tang Prize in Biopharmaceutical Science and the Nobel Prize in Physiology or Medicine in 2018. Stimulatory checkpoint molecules Four stimulatory checkpoint molecules are members of the tumor necrosis factor (TNF) receptor superfamily—CD27, CD40, OX40, GITR and CD137. Another two stimulatory checkpoint molecules belong to the B7-CD28 superfamily—CD28 itself and ICOS. * CD27: This molecule supports antigen-specific ex ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Institut Gustave Roussy
Gustave Roussy is the first leader cancer-research hospital in Europe and ranked among the top 3 best specialized hospitals in the world . It is a centre for high quality patient care, research and teaching. It is highly-known for the treatment of (among others): skin cancers like melanoma, breast cancer, and lung cancer. It provides access to care with many expert doctors who have historically revolutionized the treatment of cancer and contributed to the surge of new molecules in the treatment of cancers and tumors. It is located in the Parisian area. It is named after Gustave Roussy, a Swiss-French neuropathologist. In April 2019, three new interventional radiology rooms were inaugurated, making it the largest platform of this type in Europe, entirely dedicated to oncology. Interventional radiology is a so-called "minimally invasive" diagnostic and treatment technique, which uses images to guide access to deep-lying organs, without having to "open up" patients. Gustave Roussy ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
IMP321
Eftilagimod alpha (International Nonproprietary Name, INN; development code IMP321 or efti) is a large molecule, large-molecule cancer drug being developed by the clinical-stage biotechnology company Immutep. Efti is a soluble version of the immune checkpoint molecule LAG3, LAG-3. It is an APC Activator used to increase an immune response to tumors, and is administered by subcutaneous injection. Efti has three intended clinical settings: * as adjuvant to cancer vaccines (in a low, effective dose of ~250 µg) * as Therapy, first-line 'chemo-immunotherapy,' that is, combined with standard chemotherapy (e.g. paclitaxel) * in combination immunotherapy with PD-1 treatments (e.g. pembrolizumab) Eftilagimod alpha is in Phase II clinical testing. Currently, the main indications for the drug are metastatic breast cancer, Non-small-cell lung carcinoma, non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC), and Head and neck cancer, head and neck squamous cell carcinoma (HNSCC). Background Eftilagimod a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
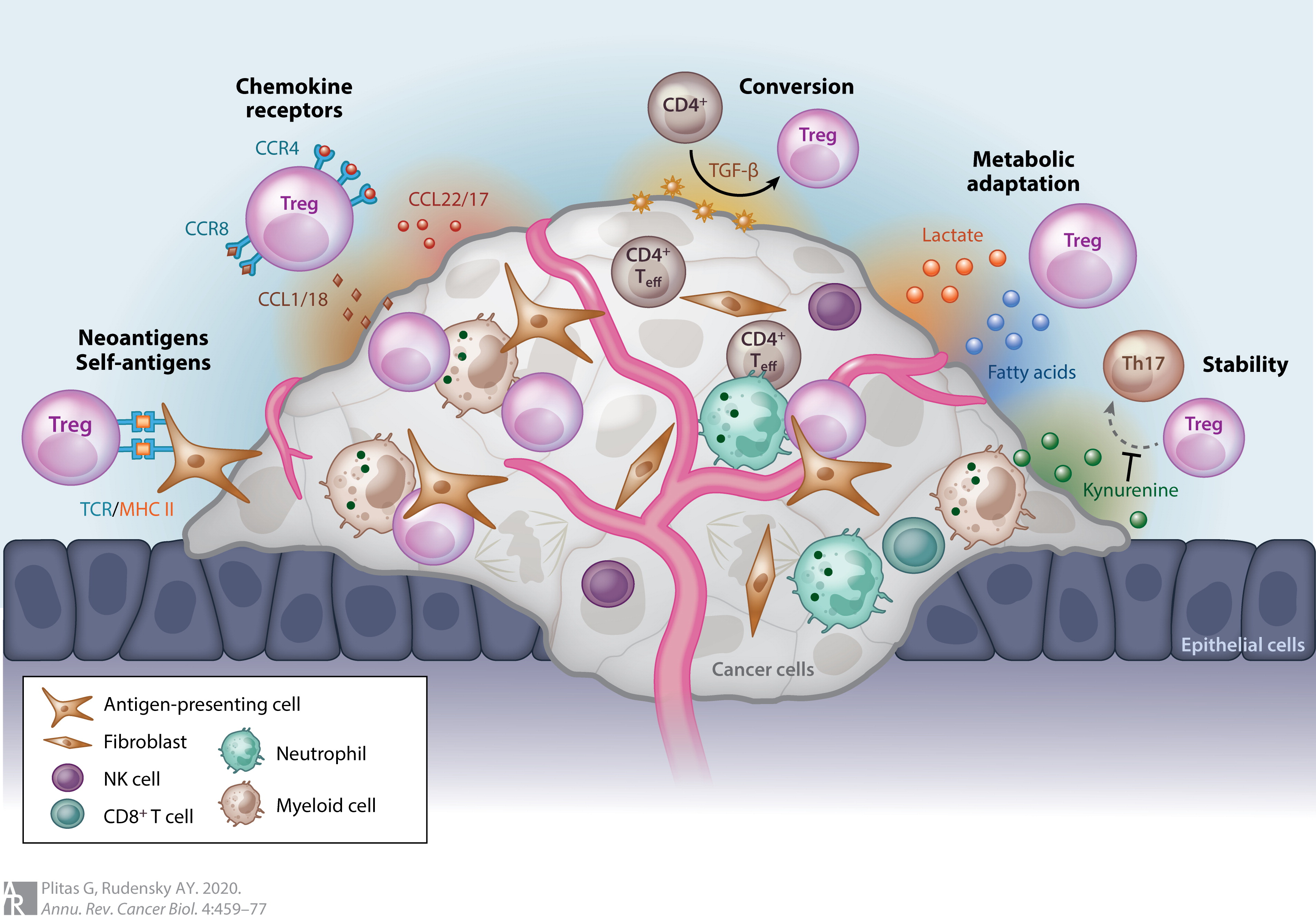
Regulatory T Cell
The regulatory T cells (Tregs or Treg cells), formerly known as suppressor T cells, are a subpopulation of T cells that modulate the immune system, maintain tolerance to self-antigens, and prevent autoimmune disease. Treg cells are immunosuppressive and generally suppress or downregulate induction and proliferation of effector T cells. Treg cells express the biomarkers CD4, FOXP3, and CD25 and are thought to be derived from the same lineage as naïve CD4+ cells. Because effector T cells also express CD4 and CD25, Treg cells are very difficult to effectively discern from effector CD4+, making them difficult to study. Research has found that the cytokine transforming growth factor beta (TGF-β) is essential for Treg cells to differentiate from naïve CD4+ cells and is important in maintaining Treg cell homeostasis. Mouse models have suggested that modulation of Treg cells can treat autoimmune disease and cancer and can facilitate orga ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Treg
The regulatory T cells (Tregs or Treg cells), formerly known as suppressor T cells, are a subpopulation of T cells that modulate the immune system, maintain immune tolerance, tolerance to self-antigens, and prevent autoimmune disease. Treg cells are immunosuppression, immunosuppressive and generally suppress or downregulation and upregulation, downregulate induction and proliferation of effector T cells. Treg cells express the biomarkers CD4, FOXP3, and CD25 and are thought to be derived from the same cell lineage, lineage as naïve T helper cell, CD4+ cells. Because effector T cells also express CD4 and CD25, Treg cells are very difficult to effectively discern from effector CD4+, making them difficult to study. Research has found that the cytokine Transforming growth factor beta, transforming growth factor beta (TGF-β) is essential for Treg cells to differentiate from naïve CD4+ cells and is important in maintaining Treg cell homeostasis. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
GSK2831781
GSK2831781 is a monoclonal antibody being developed by GlaxoSmithKline (GSK) for autoimmune diseases. The antibody targets the T cell activation marker LAG-3, which is mainly expressed in inflamed tissues. In GSK's March 2015 ''Product development pipeline'' document the antibody is listed under 'Immuno-inflammation' candidates. GSK2831781 entered a Phase I clinical trial in psoriasis early in 2015. History GSK2831781 originated from a chimeric monoclonal antibody to LAG-3 developed in 2008 by the French biotechnology company Immutep. That company had been built around drugs targeting LAG-3 and was associated with Frédéric Triebel, an immunologist generally regarded as a leading authority on LAG-3. In discovering the Immutep antibody, Triebel worked with two researchers from the University of Nantes, where there was an INSERM unit focused on transplantation immunology called ITUN (Institut de Transplantation Urologie Nephrologie). Triebel et al. codenamed their initial m ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Programmed Cell Death 1
Programmed cell death protein 1, also known as PD-1 and CD279 (cluster of differentiation 279), is a protein on the surface of T and B cells that has a role in regulating the immune system's response to the cells of the human body by down-regulating the immune system and promoting self-tolerance by suppressing T cell inflammatory activity. This prevents autoimmune diseases, but it can also prevent the immune system from killing cancer cells. PD-1 is an immune checkpoint and guards against autoimmunity through two mechanisms. First, it promotes apoptosis (programmed cell death) of antigen-specific T-cells in lymph nodes. Second, it reduces apoptosis in regulatory T cells (anti-inflammatory, suppressive T cells). PD-1 inhibitors, a new class of drugs that block PD-1, activate the immune system to attack tumors and are used to treat certain types of cancer. The PD-1 protein in humans is encoded by the ''PDCD1'' gene. PD-1 is a cell surface receptor that belongs to the immunoglobul ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
PD-1
Programmed cell death protein 1, also known as PD-1 and CD279 (cluster of differentiation 279), is a protein on the surface of T and B cells that has a role in regulating the immune system's response to the cells of the human body by down-regulating the immune system and promoting self-tolerance by suppressing T cell inflammatory activity. This prevents autoimmune diseases, but it can also prevent the immune system from killing cancer cells. PD-1 is an immune checkpoint and guards against autoimmunity through two mechanisms. First, it promotes apoptosis (programmed cell death) of antigen-specific T-cells in lymph nodes. Second, it reduces apoptosis in regulatory T cells (anti-inflammatory, suppressive T cells). PD-1 inhibitors, a new class of drugs that block PD-1, activate the immune system to attack tumors and are used to treat certain types of cancer. The PD-1 protein in humans is encoded by the ''PDCD1'' gene. PD-1 is a cell surface receptor that belongs to the immunoglobu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |