|
Léanord
Léanord (''Laboratoire d'Electronique et d'Automatisme du Nord)'' was a French computer brand, founded in 1960 at Haubourdin, near Lille. It was a subsidiary of Creusot-Loire and started to develop computers in the late 1970s. The first machines, called Picolog 8, Picolog 80 and Picodidac 80 were based on Intel 8008, 8080 and 8085 microprocessors and designed for automation and machine code learning. Léanord's first microcomputer was the Silex, released in 1978. Based on a licensed Apple II motherboard with a MOS Technology 6502, MOS 6502 running at 1Mhz and 32Kb RAM, the machine was expensive for the time (costing 29,000 French franc, Francs) and came with ''SILBasic'' (a BASIC interpreter), ''SILPascal'' (a Pascal (programming language), Pascal interpreter) and ''SILDOS'' (a disk operating system). It had an 8-inch floppy disc drive and came in a 54x35x59 cm box, that also included the keyboard and monitor. In 1979 Léanord released the Sil'z, similar in appearance to ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Computing For All
The Computing for All plan (''Plan Informatique pour Tous'' – ''IPT'') was a French government plan to introduce computers to the country's 11 million pupils. A second goal was to support national industry. It followed several introductory computer science programs in schools since 1971. The IPT plan was presented to the press on January 25, 1985 by Laurent Fabius, Prime Minister at the time. It aimed to set up, from the start of that school year, more than 120,000 machines in 50,000 schools and to train 110,000 teachers. Its estimated cost was 1.8 billion francs, including 1.5 billion for equipment. The plan was abandoned in 1989. Description The selection of industry partners was entrusted to Gilbert Trigano, co-founder of Club Méditerranée, connected with French companies such as Exelvision, Léanord, SMT Goupil, Thomson, Bull, LogAbax, etc. This choice was political because its initiator, Jean-Jacques Servan-Schreiber, had indicated his preference for Macintosh, which ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Haubourdin
Haubourdin () is a commune in the Nord department in northern France. It is part of the Métropole Européenne de Lille. Population Heraldry See also *Communes of the Nord department The following is a list of the 647 communes of the Nord department of the French Republic. The communes cooperate in the following intercommunalities (as of 2025): References Communes of Nord (French department) French Flanders {{LilleArrondissement-geo-stub ...[...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Zilog Z80
The Zilog Z80 is an 8-bit computing, 8-bit microprocessor designed by Zilog that played an important role in the evolution of early personal computing. Launched in 1976, it was designed to be Backward compatibility, software-compatible with the Intel 8080, offering a compelling alternative due to its better Integrated circuit, integration and increased performance. Along with the 8080's seven Processor register, registers and flags register, the Z80 introduced an alternate register set, two 16-bit index registers, and additional instructions, including bit manipulation and block copy/search. Originally intended for use in embedded systems like the 8080, the Z80's combination of compatibility, affordability, and superior performance led to widespread adoption in video game systems and home computers throughout the late 1970s and early 1980s, helping to fuel the personal computing revolution. The Z80 was used in iconic products such as the Osborne 1, TRS-80, Radio Shack TRS-80, Col ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Backplane
A backplane or backplane system is a group of electrical connectors in parallel with each other, so that each pin of each connector is linked to the same relative pin of all the other connectors, forming a computer bus. It is used to connect several printed circuit boards together to make up a complete computer system. Backplanes commonly use a printed circuit board, but wire-wrapped backplanes have also been used in minicomputers and high-reliability applications. A backplane is generally differentiated from a motherboard by the lack of on-board processing and storage elements. A backplane uses plug-in cards for storage and processing. Usage Early microcomputer systems like the Altair 8800 used a backplane for the processor and expansion cards. Backplanes are normally used in preference to cables because of their greater reliability. In a cabled system, the cables need to be flexed every time that a card is added or removed from the system; this flexing eventually cause ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Industry Standard Architecture
Industry Standard Architecture (ISA) is the 16-bit internal bus (computing), bus of IBM PC/AT and similar computers based on the Intel 80286 and its immediate successors during the 1980s. The bus was (largely) backward compatible with the 8-bit bus of the 8088-based IBM PC, including the IBM PC/XT as well as IBM PC compatibles. Originally referred to as the PC bus (8-bit) or AT bus (16-bit), it was also termed ''I/O Channel'' by IBM. The ISA term was coined as a retronym by IBM PC clone manufacturers in the late 1980s or early 1990s as a reaction to IBM attempts to replace the AT bus with its new and incompatible Micro Channel architecture. The 16-bit ISA bus was also used with 32-bit processors for several years. An attempt to extend it to 32 bits, called Extended Industry Standard Architecture (EISA), was not very successful, however. Later buses such as VESA Local Bus and Peripheral Component Interconnect, PCI were used instead, often along with ISA slots on the same mainbo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
IBM PC Compatible
An IBM PC compatible is any personal computer that is hardware- and software-compatible with the IBM Personal Computer (IBM PC) and its subsequent models. Like the original IBM PC, an IBM PC–compatible computer uses an x86-based central processing unit, sourced either from Intel or a second source like AMD, Cyrix or other vendors such as Texas Instruments, Fujitsu, OKI, Mitsubishi or NEC and is capable of using interchangeable commodity hardware such as expansion cards. Initially such computers were referred to as PC clones, IBM clones or IBM PC clones, but the term "IBM PC compatible" is now a historical description only, as the vast majority of microcomputers produced since the 1990s are IBM compatible. IBM itself no longer sells personal computers, having sold its division to Lenovo in 2005. " Wintel" is a similar description that is more commonly used for modern computers. The designation "PC", as used in much of personal computer history, has not meant "pe ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Microsoft BASIC
Microsoft BASIC is the foundation software product of the Microsoft company and evolved into a line of BASIC interpreters and compiler(s) adapted for many different microcomputers. It first appeared in 1975 as Altair BASIC, which was the first version of BASIC published by Microsoft as well as the first high-level programming language available for the Altair 8800 microcomputer. During the home computer craze of the late-1970s and early-1980s, Microsoft BASIC was ported to and supplied with many home computer designs. Slight variations to add support for machine-specific functions, especially graphics, led to a profusion of related designs like Commodore BASIC and Atari Microsoft BASIC. As the early home computers gave way to newer designs like the IBM Personal Computer and Macintosh, BASIC was no longer as widely used, although it retained a strong following. The release of Visual Basic rebooted its popularity and it remains in wide use on Microsoft Windows platforms in its m ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
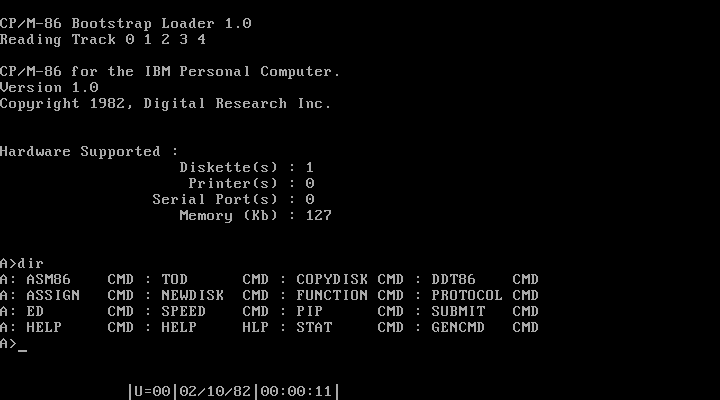
CP/M-86
CP/M-86 is a discontinued version of the CP/M operating system that Digital Research (DR) made for the Intel 8086 and Intel 8088. The system commands are the same as in CP/M-80. Executable files used the relocatable .CMD file format. Digital Research also produced a multi-user multitasking operating system compatible with CP/M-86, MP/M-86, which later evolved into Concurrent CP/M-86. When an emulator was added to provide PC DOS compatibility, the system was renamed Concurrent DOS, which later became Multiuser DOS, of which REAL/32 is the latest incarnation. The FlexOS, DOS Plus, and DR DOS families of operating systems started as derivations of Concurrent DOS as well. History Digital Research's CP/M-86 was originally announced to be released in November 1979, but was delayed repeatedly. When IBM contacted other companies to obtain components for the IBM PC, the as-yet unreleased CP/M-86 was its first choice for an operating system because CP/M had the most applica ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Intel 8088
The Intel 8088 ("''eighty-eighty-eight''", also called iAPX 88) microprocessor is a variant of the Intel 8086. Introduced on June 1, 1979, the 8088 has an eight-bit external data bus instead of the 16-bit bus of the 8086. The 16-bit registers and the one megabyte address range are unchanged, however. In fact, according to the Intel documentation, the 8086 and 8088 have the same execution unit (EU)—only the bus interface unit (BIU) is different. The 8088 was used in the original IBM PC and in IBM PC compatible clones. History and description The 8088 was designed at Intel's laboratory in Haifa, Israel, as were a large number of Intel's processors. The 8088 was targeted at economical systems by allowing the use of an eight-bit data path and eight-bit support and peripheral chips; complex circuit boards were still fairly cumbersome and expensive when it was released. The prefetch queue of the 8088 was shortened to four bytes, from the 8086's six bytes, and the prefe ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lille University Of Science And Technology
The Lille 1 University of Science and Technology (, USTL) was a French university located on a dedicated main campus in Villeneuve d'Ascq, near Lille (Hauts-de-France - European Metropolis of Lille), with 20,000 full-time students plus 14,500 students in continuing education (2004). 1,310 permanent faculty members plus 1,200 staff and around 140 CNRS researchers work there in the different University Lille 1 institutes and 43 research labs. University Lille 1 was a member of the European Doctoral College Lille Nord de France, which produces 400 doctorate dissertations every year. The university is ranked in the world top 200 universities in mathematics by the Shanghai ranking. University Lille 1 was established as Faculty of Science in 1854 in Lille, although its academic roots extend back to 1559. It later moved to Villeneuve d'Ascq in 1967. The University focuses on science and technology. Law, business management and medical fields are taught in the independent campus of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
RS-422
RS-422, also known as TIA/EIA-422, is a technical standard originated by the Electronic Industries Alliance, first issued in 1975, that specifies the electrical characteristics of a digital signaling circuit. It was meant to be the foundation of a suite of standards that would replace the older RS-232C standard with standards that offered much higher speed, better immunity from noise, and longer cable lengths. RS-422 systems can transmit data at rates as high as 10 Mbit/s, or may be sent on cables as long as at lower rates. It is closely related to RS-423, which uses the same signaling systems but on a different wiring arrangement. RS-422 specifies differential signaling, with every data line paired with a dedicated return line. It is the voltage difference between these two lines that defines the mark and space, rather than, as in RS-232, the difference in voltage between a data line and a local ground. As the ground voltage can differ at either end of the cable, this requ ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Computer Network
A computer network is a collection of communicating computers and other devices, such as printers and smart phones. In order to communicate, the computers and devices must be connected by wired media like copper cables, optical fibers, or by wireless communication. The devices may be connected in a variety of network topologies. In order to communicate over the network, computers use agreed-on rules, called communication protocols, over whatever medium is used. The computer network can include personal computers, Server (computing), servers, networking hardware, or other specialized or general-purpose Host (network), hosts. They are identified by network addresses and may have hostnames. Hostnames serve as memorable labels for the nodes and are rarely changed after initial assignment. Network addresses serve for locating and identifying the nodes by communication protocols such as the Internet Protocol. Computer networks may be classified by many criteria, including the tr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |