|
Lumbar Arteries
The lumbar arteries are arteries located in the lower back or lumbar region. The lumbar arteries are in parallel with the intercostals. They are usually four in number on either side, and arise from the back of the aorta, opposite the bodies of the upper four lumbar vertebrae. A fifth pair, small in size, is occasionally present: they arise from the middle sacral artery. They run lateralward and backward on the bodies of the lumbar vertebrae, behind the sympathetic trunk, to the intervals between the adjacent transverse processes, and are then continued into the abdominal wall. The arteries of the right side pass behind the inferior vena cava, and the upper two on each side run behind the corresponding crus of the diaphragm. The arteries of both sides pass beneath the tendinous arches which give origin to the psoas major, and are then continued behind this muscle and the lumbar plexus. They now cross the quadratus lumborum, the upper three arteries running behind, the las ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pelvis
The pelvis (plural pelves or pelvises) is the lower part of the trunk, between the abdomen and the thighs (sometimes also called pelvic region), together with its embedded skeleton (sometimes also called bony pelvis, or pelvic skeleton). The pelvic region of the trunk includes the bony pelvis, the pelvic cavity (the space enclosed by the bony pelvis), the pelvic floor, below the pelvic cavity, and the perineum, below the pelvic floor. The pelvic skeleton is formed in the area of the back, by the sacrum and the coccyx and anteriorly and to the left and right sides, by a pair of hip bones. The two hip bones connect the spine with the lower limbs. They are attached to the sacrum posteriorly, connected to each other anteriorly, and joined with the two femurs at the hip joints. The gap enclosed by the bony pelvis, called the pelvic cavity, is the section of the body underneath the abdomen and mainly consists of the reproductive organs (sex organs) and the rectum, while the pelvic f ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
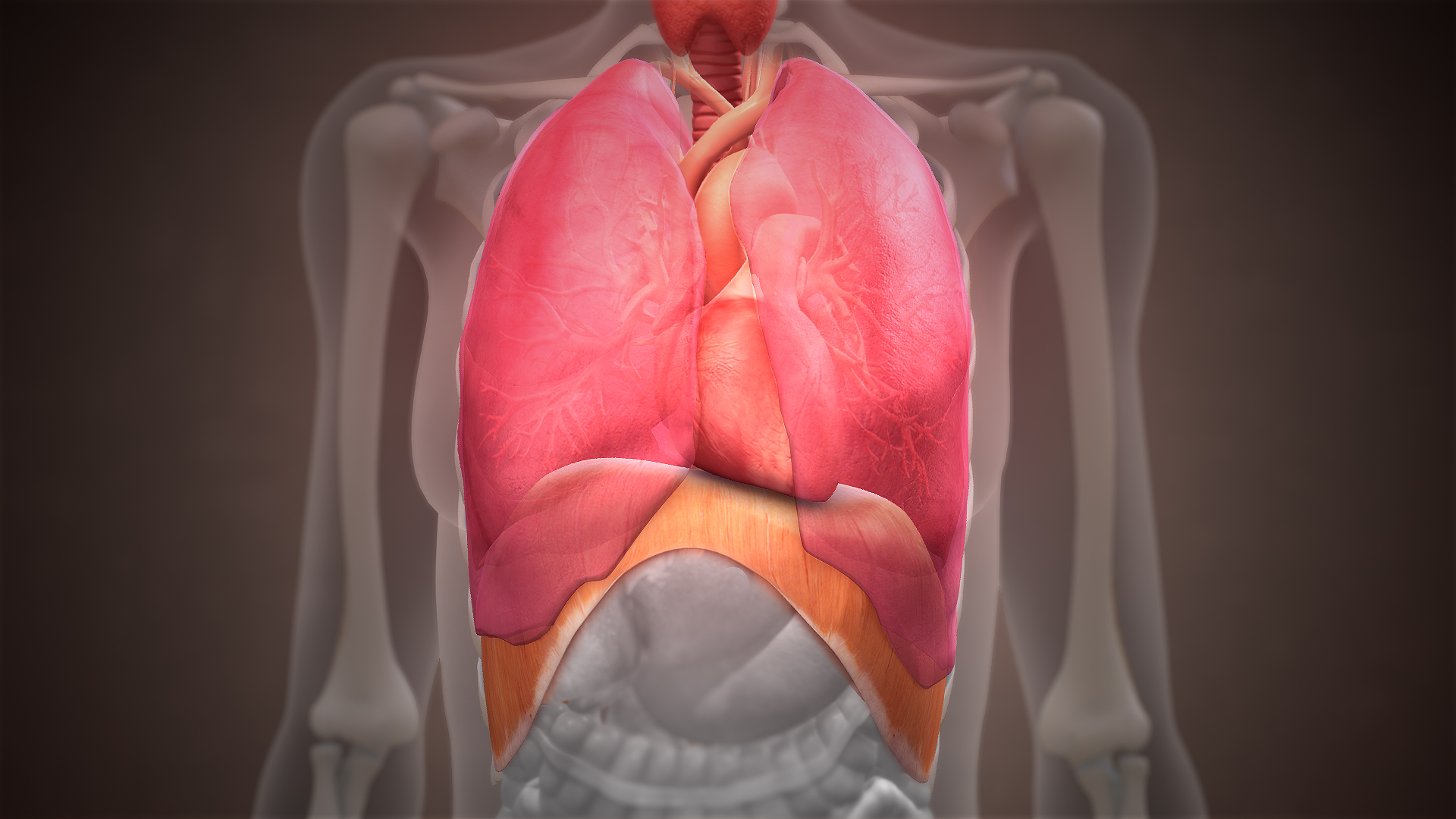
Diaphragm (anatomy)
The thoracic diaphragm, or simply the diaphragm ( grc, διάφραγμα, diáphragma, partition), is a sheet of internal skeletal muscle in humans and other mammals that extends across the bottom of the thoracic cavity. The diaphragm is the most important muscle of respiration, and separates the thoracic cavity, containing the heart and lungs, from the abdominal cavity: as the diaphragm contracts, the volume of the thoracic cavity increases, creating a negative pressure there, which draws air into the lungs. Its high oxygen consumption is noted by the many mitochondria and capillaries present; more than in any other skeletal muscle. The term ''diaphragm'' in anatomy, created by Gerard of Cremona, can refer to other flat structures such as the urogenital diaphragm or pelvic diaphragm, but "the diaphragm" generally refers to the thoracic diaphragm. In humans, the diaphragm is slightly asymmetric—its right half is higher up (superior) to the left half, since the large liver res ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Deep Iliac Circumflex
The deep circumflex iliac artery (or deep iliac circumflex artery) is an artery in the pelvis that travels along the iliac crest of the pelvic bone. Course The deep circumflex iliac artery arises from the lateral aspect of the external iliac artery nearly opposite the origin of the inferior epigastric artery. It ascends obliquely and laterally, posterior to the inguinal ligament, contained in a fibrous sheath formed by the junction of the transversalis fascia and iliac fascia. It travels to the anterior superior iliac spine, where it anastomoses with the ascending branch of the lateral femoral circumflex artery. It then pierces the transversalis fascia and passes medially along the inner lip of the crest of the ilium to a point where it perforates the transversus abdominis muscle. From there, it travels posteriorly between the transversus abdominis muscle and the internal oblique muscle to anastomose with the iliolumbar artery and the superior gluteal artery. Opposite the ant ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Iliolumbar Artery
The iliolumbar artery is the first branch of the posterior trunk of the internal iliac artery. Structure The iliolumbar artery is the first branch of the posterior trunk of the internal iliac artery. It turns upward behind the obturator nerve and the external iliac artery and vein, to the medial border of the psoas major muscle, behind which it divides into: * Lumbar branch of iliolumbar artery * Iliac branch of iliolumbar artery The iliac branch of the iliolumbar artery (ramus iliacus) descends to supply the iliacus muscle; some offsets, running between the muscle and the bone, anastomose with the iliac branches of the obturator artery; one of these enters an oblique ca ... Anastomoses *1. Last lumbar→iliolumbar *2. Lateral sacral↔lateral sacral *3. Middle sacral→lateral sacral *4. Superior hemorrhoidal→middle hemorrhoidal *5. Medial femoral circumflex→inferior gluteal *6. Medial femoral circumflex↔obturator *7. Lateral femoral circumflex→superior gluteal *8. Dee ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Subcostal Arteries
The subcostal arteries, so named because they lie below the last ribs, constitute the lowest pair of branches derived from the thoracic aorta, and are in series with the intercostal arteries. Each passes along the lower border of the twelfth rib behind the kidney and in front of the Quadratus lumborum muscle, and is accompanied by the twelfth thoracic nerve. It then pierces the posterior aponeurosis of the Transversus abdominis, and, passing forward between this muscle and the Internal Oblique, anastomoses with the superior epigastric, lower intercostal, and lumbar arteries. Each subcostal artery gives off a posterior branch which has a similar distribution to the posterior ramus of an intercostal artery. References External links * - "Branches of the ascending aorta, arch of the aorta, and the descending aorta In human anatomy, the descending aorta is part of the aorta, the largest artery in the body. The descending aorta begins at the aortic arch and runs down throu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lower Intercostal
The intercostal arteries are a group of arteries that supply the area between the ribs ("costae"), called the intercostal space. The highest intercostal artery (supreme intercostal artery or superior intercostal artery) is an artery in the human body that usually gives rise to the first and second posterior intercostal arteries, which supply blood to their corresponding intercostal space. It usually arises from the costocervical trunk, which is a branch of the subclavian artery. Some anatomists may contend that there is no supreme intercostal artery, only a supreme intercostal vein. The anterior intercostal branches of internal thoracic artery supply the upper five or six intercostal spaces. The internal thoracic artery (previously called as internal mammary artery) then divides into the superior epigastric artery and musculophrenic artery. The latter gives out the remaining anterior intercostal branches. Two in number in each space, these small vessels pass lateralward, o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Obliquus Internus
The abdominal internal oblique muscle, also internal oblique muscle or interior oblique, is an abdominal muscle in the abdominal wall that lies below the external oblique muscle and just above the transverse abdominal muscle. Structure Its fibers run perpendicular to the external oblique muscle, beginning in the thoracolumbar fascia of the lower back, the anterior 2/3 of the iliac crest (upper part of hip bone) and the lateral half of the inguinal ligament. The muscle fibers run from these points superomedially (up and towards midline) to the muscle's insertions on the inferior borders of the 10th through 12th ribs and the linea alba. In males, the cremaster muscle is also attached to the internal oblique. Nerve supply The internal oblique is supplied by the lower intercostal nerves, as well as the iliohypogastric nerve and the ilioinguinal nerve. Function The internal oblique performs two major functions. Firstly as an accessory muscle of respiration, it acts as an anta ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Transversus Abdominis
The transverse abdominal muscle (TVA), also known as the transverse abdominis, transversalis muscle and transversus abdominis muscle, is a muscle layer of the anterior and lateral (front and side) abdominal wall which is deep to (layered below) the internal oblique muscle. It is thought by most fitness instructors to be a significant component of the core. Structure The transverse abdominal, so called for the direction of its fibers, is the innermost of the flat muscles of the abdomen. It is positioned immediately inside of the internal oblique muscle. The transverse abdominal arises as fleshy fibers, from the lateral third of the inguinal ligament, from the anterior three-fourths of the inner lip of the iliac crest, from the inner surfaces of the cartilages of the lower six ribs, interdigitating with the diaphragm, and from the thoracolumbar fascia. It ends anteriorly in a broad aponeurosis (the Spigelian fascia), the lower fibers of which curve inferomedially (medially and do ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Quadratus Lumborum
The quadratus lumborum muscle, informally called the ''QL'', is a paired muscle of the left and right posterior abdominal wall. It is the deepest abdominal muscle, and commonly referred to as a back muscle. Each is irregular and quadrilateral in shape. The quadratus lumborum muscles originate from the wings of the ilium; their insertions are on the transverse processes of the upper four lumbar vertebrae plus the lower posterior border of the twelfth rib. Contraction of one of the pair of muscles causes '' lateral flexion'' of the lumbar spine, ''elevation'' of the pelvis, or both. Contraction of both causes ''extension'' of the lumbar spine. A disorder of the quadratus lumborum muscles is pain due to muscle fatigue from constant contraction due to prolonged sitting, such as at a computer or in a car.Core Topics in Pain, p. 131, Anita Holdcraft and Sian Jaggar, 2005. Kyphosis and weak gluteal muscles can also contribute to the likelihood of quadratus lumborum pain. Structure The ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lumbar Plexus
The lumbar plexus is a web of nerves (a nervous plexus) in the lumbar region of the body which forms part of the larger lumbosacral plexus. It is formed by the Ventral ramus of spinal nerve, divisions of the first four lumbar nerves (L1-L4) and from contributions of the subcostal nerve (T12), which is the last Thoracic nerves, thoracic nerve. Additionally, the ventral rami of the fourth lumbar nerve pass communicating branches, the lumbosacral trunk, to the sacral plexus. The nerves of the lumbar plexus pass in front of the hip joint and mainly support the anterior part of the thigh.''Thieme Atlas of anatomy'' (2006), pp 470-471 The plexus is formed lateral to the intervertebral foramina and passes through Psoas major muscle, psoas major. Its smaller motor branches are distributed directly to psoas major, while the larger branches leave the muscle at various sites to run obliquely down through the pelvis to leave under the inguinal ligament with the exception of the obturator n ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Psoas Major
The psoas major ( or ; from grc, ψόᾱ, psóā, muscles of the loins) is a long fusiform muscle located in the lateral lumbar region between the vertebral column and the brim of the lesser pelvis. It joins the iliacus muscle to form the iliopsoas. In animals, this muscle is equivalent to the tenderloin. Structure The psoas major is divided into a superficial and a deep part. The deep part originates from the transverse processes of lumbar vertebrae L1–L5. The superficial part originates from the lateral surfaces of the last thoracic vertebra, lumbar vertebrae L1–L4, and the neighboring intervertebral discs. The lumbar plexus lies between the two layers. Together, the iliacus muscle and the psoas major form the iliopsoas, which is surrounded by the iliac fascia. The iliopsoas runs across the iliopubic eminence through the muscular lacuna to its insertion on the lesser trochanter of the femur. The iliopectineal bursa separates the tendon of the iliopsoas muscle from th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tendinous Arch Of Pelvic Fascia
At the level of a line extending from the lower part of the pubic symphysis to the spine of the ischium is a thickened whitish band in this upper layer of the diaphragmatic part of the pelvic fascia. It is termed the tendinous arch or white line of the pelvic fascia, and marks the line of attachment of the special fascia (pars endopelvina fasciae pelvis) which is associated with the pelvic viscera In biology, an organ is a collection of tissues joined in a structural unit to serve a common function. In the hierarchy of life, an organ lies between tissue and an organ system. Tissues are formed from same type cells to act together in a f .... It joins the fascia of the pubocervical fascia that covers the anterior wall of the vagina. If this fascia falls, the ipsilateral side of the vagina falls, carrying with it the bladder and the urethra, and thus contributing to urinary incontinence. References External links * - "The Female Pelvis: Muscles of the Pelvic Diaphragm" * ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |