|
Lysosomal Cystine Transporter Family
The lysosomal cystine transporter (LCT) familyTC# 2.A.43 is part of the TOG Superfamily and includes secondary transport proteins that are derived from animals, plants, fungi and other eukaryotes. They exhibit 7 putative transmembrane α-helical spanners ( TMSs) and vary in size between about 200 and 500 amino acyl residues, although most have between 300 and 400 residues. These proteins are found in intracellular organelles of eukaryotes, many in lysosomes. The few that have been characterized transport CystineTC# 2.A.43.1.1, basic amino acids such as L-lysine and L-arginineTC# 2.A.43.2.1 and drugs such as fluconazole and caspofunginTC# 2.A.43.2.7. Cystinosin A protein mutated in the rare human genetic disease, nephropathic intermediate cystinosis, also called cystinosinTC# 2.A.43.1.1, is encoded by the CTNS gene. In cystinotic renal proximal tubules (RPTs), diminished cystinosin function appears to result in reduced reabsorption of solutes by other secondary transporters such a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
TOG Superfamily
The transporter-opsin-G protein-coupled receptor (TOG) superfamily is a protein superfamily of integral membrane proteins, usually of 7 or 8 transmembrane alpha-helical segments (TMSs). It includes (1) ion-translocating microbial rhodopsins and (2) G protein-coupled receptors (GPCRs), (3) Sweet sugar transporters, (4) nicotinamide ribonucleoside uptake permeases (PnuCTC# 4.B.1, (5) 4-toluene sulfonate uptake permeases (TSUP)TC# 2.A.102, (6) Ni2+–Co2+ transporters (NiCoT)TC# 2.A.52, (7) organic solute transporters (OST)TC# 2.A.82, (8) phosphate:Na+ symporters (PNaS)TC# 2.A.58 and (9) lysosomal cystine transporters (LCT)TC# 2.A.43. Families Currently recognized families Family (from la, familia) is a group of people related either by consanguinity (by recognized birth) or affinity (by marriage or other relationship). The purpose of the family is to maintain the well-being of its members and of society. Ideal ... within the TOG Superfamily (with TC numbers in blue) incl ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Alpha-helical
The alpha helix (α-helix) is a common motif in the secondary structure of proteins and is a right hand-helix conformation in which every backbone N−H group hydrogen bonds to the backbone C=O group of the amino acid located four residues earlier along the protein sequence. The alpha helix is also called a classic Pauling–Corey–Branson α-helix. The name 3.613-helix is also used for this type of helix, denoting the average number of residues per helical turn, with 13 atoms being involved in the ring formed by the hydrogen bond. Among types of local structure in proteins, the α-helix is the most extreme and the most predictable from sequence, as well as the most prevalent. Discovery In the early 1930s, William Astbury showed that there were drastic changes in the X-ray fiber diffraction of moist wool or hair fibers upon significant stretching. The data suggested that the unstretched fibers had a coiled molecular structure with a characteristic repeat of ≈. Astb ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Transmembrane Segment
A transmembrane domain (TMD) is a membrane-spanning protein domain. TMDs generally adopt an alpha helix topological conformation, although some TMDs such as those in porins can adopt a different conformation. Because the interior of the lipid bilayer is hydrophobic, the amino acid residues in TMDs are often hydrophobic, although proteins such as membrane pumps and ion channels can contain polar residues. TMDs vary greatly in length, sequence, and hydrophobicity, adopting organelle-specific properties. Functions of transmembrane domains Transmembrane domains are known to perform a variety of functions. These include: * Anchoring transmembrane proteins to the membrane. *Facilitating molecular transport of molecules such as ions and proteins across biological membranes; usually hydrophilic residues and binding sites in the TMDs help in this process. *Signal transduction across the membrane; many transmembrane proteins, such as G protein-coupled receptors, receive extracellular s ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fluconazole
Fluconazole is an antifungal medication used for a number of fungal infections. This includes candidiasis, blastomycosis, coccidiodomycosis, cryptococcosis, histoplasmosis, dermatophytosis, and pityriasis versicolor. It is also used to prevent candidiasis in those who are at high risk such as following organ transplantation, low birth weight babies, and those with neutropenia, low blood neutrophil counts. It is given either by mouth or by intravenous, injection into a vein. Common side effects include vomiting, diarrhea, rash, and elevated transaminases, increased liver enzymes. Serious side effects may include liver problems, QT prolongation, and seizures. During pregnancy it may increase the risk of miscarriage while large doses may cause birth defects. Fluconazole is in the azole antifungal family of medication. It is believed to work by affecting the fungal cellular membrane. Fluconazole was patented in 1981 and came into commercial use in 1988. It is on the WHO Model Lis ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Caspofungin
Caspofungin (INN) (brand name Cancidas) is a lipopeptide antifungal drug from Merck & Co., Inc. discovered by James Balkovec, Regina Black and Frances A. Bouffard. It is a member of a new class of antifungals termed the echinocandins. It works by inhibiting the enzyme (1→3)-β-D-glucan synthase and thereby disturbing the integrity of the fungal cell wall. Caspofungin was the first inhibitor of fungal (1→3)-β-D-glucan synthesis to be approved by the United States Food and Drug Administration. Caspofungin is administered intravenously. It is on the World Health Organization's List of Essential Medicines. Spectrum of Activity Caspofungin has been effective in treating fungal infections caused by ''Aspergillus'' and ''Candida'' species. It is a member of the echinocandin family, a new class of antifungal agents with broad spectrum of activity against all Candida species. In comparison to treatment with either fluconazole or Amphotericin B, all three drugs in this class ha ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
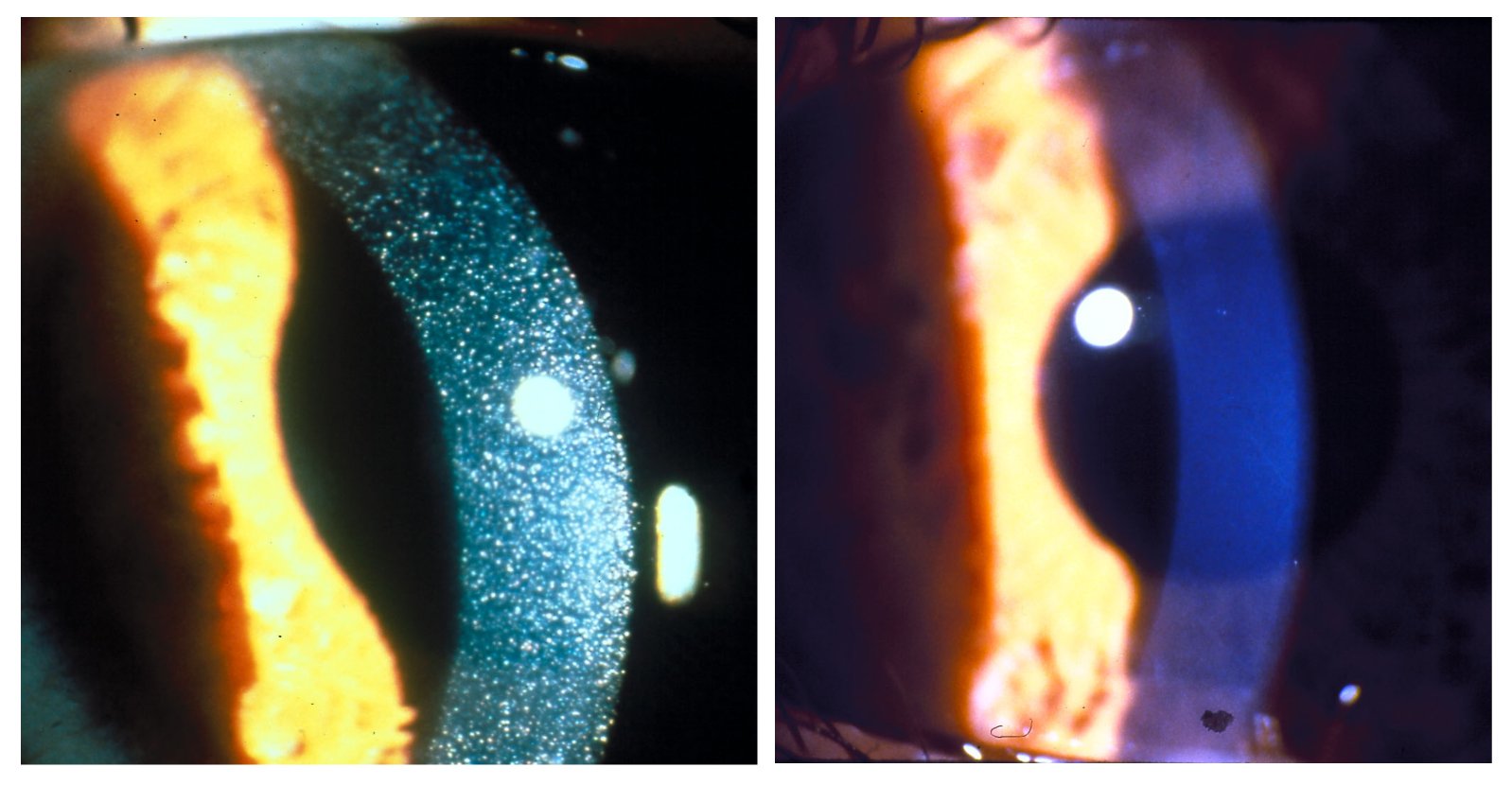
Cystinosis
Cystinosis is a lysosomal storage disease characterized by the abnormal accumulation of cystine, the oxidized dimer of the amino acid cysteine. It is a genetic disorder that follows an autosomal recessive inheritance pattern. It is a rare autosomal recessive disorder resulting from accumulation of free cystine in lysosomes, eventually leading to intracellular crystal formation throughout the body. Cystinosis is the most common cause of Fanconi syndrome in the pediatric age group. Fanconi syndrome occurs when the function of cells in renal tubules is impaired, leading to abnormal amounts of carbohydrates and amino acids in the urine, excessive urination, and low blood levels of potassium and phosphates. Cystinosis was the first documented genetic disease belonging to the group of lysosomal storage disease disorders.Nesterova G, Gahl WA. Cystinosis: the evolution of a treatable disease. Pediatr Nephrol 2012;28:51–9. Cystinosis is caused by mutations in the '' CTNS'' gene that code ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
CTNS (gene)
''CTNS may also refer to the Center for Theology and the Natural Sciences.'' ''CTNS'' is the gene that encodes the protein cystinosin in humans. Cystinosin is a lysosomal seven-transmembrane protein that functions as an active transporter for the export of cystine molecules out of the lysosome. Mutations in ''CTNS'' are responsible for cystinosis, an autosomal recessive lysosomal storage disease. Gene ''The CTNS'' gene is located on the p arm of human chromosome 17, at position 13.2. It spans base pairs 3,636,468 and 3,661,542, and comprises 12 exons. In 1995, the gene was localized to the short arm of chromosome 17. An international collaborative effort finally succeeded in isolating ''CTNS'' by positional cloning in 1998. The CTNSN323K, CTNSK280R, and CTNSN288K mutations completely stop the movement of CySS out of the lysosome via cystinosin. /sup> interestingly, CTNSN323K and CTNSK280R are related to juvenile nephropathic cystinosis while CTNSN288K mutations are found in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sodium/phosphate Cotransporter
The sodium/phosphate cotransporter is a member of the phosphate:Na+ symporter (PNaS) family within the TOG Superfamily of transport proteins as specified in the Transporter Classification Database (TCDB). Nomenclature Sodium/phosphate cotransporters are also known as: * Na+-Pi cotransport proteins (NaPi-2a) * Sodium-dependent phosphate transporters * Sodium-dependent phosphate symporters * Phosphate:Na+ symporters PNaS family The Phosphate:Na+ Symporter (PNaS) family (TC# ) includes several closely related, functionally characterized, sodium-dependent, inorganic phosphate (Pi) transporter (NPT) proteins from mammals. Other organisms that possess PNaS family members include many in eukaryotic, bacterial and archaeal phyla. Bacterial sodium:phosphate symporters, NptA of ''Vibrio cholerae''TC#2.A.58.1.2 and YjbB of ''E. coli''TC# 2.A.58.2.1 have been functionally characterized. The well-characterized mammalian proteins are found in renal (IIa isoform) and intestinal (IIb isof ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lumen (anatomy)
In biology, a lumen (plural lumina) is the inside space of a tubular structure, such as an artery or intestine. It comes . It can refer to: *The interior of a vessel, such as the central space in an artery, vein or capillary through which blood flows. *The interior of the gastrointestinal tract *The pathways of the bronchi in the lungs *The interior of renal tubules and urinary collecting ducts *The pathways of the female genital tract, starting with a single pathway of the vagina, splitting up in two lumina in the uterus, both of which continue through the Fallopian tubes In cell biology, a lumen is a membrane-defined space that is found inside several organelles, cellular components, or structures: *thylakoid, endoplasmic reticulum, Golgi apparatus, lysosome, mitochondrion, or microtubule Transluminal procedures ''Transluminal procedures'' are procedures occurring through lumina, including: *Natural orifice transluminal endoscopic surgery in the lumina of, for example, the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Glycolipid
Glycolipids are lipids with a carbohydrate attached by a glycosidic (covalent) bond. Their role is to maintain the stability of the cell membrane and to facilitate cellular recognition, which is crucial to the immune response and in the connections that allow cells to connect to one another to form tissues. Glycolipids are found on the surface of all eukaryotic cell membranes, where they extend from the phospholipid bilayer into the extracellular environment. Structure The essential feature of a glycolipid is the presence of a monosaccharide or oligosaccharide bound to a lipid moiety. The most common lipids in cellular membranes are glycerolipids and sphingolipids, which have glycerol or a sphingosine backbones, respectively. Fatty acids are connected to this backbone, so that the lipid as a whole has a polar head and a non-polar tail. The lipid bilayer of the cell membrane consists of two layers of lipids, with the inner and outer surfaces of the membrane made up of the pol ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Microbial Rhodopsin
Microbial rhodopsins, also known as bacterial rhodopsins are retinal-binding proteins that provide light-dependent ion transport and sensory functions in halophilic and other bacteria. They are integral membrane proteins with seven transmembrane helices, the last of which contains the attachment point (a conserved lysine) for retinal. This protein family includes light-driven proton pumps, ion pumps and ion channels, as well as light sensors. For example, the proteins from halobacteria include bacteriorhodopsin and archaerhodopsin, which are light-driven proton pumps; halorhodopsin, a light-driven chloride pump; and sensory rhodopsin, which mediates both photoattractant (in the red) and photophobic (in the ultra-violet) responses. Proteins from other bacteria include proteorhodopsin. Contrary to their name, microbial rhodopsins are found not only in Archaea and Bacteria, but also in Eukaryota (such as algae) and viruses; although they are rare in complex multicellular org ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |

.png)
.jpg)