|
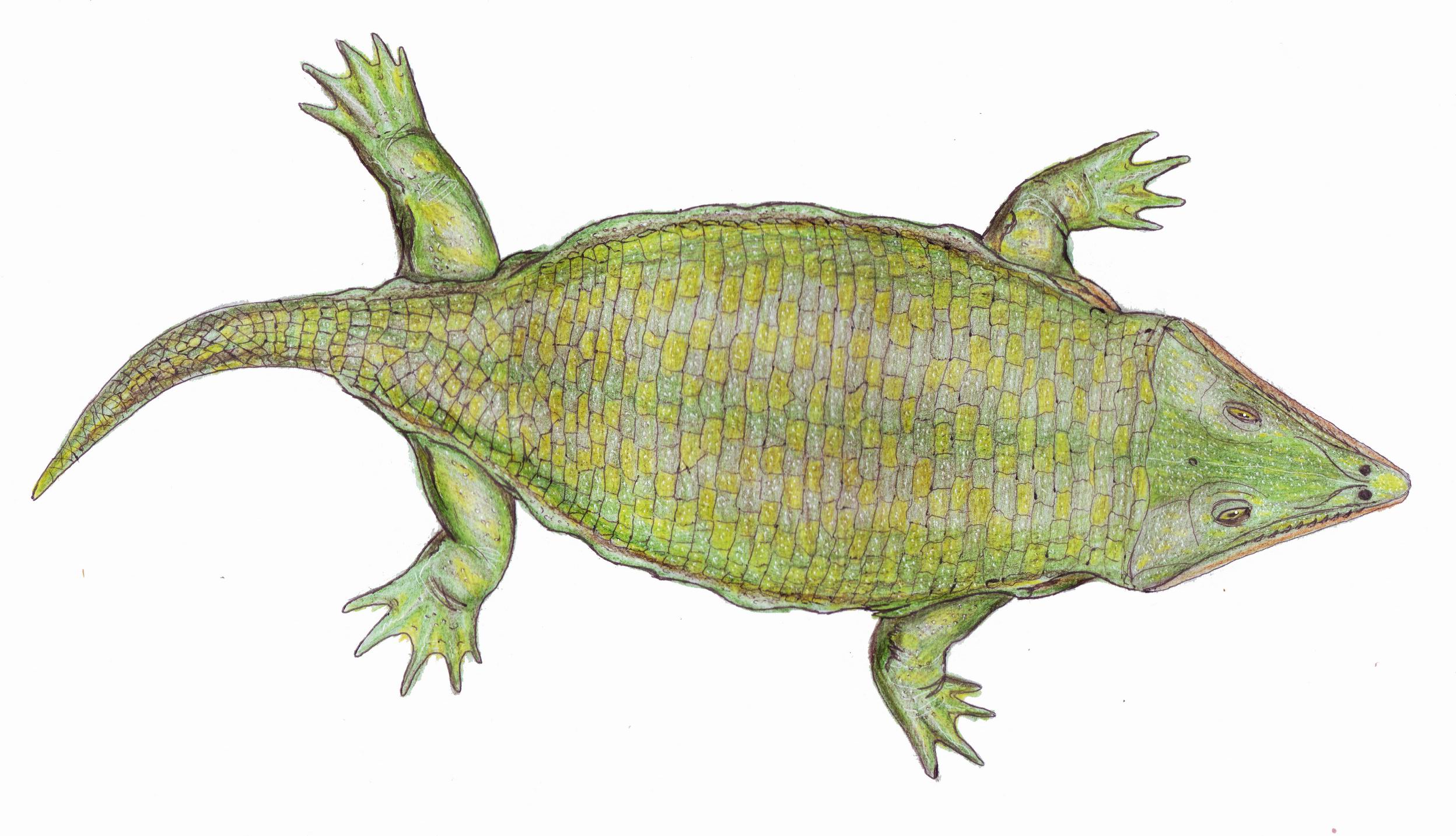
Lyrocephaliscus
''Lyrocephaliscus'' is an extinct genus of trematosaurian temnospondyl within the family Trematosauridae. Classification Below is a cladogram from Steyer (2002) showing the phylogenetic relationships of trematosaurids: See also * Prehistoric amphibian * List of prehistoric amphibians This list of prehistoric amphibians is an attempt to create a comprehensive listing of all genera from the fossil record that have ever been considered to be amphibians, excluding purely vernacular terms. The list includes all commonly accepted g ... References Trematosauroids Fossil taxa described in 1914 {{temnospondyli-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Trematosauroids
Trematosauroidea are an important group of Triassic temnospondyl amphibians. They flourished briefly during the Early Triassic, occurring worldwide before declining at the start of the Middle Triassic, although the group continued until the Late Triassic. They were medium-sized temnospondyls with wedge-shaped tails, narrow skulls, and, in advanced forms, elongated snouts. The latter feature was probably an adaptation for feeding on fish. The largest and most specialized family, the Trematosauridae, are the only batrachomorphs to have adapted to a marine lifestyle with the exception of the modern crab-eating frog. A temnospondyl ilium was described in 2004 from the Callovian Toutunhe Formation in the Junggar Basin of China. Although the isolated bone was impossible to identify on the species level, it was referred to Trematosauroidea. The presence of this bone in the Toutunhe Formation extends the range of trematosauroids into the Middle Jurassic, making it one of only three ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Temnospondyl
Temnospondyli (from Greek language, Greek τέμνειν, ''temnein'' 'to cut' and σπόνδυλος, ''spondylos'' 'vertebra') is a diverse order (biology), order of small to giant tetrapods—often considered Labyrinthodontia, primitive amphibians—that flourished worldwide during the Carboniferous, Permian, and Triassic periods. A few species continued into the Jurassic and Cretaceous periods. Fossils have been found on every continent. During about 210 million years of evolutionary history, they adapted to a wide range of habitats, including freshwater, terrestrial, and even coastal marine environments. Their life history is well understood, with fossils known from the larval stage, metamorphosis, and maturity. Most temnospondyls were semiaquatic, although some were almost fully terrestrial, returning to the water only to breed. These temnospondyls were some of the first vertebrates fully adapted to life on land. Although temnospondyls are considered amphibians, many had cha ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
List Of Prehistoric Amphibians
This list of prehistoric amphibians is an attempt to create a comprehensive listing of all genera from the fossil record that have ever been considered to be amphibians, excluding purely vernacular terms. The list includes all commonly accepted genera, but also genera that are now considered invalid, doubtful ('' nomina dubia''), or were not formally published (''nomina nuda''), as well as junior synonyms of more established names, and genera that are no longer considered amphibians. Modern forms are excluded from this list. The list currently includes 454 names. Naming conventions and terminology Naming conventions and terminology follow the International Code of Zoological Nomenclature. Technical terms used include: * Junior synonym: A name which describes the same taxon as a previously published name. If two or more genera are formally designated and the type specimens are later assigned to the same genus, the first to be published (in chronological order) is the senior synon ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Prehistoric Amphibian
This list of prehistoric amphibians is an attempt to create a comprehensive listing of all Genus, genera from the fossil record that have ever been considered to be amphibians, excluding purely vernacular terms. The list includes all commonly accepted genera, but also genera that are now considered invalid, doubtful (''nomen dubium, nomina dubia''), or were not formally published (''nomen nudum, nomina nuda''), as well as synonym (zoology), junior synonyms of more established names, and genera that are no longer considered amphibians. Modern forms are excluded from this list. The list currently includes 454 names. Naming conventions and terminology Naming conventions and terminology follow the International Code of Zoological Nomenclature. Technical terms used include: * Synonym (zoology), Junior synonym: A name which describes the same taxon as a previously published name. If two or more genera are formally designated and the type (zoology), type specimens are later assigned to th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lonchorhynchinae
Lonchorhynchinae is a subfamily of temnospondyl amphibians within the family Trematosauridae. Classification Below is a cladogram from Steyer (2002) showing the phylogenetic In biology, phylogenetics (; from Greek φυλή/ φῦλον [] "tribe, clan, race", and wikt:γενετικός, γενετικός [] "origin, source, birth") is the study of the evolutionary history and relationships among or within groups o ... relationships of trematosaurids: References External linksMikko’s Phylogeny Archive Triassic temnospondyls Triassic first appearances {{temnospondyli-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Trematosuchus
''Trematosuchus'' is an extinct genus of trematosaurian temnospondyl within the family Trematosauridae from South Africa. It was first named by Haughton in 1915 as '' Trematosaurus sobeyi''. It was assigned to its own genus ''Trematosuchus'' by Watson in 1919. Classification Below is a cladogram from Steyer (2002) showing the phylogenetic relationships of trematosaurids: See also * Prehistoric amphibian * List of prehistoric amphibians This list of prehistoric amphibians is an attempt to create a comprehensive listing of all Genus, genera from the fossil record that have ever been considered to be amphibians, excluding purely vernacular terms. The list includes all commonly accep ... References Trematosaurines Prehistoric amphibians of Africa Fossil taxa described in 1919 {{temnospondyli-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Trematosaurus
''Trematosaurus'' is an extinct genus of trematosaurid temnospondyl amphibian found in Germany and Russia. It was first named by Hermann Burmeister in 1849 and the type species is ''Trematosaurus brauni''. History of study ''Trematosaurus'' was one of the first temnospondyls to be described. The type locality, called Merkel's Quarry, is in east-central Germany at Bernburg an der Saale within the Bausandstein (Olenekian) and was collected for several decades from the 1840s into the early 20th century, producing extensive cranial remains, although the majority of these are preserved as internal molds (steinkerns) or natural molds. The name ''Trematosaurus'' was in fact coined in 1842 by Carl von Braun, a frequent collector who used the Greek suffix ''trema'' ('hole') in reference to the pineal foramen to form the generic epithet, but as he provided no formal description, the name was not considered valid until the work of Burmeister, who named the type species after Braun. Burm ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Platystega
''Platystega'' is an extinct genus of trematosaurian temnospondyl within the family Trematosauridae. Classification Below is a cladogram from Steyer (2002) showing the phylogenetic relationships of trematosaurids: See also * Prehistoric amphibian * List of prehistoric amphibians This list of prehistoric amphibians is an attempt to create a comprehensive listing of all genera from the fossil record that have ever been considered to be amphibians, excluding purely vernacular terms. The list includes all commonly accepted g ... References Trematosaurines {{temnospondyli-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Trematosaurinae
Trematosaurinae is a subfamily of temnospondyl amphibians within the family Trematosauridae. Like all trematosaurids, they were marine piscivores, resembling crocodiles in their general build. Unlike the long, almost gharial-like snouts of the Lonchorhynchinae, the Trematosaurinae had more "normal" crocodile-like skulls.Damani, Ross (2004). “Cranial anatomy and relationships of Microposaurus casei, a temnospondyl from the MiddleTriassic of South Africa”. ''Journal of Vertebrate Paleontology'', 24(3): 533–541 Classification Below is a cladogram from Steyer (2002) showing the phylogenetic In biology, phylogenetics (; from Greek φυλή/ φῦλον [] "tribe, clan, race", and wikt:γενετικός, γενετικός [] "origin, source, birth") is the study of the evolutionary history and relationships among or within groups o ... relationships of trematosaurids: References External linksMikko’s Phylogeny Archive Triassic temnospondyls Trematosaurines Triass ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Trematosauroidea
Trematosauroidea are an important group of Triassic temnospondyl amphibians. They flourished briefly during the Early Triassic, occurring worldwide before declining at the start of the Middle Triassic, although the group continued until the Late Triassic. They were medium-sized temnospondyls with wedge-shaped tails, narrow skulls, and, in advanced forms, elongated snouts. The latter feature was probably an adaptation for feeding on fish. The largest and most specialized family, the Trematosauridae, are the only batrachomorphs to have adapted to a marine lifestyle with the exception of the modern crab-eating frog. A temnospondyl ilium was described in 2004 from the Callovian Toutunhe Formation in the Junggar Basin of China. Although the isolated bone was impossible to identify on the species level, it was referred to Trematosauroidea. The presence of this bone in the Toutunhe Formation extends the range of trematosauroids into the Middle Jurassic, making it one of only three gro ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Temnospondyli
Temnospondyli (from Greek τέμνειν, ''temnein'' 'to cut' and σπόνδυλος, ''spondylos'' 'vertebra') is a diverse order of small to giant tetrapods—often considered primitive amphibians—that flourished worldwide during the Carboniferous, Permian, and Triassic periods. A few species continued into the Jurassic and Cretaceous periods. Fossils have been found on every continent. During about 210 million years of evolutionary history, they adapted to a wide range of habitats, including freshwater, terrestrial, and even coastal marine environments. Their life history is well understood, with fossils known from the larval stage, metamorphosis, and maturity. Most temnospondyls were semiaquatic, although some were almost fully terrestrial, returning to the water only to breed. These temnospondyls were some of the first vertebrates fully adapted to life on land. Although temnospondyls are considered amphibians, many had characteristics, such as scales and armour-like bon ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Trematosauridae
Trematosauridae are a family of large marine temnospondyl amphibians with many members. They first appeared during the Induan age of the Early Triassic, and existed until around the Carnian stage of the Late Triassic, although by then they were very rare. By the Middle Triassic they had become widespread throughout Laurasia and Gondwana with fossils being found in Europe, Asia, Madagascar, and Australia. They are one of the most derived families of the Trematosauroidea superfamily in that they are the only family that have fully marine lifestyles. Long, slender snouts that are characteristic of the trematosaurids, with some members having rostrums resembling those of modern-day gavials. Traditionally, two subfamilies within Trematosauridae can be identified, the relatively short-nosed Trematosaurinae and the long-nosed Lonchorhynchinae._A_third_subfamily,_Tertreminae.html" ;"title=".... A third subfamily, Tertreminae">.... A third subfamily, Tertreminae, was named in 2000 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |