|
Luciferin Binding Protein
Luciferin (from the Latin ''lucifer'', "light-bearer") is a generic term for the light-emitting compound found in organisms that generate bioluminescence. Luciferins typically undergo an enzyme-catalyzed reaction with molecular oxygen. The resulting transformation, which usually involves splitting off a molecular fragment, produces an excited state intermediate that emits light upon decaying to its ground state. The term may refer to molecules that are substrates for both luciferases and photoproteins. Types Luciferins are a class of small-molecule substrates that react with oxygen in the presence of a luciferase (an enzyme) to release energy in the form of light. It is not known just how many types of luciferins there are, but some of the better-studied compounds are listed below. Because of the chemical diversity of luciferins, there is no clear unifying mechanism of action, except that all require molecular oxygen, The variety of luciferins and luciferases, their diverse ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Oxygen
Oxygen is the chemical element with the symbol O and atomic number 8. It is a member of the chalcogen group in the periodic table, a highly reactive nonmetal, and an oxidizing agent that readily forms oxides with most elements as well as with other compounds. Oxygen is Earth's most abundant element, and after hydrogen and helium, it is the third-most abundant element in the universe. At standard temperature and pressure, two atoms of the element bind to form dioxygen, a colorless and odorless diatomic gas with the formula . Diatomic oxygen gas currently constitutes 20.95% of the Earth's atmosphere, though this has changed considerably over long periods of time. Oxygen makes up almost half of the Earth's crust in the form of oxides.Atkins, P.; Jones, L.; Laverman, L. (2016).''Chemical Principles'', 7th edition. Freeman. Many major classes of organic molecules in living organisms contain oxygen atoms, such as proteins, nucleic acids, carbohydrates, and fats, as ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Brittle Star
Brittle stars, serpent stars, or ophiuroids (; ; referring to the serpent-like arms of the brittle star) are echinoderms in the class Ophiuroidea, closely related to starfish. They crawl across the sea floor using their flexible arms for locomotion. The ophiuroids generally have five long, slender, whip-like arms which may reach up to in length on the largest specimens. The Ophiuroidea contain two large clades, Ophiurida (brittle stars) and Euryalida (basket stars). Over 2,000 species of brittle stars live today. More than 1,200 of these species are found in deep waters, greater than 200 m deep. Range The ophiuroids diverged in the Early Ordovician, about 500 million years ago. Ophiuroids can be found today in all of the major marine provinces, from the poles to the tropics. Basket stars are usually confined to the deeper parts of this range; Ophiuroids are known even from abyssal (>6,000 m) depths. However, brittle stars are also common members of reef communities, where t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Squid
True squid are molluscs with an elongated soft body, large eyes, eight arms, and two tentacles in the superorder Decapodiformes, though many other molluscs within the broader Neocoleoidea are also called squid despite not strictly fitting these criteria. Like all other cephalopods, squid have a distinct head, bilateral symmetry, and a mantle. They are mainly soft-bodied, like octopuses, but have a small internal skeleton in the form of a rod-like gladius (cephalopod), gladius or pen, made of chitin. Squid diverged from other cephalopods during the Jurassic and occupy a similar role to teleost fish as open water predators of similar size and behaviour. They play an important role in the open water food web. The two long tentacles are used to grab prey and the eight arms to hold and control it. The beak then cuts the food into suitable size chunks for swallowing. Squid are rapid swimmers, moving by Aquatic locomotion#Jet propulsion, jet propulsion, and largely locate their ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cnidarian
Cnidaria () is a phylum under kingdom Animalia containing over 11,000 species of aquatic animals found both in freshwater and marine environments, predominantly the latter. Their distinguishing feature is cnidocytes, specialized cells that they use mainly for capturing prey. Their bodies consist of mesoglea, a non-living jelly-like substance, sandwiched between two layers of epithelium that are mostly one cell thick. Cnidarians mostly have two basic body forms: swimming medusae and sessile polyps, both of which are radially symmetrical with mouths surrounded by tentacles that bear cnidocytes. Both forms have a single orifice and body cavity that are used for digestion and respiration. Many cnidarian species produce colonies that are single organisms composed of medusa-like or polyp-like zooids, or both (hence they are trimorphic). Cnidarians' activities are coordinated by a decentralized nerve net and simple receptors. Several free-swimming species of Cubozoa and Scyphozo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ctenophore
Ctenophora (; ctenophore ; ) comprise a phylum of marine invertebrates, commonly known as comb jellies, that inhabit sea waters worldwide. They are notable for the groups of cilia they use for swimming (commonly referred to as "combs"), and they are the largest animals to swim with the help of cilia. Depending on the species, adult ctenophores range from a few millimeters to in size. Only 100 to 150 species have been validated, and possibly another 25 have not been fully described and named. The textbook examples are cydippids with egg-shaped bodies and a pair of retractable tentacles fringed with tentilla ("little tentacles") that are covered with colloblasts, sticky cells that capture prey. Their bodies consist of a mass of jelly, with a layer two cells thick on the outside, and another lining the internal cavity. The phylum has a wide range of body forms, including the egg-shaped cydippids with retractable tentacles that capture prey, the flat generally combless platyct ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
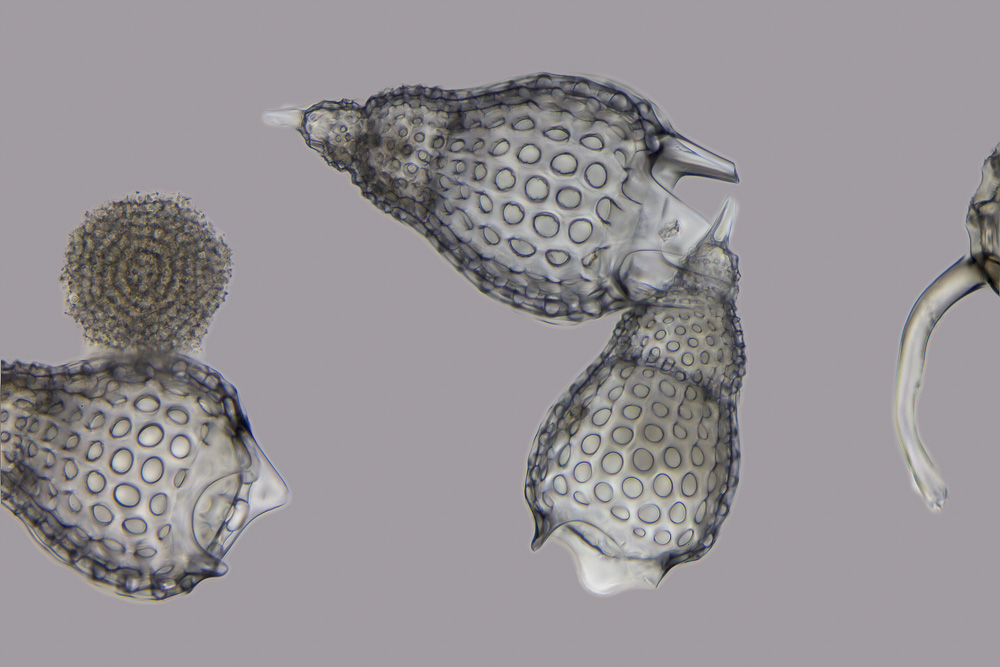
Radiolarian
The Radiolaria, also called Radiozoa, are protozoa of diameter 0.1–0.2 mm that produce intricate mineral skeletons, typically with a central capsule dividing the cell into the inner and outer portions of endoplasm and ectoplasm. The elaborate mineral skeleton is usually made of silica. They are found as zooplankton throughout the global ocean. As zooplankton, radiolarians are primarily heterotrophic, but many have photosynthetic endosymbionts and are, therefore, considered mixotrophs. The skeletal remains of some types of radiolarians make up a large part of the cover of the ocean floor as siliceous ooze. Due to their rapid change as species and intricate skeletons, radiolarians represent an important diagnostic fossil found from the Cambrian onwards. Description Radiolarians have many needle-like pseudopods supported by bundles of microtubules, which aid in the radiolarian's buoyancy. The cell nucleus and most other organelles are in the endoplasm, while the ectoplasm is ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Coelenterazine
Coelenterazine is a luciferin, a molecule that emits light after reaction with oxygen, found in many aquatic organisms across eight phyla. It is the substrate of many luciferases such as ''Renilla reniformis'' luciferase (Rluc), ''Gaussia'' luciferase (Gluc), and photoproteins, including aequorin, and obelin. All these proteins catalyze the oxidation of this substance, a reaction catalogued EC 1.13.12.5. History Coelenterazine was simultaneously isolated and characterized by two groups studying the luminescent organisms sea pansy (''Renilla reniformis'') and the cnidarian ''Aequorea victoria'', respectively. Both groups independently discovered that the same compound was used in both luminescent systems. The molecule was named after the now-obsolete phylum coelenterata. Likewise, the two main metabolites – coelenteramide and coelenteramine – were named after their respective functional groups. While coelenterazine was first discovered in ''Aequorea victoria'', it was lat ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bioluminescent Bacteria
Bioluminescent bacteria are Bioluminescence, light-producing bacteria that are predominantly present in sea water, marine sediments, the surface of decomposing fish and in the gut of marine animals. While not as common, bacterial bioluminescence is also found in terrestrial and freshwater bacteria. These bacteria may be free living (such as ''Vibrio harveyi'') or in symbiosis with animals such as the Hawaiian Bobtail Squid, Hawaiian Bobtail squid (''Aliivibrio fischeri'') or terrestrial nematodes (''Photorhabdus luminescens''). The host organisms provide these bacteria a safe home and sufficient nutrition. In exchange, the hosts use the light produced by the bacteria for camouflage, prey and/or mate attraction. Bioluminescent bacteria have evolved symbiotic relationships with other organisms in which both participants benefit close to equally. Another possible reason bacteria use luminescence reaction is for quorum sensing, an ability to regulate gene expression in response to bacter ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fatty Aldehyde
Fatty aldehydes are aliphatic, long-chain aldehydes which may be mono- or polyunsaturated. The fatty aldehydes include compounds such as octanal, nonanal, decanal or dodecanal. The nomenclature is derived from the nomenclature of the alkanes, the ending ''-al'' is added to indicate the aldehyde group. Occurrence Fatty aldehydes are a natural component of many natural ingredients such as the essential oils of various citrus fruits. Decanal, for example, is a component of orange peel. The pheromone cocktails of various insect pheromones contain fatty aldehydes. Fat aldehydes were also detected in the heart muscle of mammals. Preparation Fatty aldehydes can be prepared by dehydrogenation of fatty alcohols on copper-zinc catalysts. By the hydroformylation of alkenes, fatty aldehydes are produced on a large industrial scale. Use A large proportion of the fatty aldehydes prepared by hydroformylation is directly processed further to fatty alcohols. Many fatty aldehydes find use a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Flavin Mononucleotide
Flavin mononucleotide (FMN), or riboflavin-5′-phosphate, is a biomolecule produced from riboflavin (vitamin B2) by the enzyme riboflavin kinase and functions as the prosthetic group of various oxidoreductases, including NADH dehydrogenase, as well as cofactor in biological blue-light photo receptors. During the catalytic cycle, a reversible interconversion of the oxidized (FMN), semiquinone (FMNH•), and reduced (FMNH2) forms occurs in the various oxidoreductases. FMN is a stronger oxidizing agent than NAD and is particularly useful because it can take part in both one- and two-electron transfers. In its role as blue-light photo receptor, (oxidized) FMN stands out from the 'conventional' photo receptors as the signaling state and not an E/Z isomerization. It is the principal form in which riboflavin is found in cells and tissues. It requires more energy to produce, but is more soluble than riboflavin. In cells, FMN occurs freely circulating but also in several covalently b ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Luciferin Bacterial
Luciferin (from the Latin ''lucifer'', "light-bearer") is a generic term for the light-emitting compound found in organisms that generate bioluminescence. Luciferins typically undergo an enzyme-catalyzed reaction with molecular oxygen. The resulting transformation, which usually involves splitting off a molecular fragment, produces an excited state intermediate that emits light upon decaying to its ground state. The term may refer to molecules that are substrates for both luciferases and photoproteins. Types Luciferins are a class of small-molecule substrates that react with oxygen in the presence of a luciferase (an enzyme) to release energy in the form of light. It is not known just how many types of luciferins there are, but some of the better-studied compounds are listed below. Because of the chemical diversity of luciferins, there is no clear unifying mechanism of action, except that all require molecular oxygen, The variety of luciferins and luciferases, their diverse r ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |



.jpg)