|
Lądek-Zdrój
Lądek-Zdrój ( cs, Landek; german: Bad Landeck), known in English as Landek, is a spa town situated in Kłodzko County, Lower Silesian Voivodeship, southwestern Poland. It is the seat of the administrative district ( gmina) called Gmina Lądek-Zdrój, close to the Czech border. History and culture It lies in the Sudetes approximately south-east of Kłodzko, and south of the regional capital Wrocław. As of 2019, the town has a population of 5,572. A picturesque spa town with rich historical architecture ranging from Gothic to Renaissance and Baroque, numerous sanatoriums, parks and gardens, including an arboretum, considered one of the oldest spa towns in Poland. Located within the historic Kłodzko Land, it was granted town rights in 1282 by Duke of Wrocław and future High Duke of Poland Henryk IV Probus of the Piast dynasty. Lądek-Zdrój became famous in Poland because of Stanisław Bareja's cult film ''Teddy Bear'' (''Miś''). In 1949–1950 Greeks and Macedonian ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gmina Lądek-Zdrój
Gmina Lądek-Zdrój is an urban-rural gmina (administrative district) in Kłodzko County, Lower Silesian Voivodeship, in south-western Poland. Its seat is the town of Lądek-Zdrój, which lies approximately south-east of Kłodzko, and south of the regional capital Wrocław. The gmina covers an area of and as of 2019 its total population is 8,233. Neighbouring gminas Gmina Lądek-Zdrój is bordered by the gminas of Gmina Bystrzyca Kłodzka, Bystrzyca Kłodzka, Gmina Kłodzko, Kłodzko, Gmina Stronie Śląskie, Stronie Śląskie and Gmina Złoty Stok, Złoty Stok. It also borders the Czech Republic. Villages Apart from the town of Lądek-Zdrój, the gmina contains the villages of Kąty Bystrzyckie, Konradów, Lower Silesian Voivodeship, Konradów, Lutynia, Kłodzko County, Lutynia, Orłowiec, Radochów, Skrzynka, Lower Silesian Voivodeship, Skrzynka, Stójków, Trzebieszowice and Wójtówka, Lower Silesian Voivodeship, Wójtówka. Twin towns – sister cities Gmina Lądek-Zdr� ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kłodzko County
__NOTOC__ Kłodzko County ( pl, powiat kłodzki) is a unit of territorial administration and local government (powiat) in Lower Silesian Voivodeship, south-western Poland. It came into being on 1 January 1999 as a result of the Polish local government reforms passed in 1998. The county covers an area of ; its territory almost exactly corresponds to the former Bohemian, later Prussian, County of Kladsko (german: Grafschaft Glatz). It is located in a panhandle called Kłodzko Panhandle. The county's administrative seat is the town of Kłodzko; the other towns are: Duszniki-Zdrój, Nowa Ruda, Polanica-Zdrój, Bystrzyca Kłodzka, Kudowa-Zdrój, Lądek-Zdrój, Międzylesie, Radków, Stronie Śląskie and Szczytna. (The suffix ''Zdrój'' appearing in several of these names means "spa".) As of 2019 the total population of the county was 158,600. Neighbouring counties Kłodzko County is bordered by Wałbrzych County to the north-west, Dzierżoniów County to the north and Ząbkowice � ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lower Silesian Voivodeship
Lower Silesian Voivodeship, or Lower Silesia Province, in southwestern Poland, is one of the 16 voivodeships (provinces) into which Poland is divided. The voivodeship was created on 1 January 1999 out of the former Wrocław, Legnica, Wałbrzych and Jelenia Góra Voivodeships, following the Polish local government reforms adopted in 1998. It covers an area of , and has a total population of 2,899,986. It is one of the richest provinces in Poland as it has valuable natural resources such as copper, silver, gold, brown coal and rock materials (inter alia granite, basalt, gabbro, diabase, amphibolite, porphyry, gneiss, serpentinite, sandstone, greywacke, limestone, dolomite, bentonite, kaolinite, clay, aggregate), which are exploited by the biggest enterprises. Its well developed and varied industries attract both domestic and foreign investors. Its capital and largest city is Wrocław, situated on the Oder River. It is one of Poland's largest and most dynamic cities with a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kłodzko
Kłodzko (; cz, Kladsko; german: Glatz; la, Glacio) is a historic town in south-western Poland, in the region of Lower Silesia. It is situated in the centre of the Kłodzko Valley, on the Eastern Neisse river. Kłodzko is the seat of Kłodzko County (and of the rural Gmina Kłodzko, although the town itself is a separate urban gmina), and is situated in Lower Silesian Voivodeship. With 26,845 inhabitants (2019), Kłodzko is the main commercial centre as well as an important transport and tourist node for the area. For its historical monuments it is sometimes referred to as "Little Prague" ( pl, Mała Praga, german: Klein-Prag). It was established as a settlement in the 10th century, and is one of the oldest towns in Poland, having been granted city rights in 1233. Culturally and traditionally a part of Bohemia, administratively it has been a part of Silesia since 1763. History Prehistory The area of present-day Kłodzko has been populated at least since the 1st century BC. Ther ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kłodzko Land
Kłodzko Land ( pl, Ziemia kłodzka; cs, Kladsko; german: Glatzer Land) is a historical region in southwestern Poland. The subject of Czech-Polish rivalry in the High Middle Ages, it became a Bohemian domain since the 12th century, although with periods of rule of the Polish Piast dynasty in the Late Middle Ages. It was raised to the County of Kladsko in 1459 and was conquered by Prussia in the First Silesian War of 1740–42 and incorporated into the Province of Silesia by 1818. After World War II it passed to the Republic of Poland according to the 1945 Potsdam Agreement. The region was not destroyed during World War II, thanks to which its rich historical architecture from various periods, from the Middle Ages to modern times, has been preserved. It is also known for its several spa towns. Geography Kłodzko Land, with an approximate area of , consists of the Kłodzko Valley, a basin surrounded by several ''Mittelgebirge'' ranges of the Central and Eastern Sudetes: the Owl Mo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
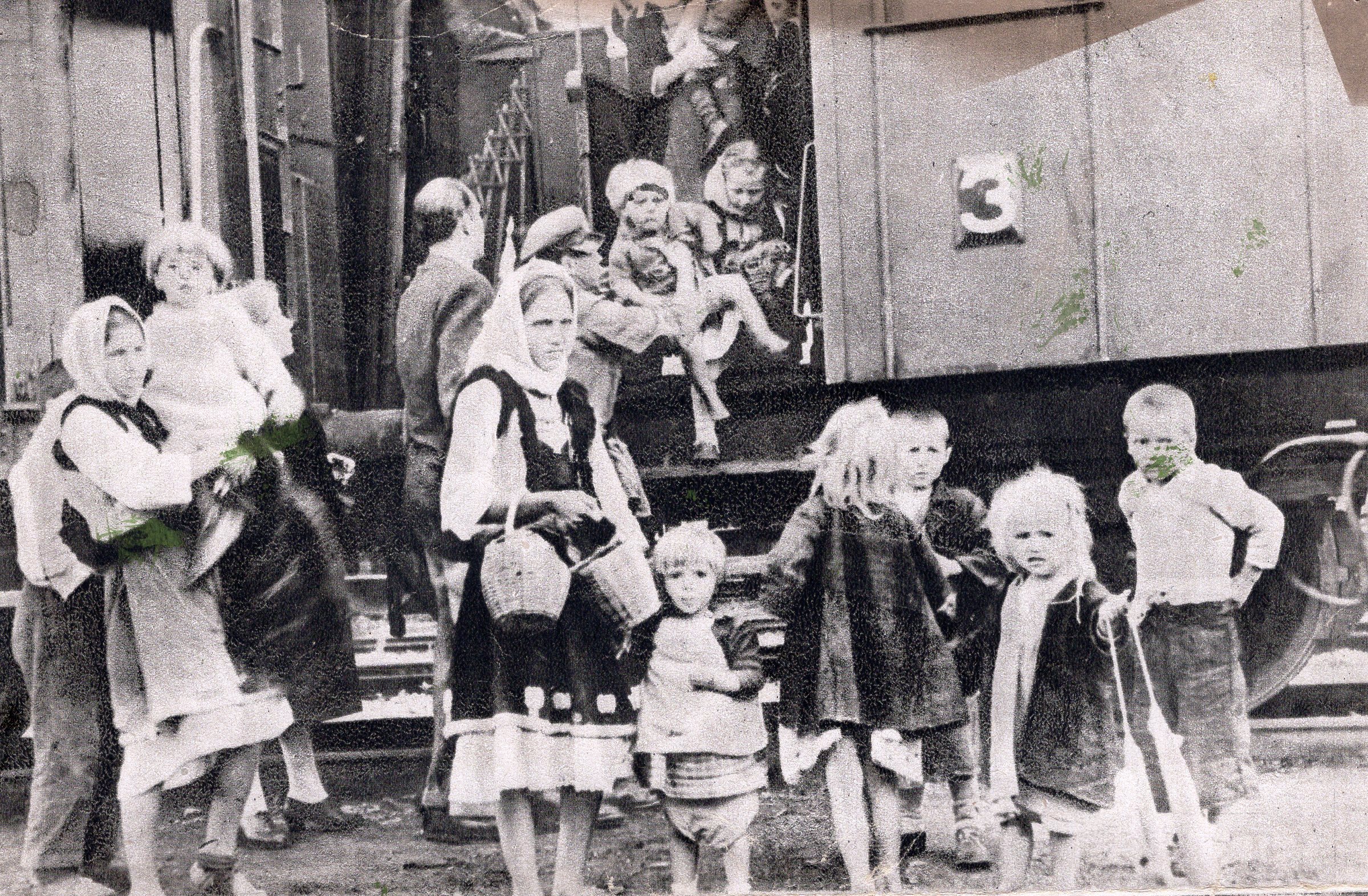
Refugees Of The Greek Civil War
During and after the Greek Civil War of 1946–1949, members and or supporters of the defeated Communist forces fled Greece as political refugees. The collapse of the Democratic Army of Greece (DSE) and subsequent evacuation of the Communist Party of Greece (KKE) to Tashkent in 1949 led thousands of people to leave the country. It has been estimated that by 1949, over 100,000 people had left Greece for Yugoslavia and the Eastern Bloc, particularly the USSR and Czechoslovakia. These included tens of thousands of child refugees who had been forcefully evacuated by the KKE. The war wrought widespread devastation right across Greece and particularly in the regions of Macedonia (Greece), Macedonia and Epirus (region), Epirus, causing many people to continue to leave the country even after it had ended. Greek Civil War After the invading Axis powers were defeated, fighting promptly broke out between the Democratic Army of Greece (DSE) and the Greek Government which had returned from exil ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Henryk IV Probus
Henryk IV Probus (Latin for ''the Righteous'') ( pl, Henryk IV Probus or ''Prawy''; german: Heinrich IV. der Gerechte) ( – 23 June 1290) was a member of the Silesian branch of the royal Polish Piast dynasty. He was Duke of Silesia at Wrocław from 1266, and from also 1288 High Duke of the Polish Seniorate Province of Kraków until his death in 1290. Life Henry IV was the only son of Duke Henry III the White of Silesia-Wrocław by his first wife Judith, daughter of Duke Konrad I of Masovia. Under the tutelage of Władysław of Salzburg and King Ottokar II of Bohemia A minor upon the early death of his father in 1266, Henry IV was placed under the guardianship of his paternal uncle, Archbishop Władysław of Salzburg. The Archbishop decided that the constant travels between Wrocław and Salzburg were inappropriate for a child, and, in 1267, sent Henry to Prague to be raised at the court of King Ottokar II of Bohemia. Ottokar after Władysław's death in 1270 also took ove ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Town Rights
Town privileges or borough rights were important features of European towns during most of the second millennium. The city law customary in Central Europe probably dates back to Italian models, which in turn were oriented towards the traditions of the self-administration of Roman cities. Judicially, a borough (or burgh) was distinguished from the countryside by means of a charter from the ruling monarch that defined its privileges and laws. Common privileges involved trade (marketplace, the storing of goods, etc.) and the establishment of guilds. Some of these privileges were permanent and could imply that the town obtained the right to be called a borough, hence the term "borough rights" (german: Stadtrecht; nl, stadsrechten). Some degree of self-government, representation by diet, and tax-relief could also be granted. Multiple tiers existed; for example, in Sweden, the basic royal charter establishing a borough enabled trade, but not foreign trade, which required a highe ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
List Of Polish Monarchs
Poland was ruled at various times either by dukes and princes (10th to 14th centuries) or by kings (11th to 18th centuries). During the latter period, a tradition of free election of monarchs made it a uniquely electable position in Europe (16th to 18th centuries). The first known Polish ruler is Duke Mieszko I, who adopted Christianity under the authority of Rome in the year 966. He was succeeded by his son, Bolesław I the Brave, who greatly expanded the boundaries of the Polish state and ruled as the first king in 1025. The following centuries gave rise to the mighty Piast dynasty, consisting of both kings such as Mieszko II Lambert, Przemysł II or Władysław I the Elbow-high and dukes like Bolesław III Wrymouth. The dynasty ceased to exist with the death of Casimir III the Great in 1370. In the same year, the Capetian House of Anjou became the ruling house with Louis I as king of both Poland and Hungary. His daughter, Jadwiga, later married Jogaila, the pagan Grand Duk ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Voivodeships Of Poland
A voivodeship (; pl, województwo ; plural: ) is the highest-level administrative division of Poland, corresponding to a province in many other countries. The term has been in use since the 14th century and is commonly translated into English as "province". The Polish local government reforms adopted in 1998, which went into effect on 1 January 1999, created sixteen new voivodeships. These replaced the 49 former voivodeships that had existed from 1 July 1975, and bear a greater resemblance (in territory, but not in name) to the voivodeships that existed between 1950 and 1975. Today's voivodeships are mostly named after historical and geographical regions, while those prior to 1998 generally took their names from the cities on which they were centered. The new units range in area from under (Opole Voivodeship) to over (Masovian Voivodeship), and in population from nearly one million (Opole Voivodeship) to over five million (Masovian Voivodeship). Administrative authority at th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Piast Dynasty
The House of Piast was the first historical ruling dynasty of Poland. The first documented Polish monarch was Duke Mieszko I (c. 930–992). The Piasts' royal rule in Poland ended in 1370 with the death of king Casimir III the Great. Branches of the Piast dynasty continued to rule in the Duchy of Masovia and in the Duchies of Silesia until the last male Silesian Piast died in 1675. The Piasts intermarried with several noble lines of Europe, and possessed numerous titles, some within the Holy Roman Empire. The Jagiellonian kings after John I Albert were also descended in the female line from Casimir III's daughter. Origin of the name The early dukes and kings of Poland are said to have regarded themselves as descendants of the semi-legendary Piast the Wheelwright (''Piast Kołodziej''), first mentioned in the '' Cronicae et gesta ducum sive principum Polonorum'' (Chronicles and deeds of the dukes or princes of the Poles), written c. 1113 by Gallus Anonymus. However, the ter ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Stanisław Bareja
Stanisław Sylwester Bareja (5 December 1929 – 14 June 1987) was a Polish filmmaker. Some of his films (mostly comedies) have reached cult status in Poland. His most famous film is ''Teddy Bear'' (''Miś''), filmed in 1980. His last work was ''Zmiennicy'', a TV series completed in 1986 and aired in 1987. On 21 September 2006 Bareja was posthumously awarded the Commander's Cross of the Order of Polonia Restituta by President Lech Kaczynski and in 2005, a street in Warsaw was named after Stanislaw Bareja. Works Director * ''Zmiennicy'' (1986) * ''Alternatywy 4'' (1983) * ''Teddy Bear'' (''Miś'', 1981) * ''What Will You Do When You Catch Me?'' (''Co mi zrobisz, jak mnie złapiesz?'', 1978) * '' Brunet Will Call'' (''Brunet wieczorową porą'', 1976) * '' Incredibly peaceful man'' (''Niespotykanie spokojny człowiek'', 1975) * ''A Jungle Book of Regulations'' (''Nie ma róży bez ognia'', 1974) * '' Man - Woman Wanted'' (''Poszukiwany poszukiwana'', 1972) * '' Adventure with a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |