|
Lymphangiogenesis
Lymphangiogenesis is the formation of lymphatic vessels from pre-existing lymphatic vessels in a method believed to be similar to angiogenesis (blood vessel development). Lymphangiogenesis plays an important physiological role in homeostasis, metabolism and immunity. Impaired or excessive lymphatic vessel formation has been implicated in a number of pathological conditions including neoplasm metastasis, oedema, rheumatoid arthritis, psoriasis, lymphangiomatosis and impaired wound healing. The role of the lymphatic system in these diseases has received renewed interest largely due to the discovery of lymphatic endothelial cell (LEC)-specific markers such as podoplanin, LYVE-1, PROX1, desmoplakin and VEGF-C receptor VEGFR-3. These specific markers have enabled insights into functional and molecular lymphatic biology. There are several known pro-lymphangiogenesis inducers such as VEGF-C, hyaluronic acid and ephrin-B2 Ephrin-B2 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the ''EFNB2'' ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
LYVE-1
Lymphatic vessel endothelial hyaluronan receptor 1 (LYVE1), also known as extracellular link domain containing 1 (XLKD1) is a Link domain-containing hyaladherin, a protein capable of binding to hyaluronic acid (HA), homologous to CD44, the main HA receptor. In humans it is encoded by the ''LYVE1'' gene. LYVE1 is a type I integral membrane glycoprotein Glycoproteins are proteins which contain oligosaccharide chains covalently attached to amino acid side-chains. The carbohydrate is attached to the protein in a cotranslational or posttranslational modification. This process is known as glycos .... It acts as a receptor and binds to both soluble and immobilized hyaluronan. This protein may function in lymphatic hyaluronan transport and have a role in tumor metastasis. LYVE-1 is a cell surface receptor on lymphatic endothelial cells that can be used as a lymphatic endothelial cell marker, allowing for the isolation of these cells for experimental purposes. The physiological rol ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
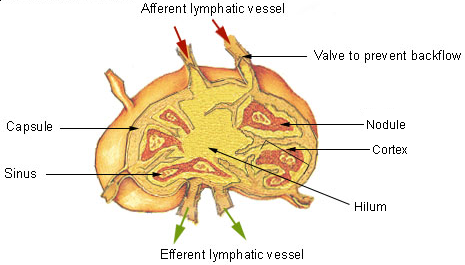
Lymphatic System
The lymphatic system, or lymphoid system, is an organ system in vertebrates that is part of the immune system, and complementary to the circulatory system. It consists of a large network of lymphatic vessels, lymph nodes, lymphatic or lymphoid organs, and lymphoid tissues. The vessels carry a clear fluid called lymph (the Latin word ''lympha'' refers to the deity of fresh water, "Lympha") back towards the heart, for re-circulation. Unlike the circulatory system that is a closed system, the lymphatic system is open. The human circulatory system processes an average of 20 litres of blood per day through capillary filtration, which removes plasma from the blood. Roughly 17 litres of the filtered blood is reabsorbed directly into the blood vessels, while the remaining three litres are left in the interstitial fluid. One of the main functions of the lymphatic system is to provide an accessory return route to the blood for the surplus three litres. The other main function is that of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lymphatic Vessel
The lymphatic vessels (or lymph vessels or lymphatics) are thin-walled vessels (tubes), structured like blood vessels, that carry lymph. As part of the lymphatic system, lymph vessels are complementary to the cardiovascular system. Lymph vessels are lined by endothelial cells, and have a thin layer of smooth muscle, and adventitia that binds the lymph vessels to the surrounding tissue. Lymph vessels are devoted to the propulsion of the lymph from the lymph capillaries, which are mainly concerned with the absorption of interstitial fluid from the tissues. Lymph capillaries are slightly bigger than their counterpart capillaries of the vascular system. Lymph vessels that carry lymph to a lymph node are called afferent lymph vessels, and those that carry it from a lymph node are called efferent lymph vessels, from where the lymph may travel to another lymph node, may be returned to a vein, or may travel to a larger lymph duct. Lymph ducts drain the lymph into one of the subclavia ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hyaluronic Acid
Hyaluronic acid (; abbreviated HA; conjugate base hyaluronate), also called hyaluronan, is an anionic, nonsulfated glycosaminoglycan distributed widely throughout connective, epithelial, and neural tissues. It is unique among glycosaminoglycans as it is non-sulfated, forms in the plasma membrane instead of the Golgi apparatus, and can be very large: human synovial HA averages about 7 million Da per molecule, or about 20,000 disaccharide monomers, while other sources mention 3–4 million Da. The average 70 kg (150 lb) person has roughly 15 grams of hyaluronan in the body, one-third of which is turned over (i.e., degraded and synthesized) per day. As one of the chief components of the extracellular matrix, it contributes significantly to cell proliferation and migration, and is involved in the progression of many malignant tumors. Hyaluronic acid is also a component of the group A streptococcal extracellular capsule, and is believed to play a role in virule ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
VEGF-C
Vascular endothelial growth factor C (VEGF-C) is a protein that is a member of the platelet-derived growth factor / vascular endothelial growth factor (PDGF/VEGF) family. It is encoded in humans by the ''VEGFC'' gene, which is located on chromosome 4q34. Functions The main function of VEGF-C is to promote the growth of lymphatic vessels (lymphangiogenesis). It acts on lymphatic endothelial cells (LECs) primarily via its receptor VEGFR-3 promoting survival, growth and migration. It was discovered in 1996 as a ligand for the orphan receptor VEGFR-3. Soon thereafter, it was shown to be a specific growth factor for lymphatic vessels in a variety of models. However, in addition to its effect on lymphatic vessels, it can also promote the growth of blood vessels and regulate their permeability. The effect on blood vessels can be mediated via its primary receptor VEGFR-3 or its secondary receptor VEGFR-2. Apart from vascular targets, VEGF-C is also important for neural development and bl ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
VEGFR-3
VEGF receptors are receptors for vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF). There are three main subtypes of VEGFR, numbered 1, 2 and 3. Also, they may be membrane-bound (mbVEGFR) or soluble (sVEGFR), depending on alternative splicing. Inhibitors of VEGFR are used in the treatment of cancer. VEGF Vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF) is an important signaling protein involved in both vasculogenesis (the formation of the circulatory system) and angiogenesis (the growth of blood vessels from pre-existing vasculature). As its name implies, VEGF activity is restricted mainly to cells of the vascular endothelium, although it does have effects on a limited number of other cell types (e.g. stimulation monocyte/macrophage migration). ''In vitro'', VEGF has been shown to stimulate endothelial cell mitogenesis and cell migration. VEGF also enhances microvascular permeability and is sometimes referred to as vascular permeability factor. Receptor biology All members of the VEGF ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Vascular Endothelial Growth Factor C
Vascular endothelial growth factor C (VEGF-C) is a protein that is a member of the platelet-derived growth factor / vascular endothelial growth factor (PDGF/VEGF) family. It is encoded in humans by the ''VEGFC'' gene, which is located on chromosome 4q34. Functions The main function of VEGF-C is to promote the growth of lymphatic vessels (lymphangiogenesis). It acts on lymphatic endothelial cells (LECs) primarily via its receptor VEGFR-3 promoting survival, growth and migration. It was discovered in 1996 as a ligand for the orphan receptor VEGFR-3. Soon thereafter, it was shown to be a specific growth factor for lymphatic vessels in a variety of models. However, in addition to its effect on lymphatic vessels, it can also promote the growth of blood vessels and regulate their permeability. The effect on blood vessels can be mediated via its primary receptor VEGFR-3 or its secondary receptor VEGFR-2. Apart from vascular targets, VEGF-C is also important for neural development and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Desmoplakin
Desmoplakin is a protein in humans that is encoded by the ''DSP'' gene. Desmoplakin is a critical component of desmosome structures in cardiac muscle and epidermal cells, which function to maintain the structural integrity at adjacent cell contacts. In cardiac muscle, desmoplakin is localized to intercalated discs which mechanically couple cardiac cells to function in a coordinated syncytial structure. Mutations in desmoplakin have been shown to play a role in dilated cardiomyopathy and arrhythmogenic right ventricular cardiomyopathy, where it may present with acute myocardial injury; striate palmoplantar keratoderma, Carvajal syndrome and paraneoplastic pemphigus. Structure Desmoplakin exists as two predominant isoforms; the first, known as "DPII", has molecular weight 260.0 kDa (2272 amino acids) and the second, known as "DPI", has molecular weight 332.0 kDa (2871 amino acids). These isoforms are identical except for the shorter rod domain in DPII. DPI is the predominant isoform ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
PROX1
Prospero homeobox protein 1 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the ''PROX1'' gene. The Prox1 gene is critical for the development of multiple tissues. Prox1 activity is necessary and sufficient to specify a lymphatic endothelial cell fate in endothelial progenitors located in the embryonic veins. Interactions PROX1 has been shown to interact with EP300. Production PROX1 is produced primarily in the dentate gyrus in the mouse, and in the dentate gyrus and white matter in humans. Gene expression data for mouse, human and macaque from the Allen Brain Atlases can be founhere Clinical significance PROX1 is used as a marker for lymphatic endothelium The endothelium is a single layer of squamous endothelial cells that line the interior surface of blood vessels and lymphatic vessels. The endothelium forms an interface between circulating blood or lymph in the lumen and the rest of the vesse ... in biopsy samples. Homologous gene PROX2 References Further reading * * * ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Podoplanin
Podoplanin is a protein that in humans is encoded by the ''PDPN'' gene. Structure and function Podoplanin is a mucin-type protein with a mass of 36- to 43-kDa. It is relatively well conserved between species, with homologues in humans, mice, rats, dogs and hamsters. This gene encodes a type-I, integral membrane, heavily O-glycosylated glycoprotein with diverse distribution in human tissues. The physiological function of this protein may be related to its mucin-type character. The homologous protein in other species has been described as a differentiation antigen and influenza-virus receptor. The specific function of this protein has not been determined but it has been proposed as a marker of lung injury. Alternatively spliced transcript variants encoding different isoforms have been identified. This protein has been found to have functions in lung alveolar cells, kidney podocytes, and lymphatic endothelial cells. More recently, this protein has been found in neural tissue in bo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lymphatic Endothelial Cell
Lymph (from Latin, , meaning "water") is the fluid that flows through the lymphatic system, a system composed of lymph vessels (channels) and intervening lymph nodes whose function, like the venous system, is to return fluid from the tissues to be recirculated. At the origin of the fluid-return process, interstitial fluid—the fluid between the cells in all body tissues—enters the lymph capillaries. This lymphatic fluid is then transported via progressively larger lymphatic vessels through lymph nodes, where substances are removed by tissue lymphocytes and circulating lymphocytes are added to the fluid, before emptying ultimately into the right or the left subclavian vein, where it mixes with central venous blood. Because it is derived from interstitial fluid, with which blood and surrounding cells continually exchange substances, lymph undergoes continual change in composition. It is generally similar to blood plasma, which is the fluid component of blood. Lymph returns ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Wound Healing
Wound healing refers to a living organism's replacement of destroyed or damaged tissue by newly produced tissue. In undamaged skin, the epidermis (surface, epithelial layer) and dermis (deeper, connective layer) form a protective barrier against the external environment. When the barrier is broken, a regulated sequence of biochemical events is set into motion to repair the damage. This process is divided into predictable phases: blood clotting (hemostasis), inflammation, tissue growth ( cell proliferation), and tissue remodeling (maturation and cell differentiation). Blood clotting may be considered to be part of the inflammation stage instead of a separate stage. The wound healing process is not only complex but fragile, and it is susceptible to interruption or failure leading to the formation of non-healing chronic wounds. Factors that contribute to non-healing chronic wounds are diabetes, venous or arterial disease, infection, and metabolic deficiencies of old age.Enoch, S ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |