|
Lucius Caecilius Metellus (tribune 49 BC)
{{AncientRome-bio-stub ...
Lucius Caecilius Metellus was tribune of the plebs in 49 BC, when he vetoed Julius Caesar's raiding of the Roman state treasury during Caesar's Civil War. Plutarch claims that Metellus' life was threatened when he interposed his veto. References 1st-century BC Romans Tribunes of the plebs Marcus Marcus, Markus, Márkus or MărcuÈ™ may refer to: * Marcus (name), a masculine given name * Marcus (praenomen), a Roman personal name Places * Marcus, a main belt asteroid, also known as (369088) Marcus 2008 GG44 * MărcuÅŸ, a village in DobârlÄ ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Caesar's Civil War
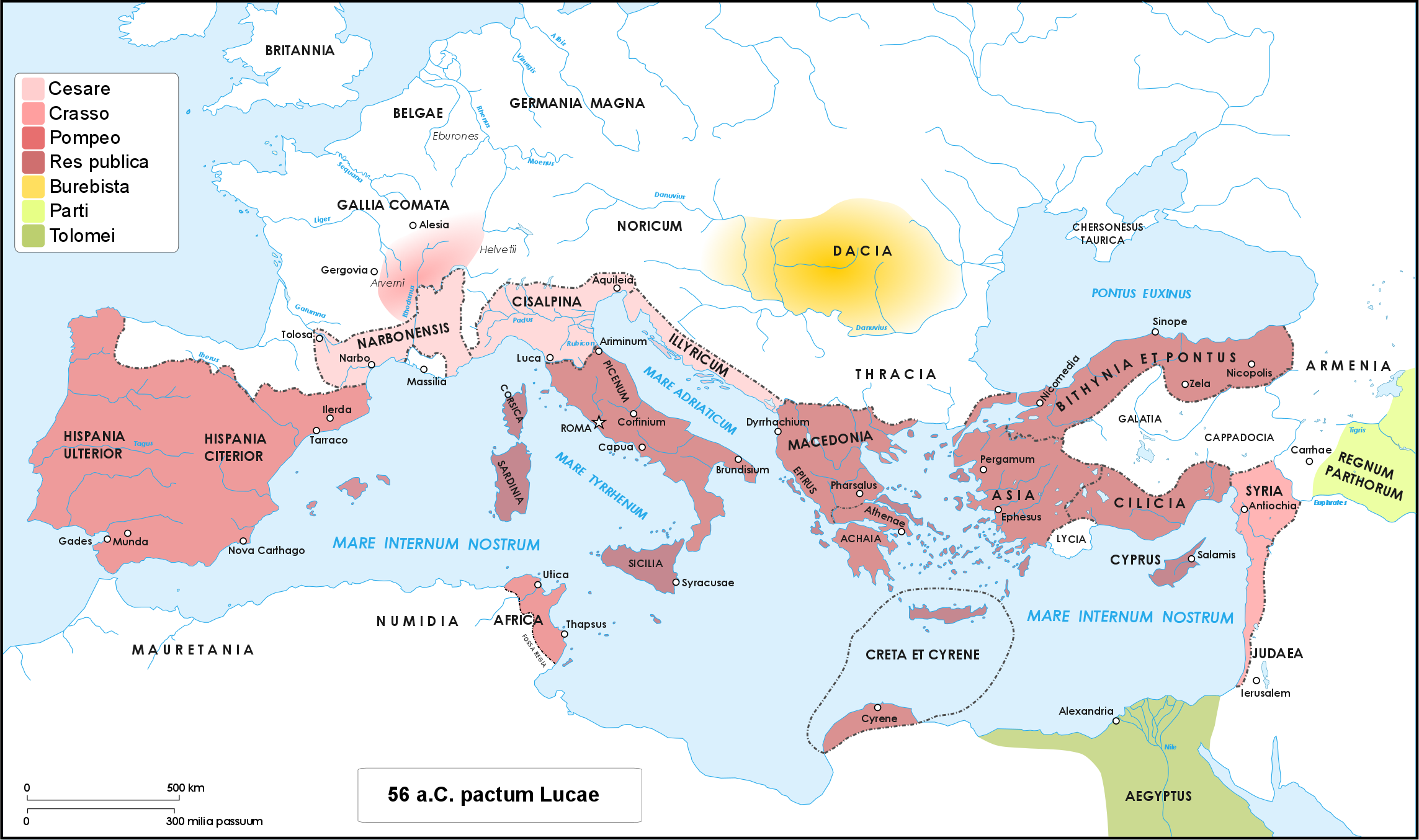
Caesar's civil war (49–45 BC) was one of the last politico-military conflicts of the Roman Republic before its reorganization into the Roman Empire. It began as a series of political and military confrontations between Gaius Julius Caesar and Gnaeus Pompeius Magnus. Before the war, Caesar had led an invasion of Gaul for almost ten years. A build-up of tensions starting in late 49 BC, with both Caesar and Pompey refusing to back down led, however, to the outbreak of civil war. Eventually, Pompey and his allies induced the Senate to demand Caesar give up his provinces and armies. Caesar refused and instead marched on Rome. The war was a four-year-long politico-military struggle, fought in Italy, Illyria, Greece, Egypt, Africa, and Hispania. Pompey defeated Caesar in 48 BC at the Battle of Dyrrhachium, but was himself defeated decisively at the Battle of Pharsalus. Many former Pompeians, including Marcus Junius Brutus and Cicero, surrendered after the battle, wh ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tribune Of The Plebs
Tribune of the plebs, tribune of the people or plebeian tribune ( la, tribunus plebis) was the first office of the Roman Republic, Roman state that was open to the plebs, plebeians, and was, throughout the history of the Republic, the most important check on the power of the Roman Senate and Roman magistrate, magistrates. These tribunes had the power to convene and preside over the ''Plebeian Council, Concilium Plebis'' (people's assembly); to summon the senate; to propose legislation; and to intervene on behalf of plebeians in legal matters; but the most significant power was to veto the actions of the Roman consul, consuls and other magistrates, thus protecting the interests of the plebeians as a class. The tribunes of the plebs were sacrosanct, meaning that any assault on their person was punishable by death. In Roman Empire, imperial times, the powers of the tribunate were granted to the Roman emperor, emperor as a matter of course, and the office itself lost its independence a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Julius Caesar
Gaius Julius Caesar (; ; 12 July 100 BC – 15 March 44 BC), was a Roman general and statesman. A member of the First Triumvirate, Caesar led the Roman armies in the Gallic Wars before defeating his political rival Pompey in a civil war, and subsequently became dictator from 49 BC until his assassination in 44 BC. He played a critical role in the events that led to the demise of the Roman Republic and the rise of the Roman Empire. In 60 BC, Caesar, Crassus and Pompey formed the First Triumvirate, an informal political alliance that dominated Roman politics for several years. Their attempts to amass power as were opposed by the within the Roman Senate, among them Cato the Younger with the frequent support of Cicero. Caesar rose to become one of the most powerful politicians in the Roman Republic through a string of military victories in the Gallic Wars, completed by 51 BC, which greatly extended Roman territory. During this time he both invaded Britain and built a b ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Caesar's Civil War
Caesar's civil war (49–45 BC) was one of the last politico-military conflicts of the Roman Republic before its reorganization into the Roman Empire. It began as a series of political and military confrontations between Gaius Julius Caesar and Gnaeus Pompeius Magnus. Before the war, Caesar had led an invasion of Gaul for almost ten years. A build-up of tensions starting in late 49 BC, with both Caesar and Pompey refusing to back down led, however, to the outbreak of civil war. Eventually, Pompey and his allies induced the Senate to demand Caesar give up his provinces and armies. Caesar refused and instead marched on Rome. The war was a four-year-long politico-military struggle, fought in Italy, Illyria, Greece, Egypt, Africa, and Hispania. Pompey defeated Caesar in 48 BC at the Battle of Dyrrhachium, but was himself defeated decisively at the Battle of Pharsalus. Many former Pompeians, including Marcus Junius Brutus and Cicero, surrendered after the battle, wh ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
1st-century BC Romans
The 1st century was the century spanning AD 1 ( I) through AD 100 ( C) according to the Julian calendar. It is often written as the or to distinguish it from the 1st century BC (or BCE) which preceded it. The 1st century is considered part of the Classical era, epoch, or historical period. The 1st century also saw the appearance of Christianity. During this period, Europe, North Africa and the Near East fell under increasing domination by the Roman Empire, which continued expanding, most notably conquering Britain under the emperor Claudius ( AD 43). The reforms introduced by Augustus during his long reign stabilized the empire after the turmoil of the previous century's civil wars. Later in the century the Julio-Claudian dynasty, which had been founded by Augustus, came to an end with the suicide of Nero in AD 68. There followed the famous Year of Four Emperors, a brief period of civil war and instability, which was finally brought to an end by Vespasian, ninth Roman em ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tribunes Of The Plebs
Tribune of the plebs, tribune of the people or plebeian tribune ( la, tribunus plebis) was the first office of the Roman state that was open to the plebeians, and was, throughout the history of the Republic, the most important check on the power of the Roman Senate and magistrates. These tribunes had the power to convene and preside over the ''Concilium Plebis'' (people's assembly); to summon the senate; to propose legislation; and to intervene on behalf of plebeians in legal matters; but the most significant power was to veto the actions of the consuls and other magistrates, thus protecting the interests of the plebeians as a class. The tribunes of the plebs were sacrosanct, meaning that any assault on their person was punishable by death. In imperial times, the powers of the tribunate were granted to the emperor as a matter of course, and the office itself lost its independence and most of its functions.''Oxford Classical Dictionary'', 2nd Ed. (1970), "Tribuni Plebis." It was cu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |