|
Lund's Node
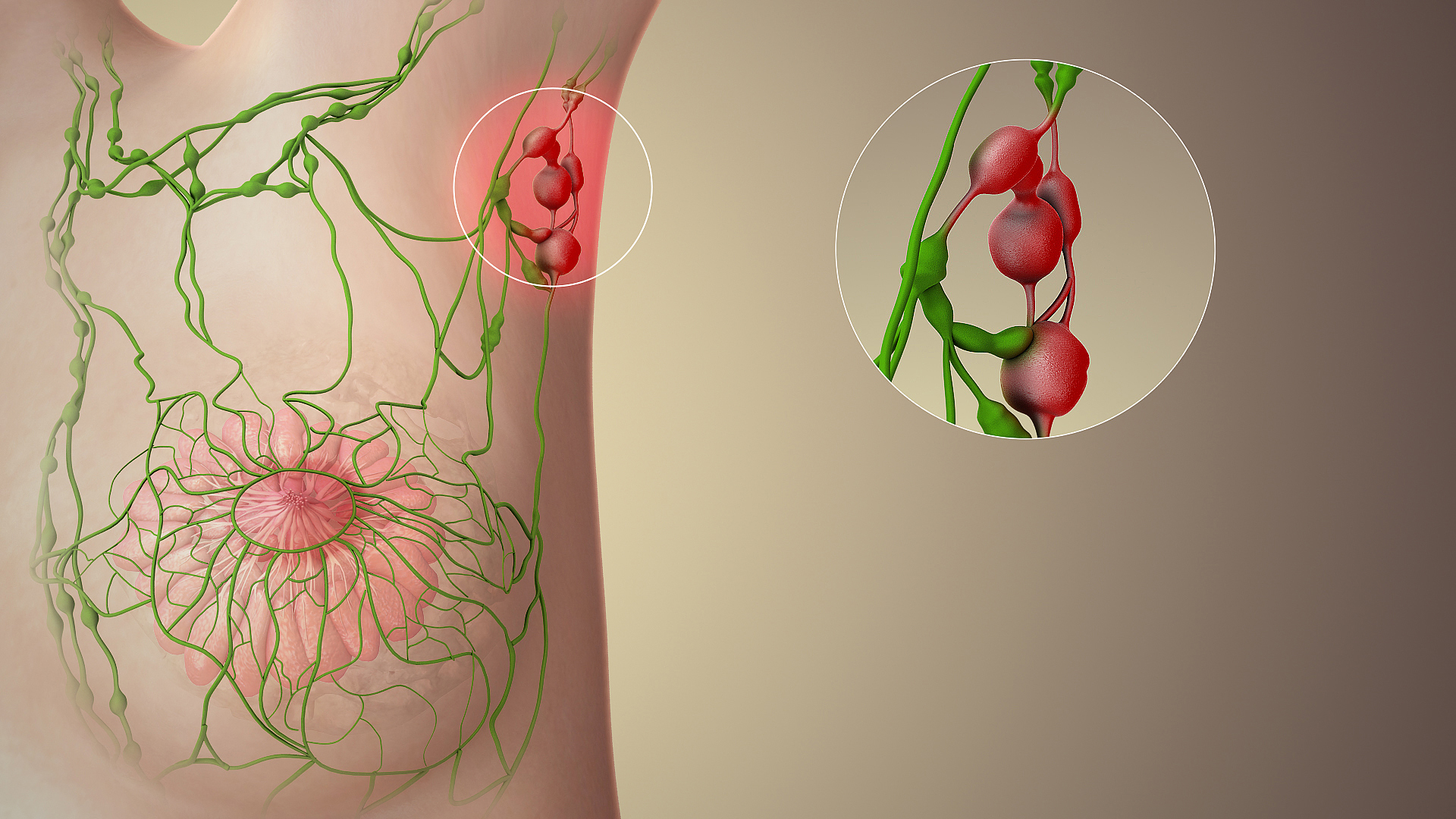
Lund's node, or Mascagni's lymph node (often erroneously referred to as Calot's node), is the sentinel lymph node of the gall bladder. It increases in size in cholecystitis and cholangitis. It is an anatomic landmark and is removed along with the gall bladder in cholecystectomy. It is situated within the Triangle of Calot, where abides the space below the cystic artery. The node is named after Fred Bates Lund (1865-1950), an American surgeon. It was also named after the Italian anatomist and physician, Paolo Mascagni Paolo Mascagni (25 January 1755 – 19 October 1815) was an Italian physician and anatomist. He is most well known for publishing the first complete description of the lymphatic system. Biography Early life Mascagni was born in the co ... (1752-1815), who first identified the node around 1787. Lymphatics of the torso Anatomic Landmarks References {{lymphatic-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sentinel Lymph Node
The sentinel lymph node is the hypothetical first lymph node or group of nodes draining a cancer. In case of established cancerous dissemination it is postulated that the sentinel lymph nodes are the target organs primarily reached by metastasizing cancer cells from the tumor. The sentinel node procedure (also termed sentinel lymph node biopsy or SLNB) is the identification, removal and analysis of the sentinel lymph nodes of a particular tumour. Physiology The spread of some forms of cancer usually follows an orderly progression, spreading first to regional lymph nodes, then the next echelon of lymph nodes, and so on, since the flow of lymph is directional, meaning that some cancers spread in a predictable fashion from where the cancer started. In these cases, if the cancer spreads it will spread first to lymph nodes (lymph glands) close to the tumor before it spreads to other parts of the body. The concept of sentinel lymph node surgery is to determine if the cancer has sprea ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gallbladder
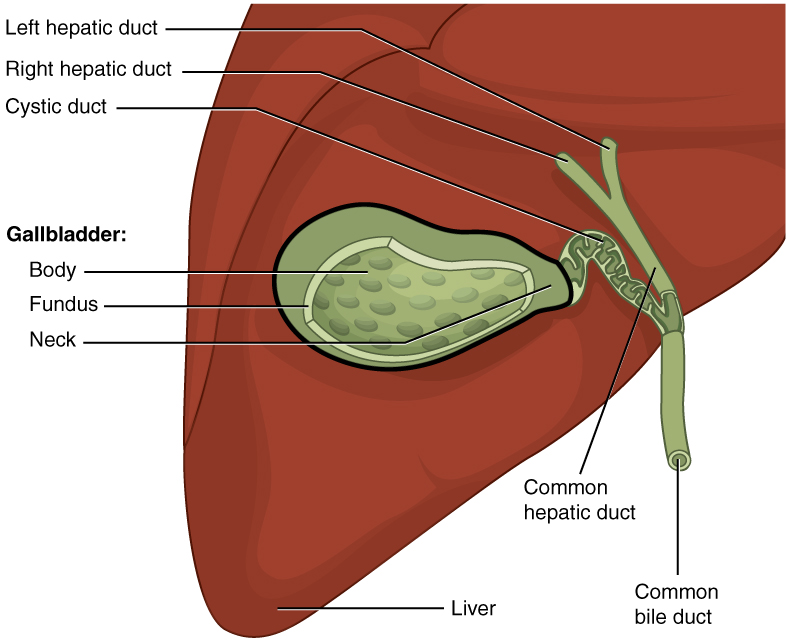
In vertebrates, the gallbladder, also known as the cholecyst, is a small hollow organ where bile is stored and concentrated before it is released into the small intestine. In humans, the pear-shaped gallbladder lies beneath the liver, although the structure and position of the gallbladder can vary significantly among animal species. It receives and stores bile, produced by the liver, via the common hepatic duct, and releases it via the common bile duct into the duodenum, where the bile helps in the digestion of fats. The gallbladder can be affected by gallstones, formed by material that cannot be dissolved – usually cholesterol or bilirubin, a product of haemoglobin breakdown. These may cause significant pain, particularly in the upper-right corner of the abdomen, and are often treated with removal of the gallbladder (called a cholecystectomy). Cholecystitis, inflammation of the gallbladder, has a wide range of causes, including result from the impaction of gallstones, inf ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cholecystitis
Cholecystitis is inflammation of the gallbladder. Symptoms include right upper abdominal pain, pain in the right shoulder, nausea, vomiting, and occasionally fever. Often gallbladder attacks (biliary colic) precede acute cholecystitis. The pain lasts longer in cholecystitis than in a typical gallbladder attack. Without appropriate treatment, recurrent episodes of cholecystitis are common. Complications of acute cholecystitis include gallstone pancreatitis, common bile duct stones, or inflammation of the common bile duct. More than 90% of the time acute cholecystitis is caused from blockage of the cystic duct by a gallstone. Risk factors for gallstones include birth control pills, pregnancy, a family history of gallstones, obesity, diabetes, liver disease, or rapid weight loss. Occasionally, acute cholecystitis occurs as a result of vasculitis or chemotherapy, or during recovery from major trauma or burns. Cholecystitis is suspected based on symptoms and laboratory testing. Abdom ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cholecystectomy
Cholecystectomy is the surgical removal of the gallbladder. Cholecystectomy is a common treatment of symptomatic gallstones and other gallbladder conditions. In 2011, cholecystectomy was the eighth most common operating room procedure performed in hospitals in the United States. Cholecystectomy can be performed either laparoscopically, or via an open surgical technique. The surgery is usually successful in relieving symptoms, but up to 10 percent of people may continue to experience similar symptoms after cholecystectomy, a condition called postcholecystectomy syndrome. Complications of cholecystectomy include bile duct injury, wound infection, bleeding, retained gallstones, abscess formation and stenosis (narrowing) of the bile duct. Medical use Pain and complications caused by gallstones are the most common reasons for removal of the gallbladder. The gallbladder can also be removed in order to treat biliary dyskinesia or gallbladder cancer. Gallstones are very common but ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Triangle Of Calot
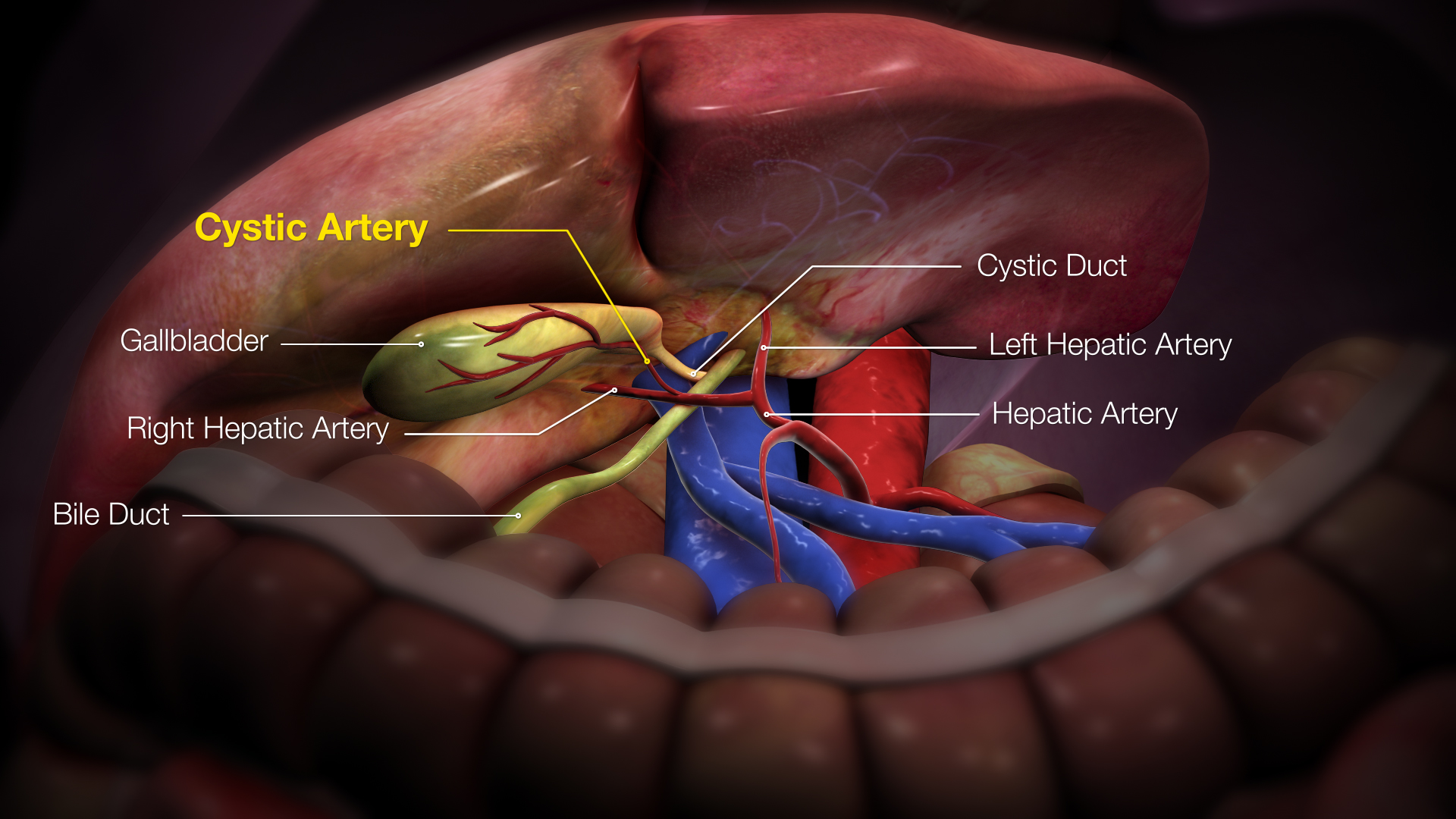
The cystohepatic triangle (or hepatobiliary triangle) is an anatomic space bordered by the cystic duct inferiorly, the common hepatic duct medially, and the inferior surface of the liver superiorly. The cystic artery lies within the hepatobiliary triangle, which is used to locate it during a laparoscopic cholecystectomy. Structure The hepatobiliary triangle is the area bound by the: * cystic duct inferiorly. * common hepatic duct medially. * inferior margin of the liver superiorly.Schwartz's Manual of Surgery BRUNICARDI C.F 10th edition It is covered in peritoneum both anteriorly and posteriorly. It contains the cystic artery and cystic lymph nodes. The right hepatic artery may also pass through the hepatobiliary triangle. Clinical significance General surgeons frequently quiz medical students on this term and the name for the lymph node located within the triangle, Mascagni's lymph node or Lund's node, however many often erroneously refer to it as "Calot's node". The latte ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cystic Artery
The cystic artery (also known as bachelor artery) supplies oxygenated blood to the gallbladder and cystic duct. Most common arrangement In the classic arrangement, occurring with a frequency of approximately 70%, a singular cystic artery originates from the geniculate flexure of the right hepatic artery in the upper portion of the hepatobiliary triangle. A site of origin from a more proximal or distal portion of the right hepatic artery is also considered relatively normal. After separating from the right hepatic artery, the cystic artery travels superiorly to the cystic duct and produces 2 to 4 minor branches, known as ''Calot’s arteries'', that supply part of the cystic duct and cervix of the gallbladder before dividing into the major superficial and deep branches at the superior aspect of the gallbladder neck: * The ''superficial branch'' (or ''anterior branch'') passes subserously over the left aspect of the gallbladder. * The ''deep branch'' (or ''posterior branch'') runs b ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fred Bates Lund
Fred may refer to: People * Fred (name), including a list of people and characters with the name Mononym * Fred (cartoonist) (1931–2013), pen name of Fred Othon Aristidès, French * Fred (footballer, born 1949) (1949–2022), Frederico Rodrigues de Oliveira, Brazilian * Fred (footballer, born 1979), Helbert Frederico Carreiro da Silva, Brazilian * Fred (footballer, born 1983), Frederico Chaves Guedes, Brazilian * Fred (footballer, born 1986), Frederico Burgel Xavier, Brazilian * Fred (footballer, born 1993), Frederico Rodrigues de Paula Santos, Brazilian * Fred Again (born 1993), British songwriter known as FRED Television and movies * '' Fred Claus'', a 2007 Christmas film * ''Fred'' (2014 film), a 2014 documentary film * Fred Figglehorn, a YouTube character created by Lucas Cruikshank ** ''Fred'' (franchise), a Nickelodeon media franchise ** '' Fred: The Movie'', a 2010 independent comedy film * ''Fred the Caveman'', French Teletoon production from 2002 * Fred Flints ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Paolo Mascagni
Paolo Mascagni (25 January 1755 – 19 October 1815) was an Italian physician and anatomist. He is most well known for publishing the first complete description of the lymphatic system. Biography Early life Mascagni was born in the comune of Pomarance (in the Province of Pisa) to Aurelio Mascagni and Elisabetta Burroni, both belonging to old gentry families of Chiusdino (in the Province of Siena). He studied philosophy and medicine at the University of Siena. Upon graduating in 1777, renowned anatomist Pietro Tabarrani took Mascagni as an assistant. Upon Tabarrani's death in 1780, Mascagni was appointed as an anatomy lecturer at the University of Siena. Career As a young man, Mascagni was interested in geological sciences, as evidenced by his several papers on the Lagoni (thermal springs) of Siena and Volterra. Upon graduation, he turned his interest to the human lymphatic system. His many discoveries in this field led to the composition and publication of ''Vasor ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lymphatics Of The Torso
The lymphatic vessels (or lymph vessels or lymphatics) are thin-walled vessels (tubes), structured like blood vessels, that carry lymph. As part of the lymphatic system, lymph vessels are complementary to the cardiovascular system. Lymph vessels are lined by endothelium, endothelial cells, and have a thin layer of smooth muscle, and adventitia that binds the lymph vessels to the surrounding tissue. Lymph vessels are devoted to the propulsion of the lymph from the lymph capillaries, which are mainly concerned with the absorption of interstitial fluid from the tissues. Lymph capillaries are slightly bigger than their counterpart capillary, capillaries of the vascular system. Lymph vessels that carry lymph to a lymph node are called afferent lymph vessels, and those that carry it from a lymph node are called efferent lymph vessels, from where the lymph may travel to another lymph node, may be returned to a vein, or may travel to a larger lymph duct. Lymph ducts drain the lymph into ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |