|
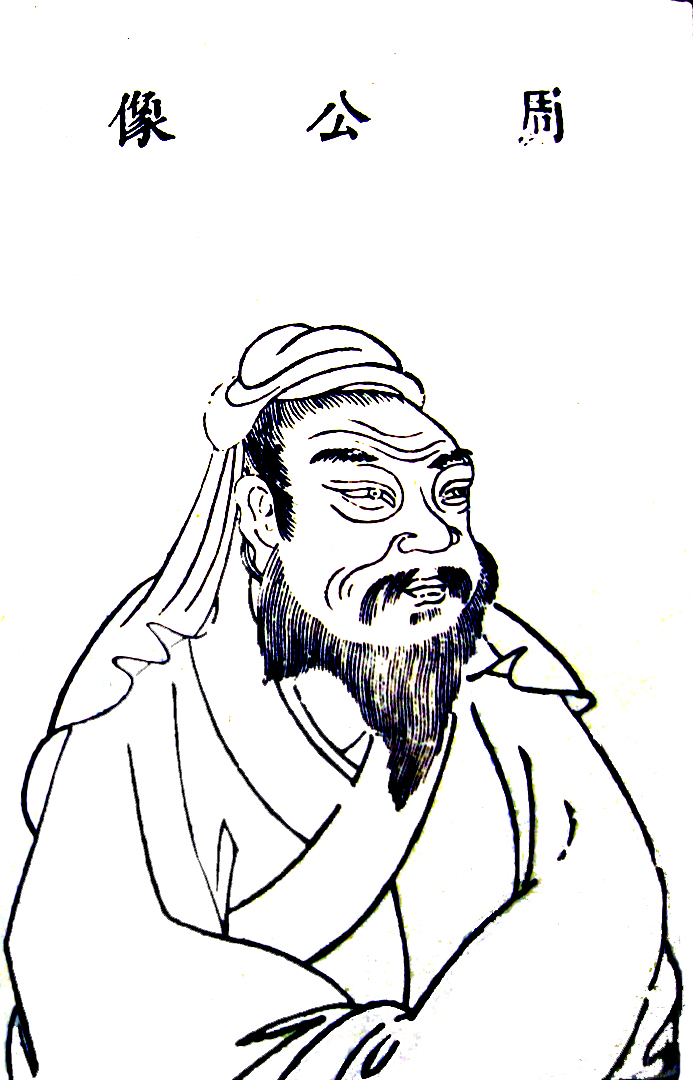
Lü Shang
Jiang Ziya ( century BC – century BC), also known by several other names, was a Chinese noble who helped kings Wen and Wu of Zhou overthrow the Shang in ancient China. Following their victory at Muye, he continued to serve as a Zhou minister. He remained loyal to the regent Duke of Zhou during the Rebellion of the Three Guards; following the Duke's punitive raids against the restive Eastern Barbarians or ''Dongyi'', Jiang was enfeoffed with their territory as the marchland of Qi. He established his seat at Yingqiu (in modern Linzi). Names The first marquis of Qi bore the given name Shang. The nobility of ancient China bore two surnames, an ancestral name and a clan name. His were Jiang (姜) and Lü (呂), respectively. He had two courtesy names, Shangfu (尚父; lit. "Esteemed Father") and Ziya (lit. "Master Ivory, Master Tusk"), which were used for respectful address by his peers. The names Jiang Shang and Jiang Ziya became the most common after the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Jiang Ziya (film)
''Jiang Ziya'' (, sometimes spelt as ''Jiang Zi Ya'') is a 2020 Chinese 3D computer-animated fantasy adventure film directed by Cheng Teng and Li Wei. Featuring the mythological and fictional version of the popular Chinese figure Jiang Ziya, the plot is loosely based on the novel ''Investiture of the Gods'' by Xu Zhonglin. It is a follow-up to 2019's ''Ne Zha'' and the second installment of the Fengshen Cinematic Universe. The film was initially scheduled for release in China on 25 January 2020, but following the COVID-19 pandemic all Chinese New Year releases were cancelled. The new release date was on 1 October 2020. The film's official English title in China is ''Legend of Deification'', and it is released as ''Jiang Ziya: Legend of Deification'' in the United Kingdom, Australia, New Zealand, and Singapore. Plot After a Fox spirit causes the downfall of the Shang dynasty, A war is waged across the three realms. Eventually, the Fox spirit is captured. Jiang Ziya, a mortal ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Rebellion Of The Three Guards
The Rebellion of the Three Guards (), or less commonly the Wu Geng Rebellion (), was a civil war, instigated by an alliance of discontent Zhou princes, Shang loyalists, vassal states and other non-Zhou peoples against the Western Zhou government under the Duke of Zhou's regency in late 11th century BC. After the fall of the Shang dynasty, King Wu of Zhou had appointed his younger brothers Guanshu, Caishu and Huoshu as the "Three Guards" of the East to secure the newly conquered Shang lands. After his death and his young son King Cheng's coronation, King Wu's brother Dan, the Duke of Zhou, declared himself regent and took over the court. This aroused the anger of the Three Guards who suspected Dan of usurpation and believed that they should serve as regents. Allied with many separatist eastern nobles, Shang loyalists under Prince Wu Geng, and several Dongyi () and Huaiyi () states, they rose in rebellion against the Duke of Zhou. The latter then launched a second "eastern campa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Courtesy Name
A courtesy name (), also known as a style name, is a name bestowed upon one at adulthood in addition to one's given name. This practice is a tradition in the East Asian cultural sphere, including China, Japan, Korea, and Vietnam.Ulrich TheobaldNames of Persons and Titles of Rulers/ref> A courtesy name is not to be confused with an art name, another frequently mentioned term for an alternative name in East Asia, which is closer to the concept of a pen name or a pseudonym. Usage A courtesy name is a name traditionally given to Chinese men at the age of 20 ''sui'', marking their coming of age. It was sometimes given to women, usually upon marriage. The practice is no longer common in modern Chinese society. According to the ''Book of Rites'', after a man reached adulthood, it was disrespectful for others of the same generation to address him by his given name. Thus, the given name was reserved for oneself and one's elders, whereas the courtesy name would be used by adults of t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lü (surname)
Lü () is the pinyin (Lǚ with the tone diacritic) and Wade–Giles romanisation of the Chinese surname written in simplified character and in traditional character. It is the 47th most common surname in China, shared by 5.6 million people, or 0.47% of the Chinese population as of 2002. It is especially common in Shandong and Henan provinces. The surname originated from the ancient State of Lü. Lü Shang ( fl. 11th century BC), the founder of the State of Qi, was the first person known to have the surname. It is 22nd on the ''Hundred Family Surnames'', contained in the verse 何呂施張 (He Lü Shi Zhang). Romanization Lü is the standard pinyin spelling of the Chinese character 吕/呂. However, when input of the umlaut is not possible, the surname is commonly romanized as Lu or Lv (v being the pinyin input shorthand for ü). On 31 October 2011, the National Standardization Committee of China issued ''The Chinese phonetic alphabet spelling rules for Chinese names'', whi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Jiang (surname 姜) , in Shanxi, China
{{disambig ...
Jiang may refer to: * ''Jiang'' (rank), rank held by general officers in the military of China *Jiang (surname), several Chinese surnames **Jiang Zemin (1926–2022), as general secretary of the Chinese Communist Party *Jiang River, an ancient river of China *Jiang County Jiang County or Jiangxian () is a county in the south of Shanxi Shanxi (; ; formerly romanised as Shansi) is a landlocked province of the People's Republic of China and is part of the North China region. The capital and largest city of the pr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chinese Clan Name
Chinese surnames are used by Han Chinese and Sinicized ethnic groups in China, Taiwan, Korea, Vietnam, and among overseas Chinese communities around the world such as Singapore and Malaysia. Written Chinese names begin with surnames, unlike the Western tradition in which surnames are written last. Around 2,000 Han Chinese surnames are currently in use, but the great proportion of Han Chinese people use only a relatively small number of these surnames; 19 surnames are used by around half of the Han Chinese people, while 100 surnames are used by around 87% of the population. A report in 2019 gives the most common Chinese surnames as Wang and Li, each shared by over 100 million people in China. The remaining top ten most common Chinese surnames are Zhang, Liu, Chen, Yang, Huang, Zhao, Wu and Zhou. Two distinct types of Chinese surnames existed in ancient China, namely ''xing'' () ancestral clan names and ''shi'' () branch lineage names. Later, the two terms began to be used i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ancestral Name
In some cultures, a surname, family name, or last name is the portion of one's personal name that indicates one's family, tribe or community. Practices vary by culture. The family name may be placed at either the start of a person's full name, as the forename, or at the end; the number of surnames given to an individual also varies. As the surname indicates genetic inheritance, all members of a family unit may have identical surnames or there may be variations; for example, a woman might marry and have a child, but later remarry and have another child by a different father, and as such both children could have different surnames. It is common to see two or more words in a surname, such as in compound surnames. Compound surnames can be composed of separate names, such as in traditional Spanish culture, they can be hyphenated together, or may contain prefixes. Using names has been documented in even the oldest historical records. Examples of surnames are documented in the 11th ce ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Surname
In some cultures, a surname, family name, or last name is the portion of one's personal name that indicates one's family, tribe or community. Practices vary by culture. The family name may be placed at either the start of a person's full name, as the forename, or at the end; the number of surnames given to an individual also varies. As the surname indicates genetic inheritance, all members of a family unit may have identical surnames or there may be variations; for example, a woman might marry and have a child, but later remarry and have another child by a different father, and as such both children could have different surnames. It is common to see two or more words in a surname, such as in compound surnames. Compound surnames can be composed of separate names, such as in traditional Spanish culture, they can be hyphenated together, or may contain prefixes. Using names has been documented in even the oldest historical records. Examples of surnames are documented in the 11th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chinese Personal Names
Chinese names or Chinese personal names are names used by individuals from Greater China and other parts of the Chinese-speaking world throughout East and Southeast Asia (ESEA). In addition, many names used in Japan, Korea and Vietnam are often ancient adaptations of Chinese characters (from Kanji, Hancha, and Chữ Hán respectively) in respect to the influences they have garnered geographically or have historical roots in Chinese, due to China's historic cultural influence in ESEA. Modern Chinese names consist of a monosymbolic (single-symbol) surname (''xìngshì''; ), which comes first, followed by a given name (''míng''; ), which is almost always disyllabic, consisting of two characters. Prior to the 21st century, most educated Chinese men also used a "courtesy name" or "style name" (''zì''; ) by which they were known among those outside their family and closest friends. Respected artists or poets will sometimes also use a professional "art name" (''hào''; ) among their ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Linzi District
Linzi District () is a district of the prefecture-level city of Zibo, in central Shandong province, China. Located near the Shengli Oil Field, Linzi's economy is driven by petro-chemical refinery. Wheat, corn and cotton are cultivated in the rural areas surrounding the urban center. The ruins of Ancient Linzi located in the northwest of the district, was the site of the ancient State of Qi's capital. Linzi is one of the most highly developed industrial districts in north China with the highest GDP in Shandong Province. Administrative divisions As 2012, this District is divided to 5 subdistricts, 7 towns and 1 township. ;Subdistricts ;Towns ;Townships * Bianhe Township () Climate People from Linzi #Zuo Si, poet of the Western Jin #Zuo Fen, poet of the Western Jin Western may refer to: Places *Western, Nebraska, a village in the US *Western, New York, a town in the US *Western Creek, Tasmania, a locality in Australia *Western Junction, Tasmania, a locality in Aust ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Yingqiu
Linzi () was the capital of the ancient Chinese state of Qi during the Zhou dynasty. The ruins of the city lie in modern-day Linzi District, Shandong, China. The city was one of the largest and richest in China during the Spring and Autumn Period. Upon occupying Linzi in 221 BC, King Ying Zheng of Qin completed his conquest of the Chinese rival states and declared himself the first emperor of China shortly afterwards. The ruins of the ancient city were excavated in 1926 by Japanese archaeologists and in 1964 by Chinese archaeologists. Layout Linzi covered an area of around with the city built between two parallel rivers that ran north–south, the Zi River to its east and the old course of the Xi River to its west. The city was surrounded by a perimeter wall of rammed earth. The city consisted of an outer city and an inner city. The outer city wall reached a maximum of in base width, averaging between in width. The inner city wall reached a maximum of in base width. The ci ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Qi (state)
Qi, or Ch'i in Wade–Giles romanization, was a state of the Zhou dynasty-era in ancient China, variously reckoned as a march, duchy, and independent kingdom. Its capital was Linzi, located in present-day Shandong. Qi was founded shortly after the Zhou overthrow of Shang in the 11th centuryBC. Its first marquis was Jiang Ziya, minister of King Wen and a legendary figure in Chinese culture. His family ruled Qi for several centuries before it was replaced by the Tian family in 386BC. In 221BC, Qi was the final major state annexed by Qin during its unification of China. History Foundation During the Zhou conquest of Shang, Jiang Ziya, a native of Ju County served as the chief minister to King Wu. After King Wu's death, Ziya remained loyal to the Duke of Zhou during the Three Guards' failed rebellion against his regency. The Shang prince Wu Geng had joined the revolt along with the Dongyi states of Yan, Xu, and Pugu. These were suppressed by 1039 BC and Jiang w ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |