|
Lucan, Dublin
Lucan ( ; ) is a suburban village to the west of Dublin, Ireland, located 12 km from Dublin city centre, on the River Liffey. It is near the Strawberry Beds and Lucan Weir, and at the confluence of the River Griffeen. It is mostly in the local government area of South Dublin, with the exception of the North Lucan areas of Laraghcon, Coldblow and Saint Catherine's Park, which are in Fingal. Lucan is in a townland and Civil parishes in Ireland, civil parish of the same name, in the Newcastle (County Dublin barony), barony of Newcastle. Road access to Lucan is from the N4 road (Ireland), N4, and the M50 motorway (Ireland), M50 motorway at Junction 7. Etymology In the Irish language, refers to the Althaea officinalis, marsh-mallow plant, used up to modern times in folk medicine (for sprains and chest infections) and sweet manufacture, and so the name could be rendered as "place of marsh-mallow plants" or "land abounding in marsh-mallows." The plant grows in the Liffey Valley ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
R109 Road (Ireland)
R1, R.I., R01 or R-1 may refer to: Biology * R1 plasmid, a plasmid found in E Coli * ATC code R01 ''Nasal preparations'', a subgroup of the Anatomical Therapeutic Chemical Classification System * Haplogroup R1 (Y-DNA), a human Y-chromosome DNA haplogroup * The R1 vein in insect wings Computing * DeepSeek-R1, an open-source large language model released by DeepSeek in January 2025 * R1 (expert system), a 1978 expert system written by John McDermott * .r01, a RAR file extension * an alternate name for the Rice Institute Computer, an innovative computer extant at Rice University from 1959 to 1971 Military equipment * R-1 tank, a Romanian tank from World War II * R-1 (missile), a post World War II Russian rocket * AEG R.I, a 1918 German super-heavy bomber design * DFW R.I, a 1916 German prototype bomber aircraft * HMS Caprice, a destroyer originally designated with Pennant Number R01 * Linke-Hofmann R.I, a World War I German prototype bomber aircraft * Polikarpov R-1, a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Irish Grid Reference System
The Irish grid reference system is a system of geographic grid references used for paper mapping in Ireland (both Northern Ireland and the Republic of Ireland). Any location in Ireland can be described in terms of its distance from the origin (0, 0), which lies off the southwest coast. The Irish grid partially overlaps the British grid, and uses a similar co-ordinate system but with a meridian more suited to its westerly location. Usage In general, neither Ireland nor Great Britain uses latitude or longitude in describing internal geographic locations. Instead grid reference systems are used for mapping. The national grid referencing system was devised by the Ordnance Survey, and is heavily used in their survey data, and in maps (whether published by the Ordnance Survey of Ireland, the Ordnance Survey of Northern Ireland or commercial map producers) based on those surveys. Additionally grid references are commonly quoted in other publications and data sources, such as guide ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
National Inventory Of Architectural Heritage
The National Inventory of Architectural Heritage (NIAH) maintains a central database of the architectural heritage of the Republic of Ireland covering the period since 1700 in complement to the Archaeological Survey of Ireland, which focuses on archaeological sites of the pre-1700 period. As of 2022, there were over 50,000 records in the database, including buildings, monuments, street furniture and other structures. It does not cover Northern Ireland. Buildings recorded in the database are given a rating, either national or regional. Formation The NIAH is a unit of the Heritage Division within the Department of Housing, Local Government and Heritage. The unit was founded in 1990 to address the obligations of the Convention for the Protection of the Architectural Heritage of Europe of which Ireland is signatory. Initially, the NIAH existed only on a non-statutory basis with the task to create and maintain an inventory of to be protected buildings and sites. The legal framework for ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
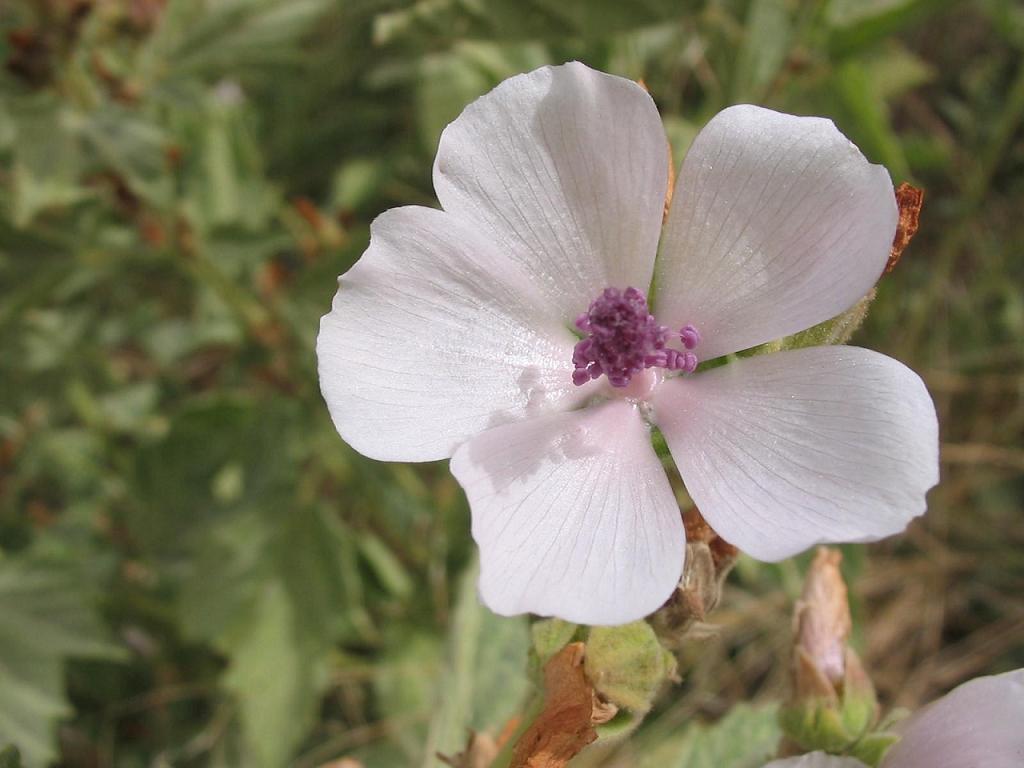
Althaea Officinalis
''Althaea officinalis'', the marsh mallow or marshmallow, is a species of flowering plant indigenous to Europe, Western Asia and North Africa, which is used in herbalism and as an ornamental plant. Description This herbaceous perennial plant, perennial grows to tall and puts out only a few lateral branches. The whole plant is softly stellate-hairy, especially the leaves, which are broadly triangular to oval, often with 3-5 shallow lobes, irregularly toothed, with cordate to cuneate bases. Leaf size varies considerably, up to long, and wide. The leaves are arranged alternately along the stem, with no stipules, on petioles up to . The inflorescences occur in the leaf axils and at the top of the stem and consist of panicles of 1-many flowers. The flowers are actinomorphic with 5 lilac/pink petals up to 2 cm long and 5 green sepals which are much shorter than the petals, and fused at the base. Below the petals is a cup-shaped epicalyx with 6-9 narrow, triangular lobes, half the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Irish Language
Irish (Standard Irish: ), also known as Irish Gaelic or simply Gaelic ( ), is a Celtic language of the Indo-European language family. It is a member of the Goidelic languages of the Insular Celtic sub branch of the family and is indigenous language, indigenous to the island of Ireland. It was the majority of the population's first language until the 19th century, when English (language), English gradually became dominant, particularly in the last decades of the century, in what is sometimes characterised as a result of linguistic imperialism. Today, Irish is still commonly spoken as a first language in Ireland's Gaeltacht regions, in which 2% of Ireland's population lived in 2022. The total number of people (aged 3 and over) in Ireland who declared they could speak Irish in April 2022 was 1,873,997, representing 40% of respondents, but of these, 472,887 said they never spoke it and a further 551,993 said they only spoke it within the education system. Linguistic analyses o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
M50 Motorway (Ireland)
The M50 motorway () is a C-shaped orbital Controlled-access highway, motorway in Dublin and the busiest motorway in Republic of Ireland, Ireland. The current route was built in various sections over the course of 27 years, from 1983 to 2010. It begins at Dublin Port, running northward through the Dublin Port Tunnel and along a portion of the Airport Motorway. It then turns west at its junction with the M1 Motorway (Republic of Ireland), M1, circling the northern, western and southern suburbs of Dublin, before merging with the N11 road (Ireland), M11 at Shankill, Dublin, Shankill in South East Dublin. The road forms part of European route E01. An orbital motorway for Dublin was first proposed in the Dublin Transportation Study of 1971. Construction began on the first section, the Western Parkway (J6-J11) in 1987, and opened to traffic in 1990. This was followed by the Northern Cross Route (J3-J6) in 1996, the Southern Cross Route (J11-J13) in 2001, and the Southeastern Motorway ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
N4 Road (Ireland)
The N4 road is a national primary road in Ireland, running from Dublin to the northwest of Ireland and Sligo town. The M6 to Galway diverges from this route after Kinnegad, while the N5 to Westport diverges at Longford town. Most sections of the N4 that are motorway-standard are designated the M4 motorway. Road standard The N4 originates at an intersection with the M50 motorway at Junction 7. This is also Junction 1 of the N/M4. The Liffey Valley Shopping Centre is located at Junction 2. The road has three lanes and a bus lane in each direction between the M50 and Junction 5 which is also the start of the M4 motorway at Leixlip. The N4 was the only one of the main inter-urban national routes whose dual-carriageway section continued into the city centre; however, the section inside the M50 was re-classified as the R148 in 2012. Heading west, the PPP motorway section (see below) ends west of Kinnegad, and the motorway terminates 5 km further west; it continues ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Placenames Database Of Ireland
The Placenames Database of Ireland (), also known as , is a database and archive of place names in Ireland. It was created by Fiontar, Dublin City University in collaboration with the Placenames Branch of the Department of Tourism, Culture, Arts, Gaeltacht, Sport and Media. The website is a public resource primarily aimed at journalists and translators, students and teachers, historians and researchers in genealogy. Placenames Commission and Placenames Branch The Placenames Commission () was established by the Department of Finance in 1946 to advise Ordnance Survey Ireland and the government of what the Irish name of places should be. Although both the 1922 Constitution of the Irish Free State and the current constitution adopted in 1937 recognised Irish as the national language, the law in regard to placenames was carried over from the 19th-century UK statutes which established the Ordnance Survey and Griffith's Valuation, under which only an English-language name had offi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Newcastle (County Dublin Barony)
Newcastle () is a feudal title of nobility and one of the Barony (Ireland), baronies of Republic of Ireland, Ireland. It was constituted as part of the old county of County Dublin, Dublin. Today, it lies in the modern Counties of Ireland, county of South Dublin. At the heart of the barony is the Civil parishes in Ireland, civil parish of the same name - Newcastle, South Dublin, Newcastle - which is one of eleven civil parishes in the barony. The ruins of the eponymous castle, also known as Newcastle-Lyons, are located in the townland of Newcastle South. The town with the biggest population in the barony is Lucan, Dublin, Lucan. Location It is one of seven and a half baronies that used to comprise the old Counties of Ireland, county of Dublin.According to the "Local Government Act, 2001", section 10(2): "The State continues to stand divided into local government areas to be known as counties and cities which are the areas set out in Parts 1 and 2, respectively, of Schedule 5." It is ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Civil Parishes In Ireland
Civil parishes () are units of territory in the island of Ireland that have their origins in old Gaelic territorial divisions. They were adopted by the Anglo-Norman Lordship of Ireland and then by the Elizabethan Kingdom of Ireland, and were formalised as land divisions at the time of the Plantations of Ireland. They no longer correspond to the boundaries of Roman Catholic or Church of Ireland parishes, which are generally larger. Their use as administrative units was gradually replaced by Poor_law_union#Ireland, Poor Law Divisions in the 19th century, although they were not formally abolished. Today they are still sometimes used for legal purposes, such as to locate property in deeds of property registered between 1833 and 1946. Origins The Irish parish was based on the Gaelic territorial unit called a ''túath'' or ''Trícha cét''. Following the Norman invasion of Ireland, the Anglo-Normans, Anglo-Norman barons retained the ''tuath'', later renamed a parish or manor, as a un ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Townland
A townland (; Ulster-Scots: ''toonlann'') is a traditional small land division used in Ireland and in the Western Isles of Scotland, typically covering . The townland system is of medieval Gaelic origin, predating the Norman invasion, and most have Irish-derived names. However, some townland names and boundaries come from Norman manors, plantation divisions, or later creations of the Ordnance Survey.Connolly, S. J., ''The Oxford Companion to Irish History, page 577. Oxford University Press, 2002. ''Maxwell, Ian, ''How to Trace Your Irish Ancestors'', page 16. howtobooks, 2009. Townlands cover the whole island of Ireland, and the total number of inhabited townlands in Ireland was 60,679 in 1911. The total number recognised by the Placenames Database of Ireland as of 2014 was 61,098, including uninhabited townlands. Etymology The term "townland" in English is derived from the Old English word ''tūn'', denoting an enclosure. The term describes the smallest unit of land di ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |