|
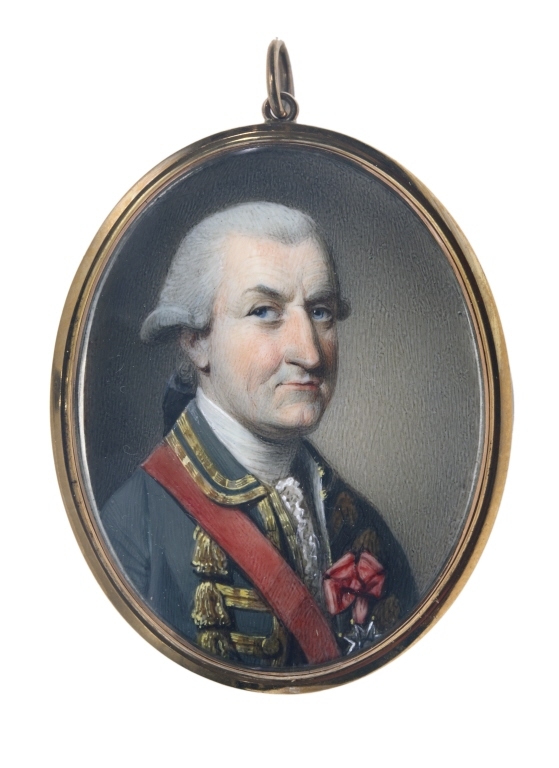
Luc De La Corne
Luc de la Corne, (1711 – October 1, 1784) also known as Saint Luc, was the son of Jean-Louis de La Corne de Chaptes (1666-1732), King's Lieutenant at Montreal, and Marie Pécaudy de Contrecœur. Saint-Luc was an officer in the Compagnies Franches de la Marine; his brother Louis de la Corne, Chevalier de la Corne, later became a very successful merchant at Montreal. Though relatively unknown, he played a major role in American and Canadian history. He is most famous for returning from the shipwreck of the '' Auguste'' off the coast of Cape Breton, Nova Scotia, at the age of fifty, during the dead of winter, to Quebec City - a trek of 700 miles (1,125 kilometres). He had a varied and courageous military career which earned him the [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Saint Luc De La Corne
In religious belief, a saint is a person who is recognized as having an exceptional degree of holiness, likeness, or closeness to God. However, the use of the term ''saint'' depends on the context and denomination. In Catholic, Eastern Orthodox, Anglican, Oriental Orthodox, and Lutheran doctrine, all of their faithful deceased in Heaven are considered to be saints, but some are considered worthy of greater honor or emulation. Official ecclesiastical recognition, and consequently a public cult of veneration, is conferred on some denominational saints through the process of canonization in the Catholic Church or glorification in the Eastern Orthodox Church after their approval. While the English word ''saint'' originated in Christianity, historians of religion tend to use the appellation "in a more general way to refer to the state of special holiness that many religions attribute to certain people", referring to the Jewish tzadik, the Islamic walī, the Hindu rishi or Sikh gur ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pierre Gaultier De Varennes, Sieur De La Vérendrye
Pierre Gaultier de Varennes, sieur de La Vérendrye (17 November 1685 – 5 December 1749) was a French Canadian military officer, fur trader, and explorer. In the 1730s, he and his four sons explored the area west of Lake Superior and established trading posts there. They were part of a process that added Western Canada to the original New France territory that was centred along the Saint Lawrence basin. He was the first known European to reach present-day North Dakota and the upper Missouri River in the United States. In the 1740s, two of his sons crossed the prairie as far as present-day Wyoming, United States and were the first Europeans to see the Rocky Mountains north of New Mexico. Early life Born in Trois-Rivières, New France, Pierre was the eldest son of René Gaultier de Varennes, who came to Canada as a soldier in 1665, and Marie, the daughter of Pierre Boucher, the first Governor of Trois-Rivières. The Gaultier family were minor nobility or landowners ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
People Of New France
A person ( : people) is a being that has certain capacities or attributes such as reason, morality, consciousness or self-consciousness, and being a part of a culturally established form of social relations such as kinship, ownership of property, or legal responsibility. The defining features of personhood and, consequently, what makes a person count as a person, differ widely among cultures and contexts. In addition to the question of personhood, of what makes a being count as a person to begin with, there are further questions about personal identity and self: both about what makes any particular person that particular person instead of another, and about what makes a person at one time the same person as they were or will be at another time despite any intervening changes. The plural form "people" is often used to refer to an entire nation or ethnic group (as in "a people"), and this was the original meaning of the word; it subsequently acquired its use as a plural form of per ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
British Indian Department
The Indian Department was established in 1755 to oversee relations between the British Empire and the First Nations of North America. The imperial government ceded control of the Indian Department to the Province of Canada in 1860, thus setting the stage for the development of the present-day Department of Crown–Indigenous Relations and Northern Affairs Canada. During its existence, the Indian Department served both a diplomatic and a military role. Its daily responsibilities were largely civil in nature, such as the administration of justice, the management of the fur trade, and the employment of blacksmiths, teachers, and missionaries. At the same time, the Department was expected to mobilize and lead Indigenous warriors in times of crisis and conflict. Theoretically, control over the Indian Department rested with the senior-most administrator in British America, initially the Commander-in-Chief of the British forces in North America, and later the Governor General of the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
1784 Deaths
Events January–March * January 6 – Treaty of Constantinople: The Ottoman Empire agrees to Russia's annexation of the Crimea. * January 14 – The Congress of the United States ratifies the Treaty of Paris with Great Britain to end the American Revolution, with the signature of President of Congress Thomas Mifflin.''Harper's Encyclopaedia of United States History from 458 A. D. to 1909'', ed. by Benson John Lossing and, Woodrow Wilson (Harper & Brothers, 1910) p167 * January 15 – Henry Cavendish's paper to the Royal Society of London, ''Experiments on Air'', reveals the composition of water. * February 24 – The Captivity of Mangalorean Catholics at Seringapatam begins. * February 28 – John Wesley ordains ministers for the Methodist Church in the United States. * March 1 – The Confederation Congress accepts Virginia's cession of all rights to the Northwest Territory and to Kentucky. * March 22 – The Emerald Buddha is insta ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
1711 Births
In the Swedish calendar it was a common year starting on Tuesday, one day ahead of the Julian and ten days behind the Gregorian calendar. Events January–March * January – Cary's Rebellion: The Lords Proprietor appoint Edward Hyde to replace Thomas Cary, as the governor of the North Carolina portion of the Province of Carolina. Hyde's policies are deemed hostile to Quaker interests, leading former governor Cary and his Quaker allies to take up arms against the province. * January 24 – The first performance of Francesco Gasparini's most famous opera ''Tamerlano'' takes place at the Teatro San Cassiano in Venice. * February – French settlers at ''Fort Louis de la Mobile'' celebrate Mardi Gras in Mobile (Alabama), by parading a large papier-mache ox head on a cart (the first Mardi Gras parade in America). * February 3 – A total lunar eclipse occurs, at 12:31 UT. * February 24 ** Thomas Cary, after declaring himself Governor of North Car ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
French Canadians In The American Revolution
French (french: français(e), link=no) may refer to: * Something of, from, or related to France ** French language, which originated in France, and its various dialects and accents ** French people, a nation and ethnic group identified with France ** French cuisine, cooking traditions and practices Fortnite French places Arts and media * The French (band), a British rock band * "French" (episode), a live-action episode of ''The Super Mario Bros. Super Show!'' * ''Française'' (film), 2008 * French Stewart (born 1964), American actor Other uses * French (surname), a surname (including a list of people with the name) * French (tunic), a particular type of military jacket or tunic used in the Russian Empire and Soviet Union * French's, an American brand of mustard condiment * French catheter scale, a unit of measurement of diameter * French Defence, a chess opening * French kiss, a type of kiss involving the tongue See also * France (other) * Franch, a surname * French ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Jane McCrea
Jane McCrea (1752 – July 27, 1777) was an American woman who was killed by a Native American warrior serving alongside a British Army expedition under the command of John Burgoyne during the American Revolutionary War. Engaged to a Loyalist officer serving under Burgoyne, her death lead to widespread outrage in the Thirteen Colonies and was used by Patriots as part of their anti-British propaganda campaign. Born in Bedminster, New Jersey, McCrea moved to Saratoga, New York where she became engaged to David Jones, a Loyalist. When the Revolutionary War broke out, Jones fled to Quebec while McCrea's brothers divided their loyalties between the British and the Patriots. During the Saratoga campaign of 1777, McCrea left her brother's home to join Jones who was stationed in Fort Ticonderoga. While staying at Fort Edward, McCrea was abducted, killed and scalped by a group of Native American warriors. Upon receiving word of the incident, Burgoyne attempted to punish the culprit ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
John Burgoyne
General John Burgoyne (24 February 1722 – 4 August 1792) was a British general, dramatist and politician who sat in the House of Commons from 1761 to 1792. He first saw action during the Seven Years' War when he participated in several battles, most notably during the Portugal Campaign of 1762. Burgoyne is best known for his role in the American Revolutionary War. He designed an invasion scheme and was appointed to command a force moving south from Canada to split away New England and end the rebellion. Burgoyne advanced from Canada but his slow movement allowed the Americans to concentrate their forces. Instead of coming to his aid according to the overall plan, the British Army in New York City moved south to capture Philadelphia. Burgoyne fought two small battles near Saratoga but was surrounded by American forces and, with no relief in sight, surrendered his entire army of 6,200 men on 17 October 1777. His surrender, says historian Edmund Morgan, "was a great turning ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Charlottetown, Prince Edward Island
Charlottetown is the capital and largest city of the Canadian province of Prince Edward Island, and the county seat of Queens County. Named after Queen Charlotte, Charlottetown was an unincorporated town until it was incorporated as a city in 1855. It was the site of the famous Charlottetown Conference in 1864, the first gathering of Canadian and Maritime statesmen to discuss the proposed Maritime Union. This conference led, instead, to the union of British North American colonies in 1867, which was the beginning of the Canadian confederation. PEI, however, did not join Confederation until 1873. From this, the city adopted as its motto ''Cunabula Foederis'', "Birthplace of Confederation". The population of Charlottetown is estimated to be 40,500 (2022); this forms the centre of a census agglomeration of 83,063 (2021), which is roughly half of the province's population (160,302). History Early history (1720–1900) The first European settlers in the area were French; person ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Auguste (ship)
Several ships have been named ''Auguste'': * was a full-rigged sailing ship that sank at Aspy Bay, Cape Breton, Nova Scotia in 1761 while carrying exiles from the fall of New France. *''Auguste'', of 10 guns and 50 men, was a French letter of marque that captured on 17 June 1800 as ''Auguste'' was sailing from Bordeaux to . She had been commissioned in February 1800. * was an 18-gun privateer commissioned at Bordeaux that captured on 6 April 1811. *''Auguste'', of Saint-Malo, was a privateer of two guns and 24 men that captured on 28 February 1809. She was a privateer barge of 47 tons ("of load"), commissioned in March 1808. Her first cruise, with two guns and 20 men under Feillet, was from March 1808 to no later than April 1808. She made another cruise in February 1809 under Huon, with 24 men and 2 guns, that ended in her capture by HMS ''Helena''.Demerliac (2004), N°2064, p. 268. * was a 14-gun privateer commissioned in Saint-Malo. She captured numerous British merchant vess ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fort William Henry
Fort William Henry was a British fort at the southern end of Lake George, in the province of New York. The fort's construction was ordered by Sir William Johnson in September 1755, during the French and Indian War, as a staging ground for attacks against the French position at Fort St. Frédéric. It was part of a chain of British and French forts along the important inland waterway from New York City to Montreal, and occupied a key forward location on the frontier between New York and New France. In 1757, the French general Louis-Joseph de Montcalm conducted a successful siege that forced the British to surrender. The Huron warriors who accompanied the French army subsequently killed many of the British prisoners. The siege and massacre were famously portrayed in James Fenimore Cooper's novel ''The Last of the Mohicans''. The fort was named for both Prince William, Duke of Cumberland, the younger son of King George II, and Prince William Henry, Duke of Glouceste ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |


_1938.jpg)




.jpg)

