|
Lubart's Castle
Lutsk Castle (;, ), also locally known as Liubart's Castle (, ''Замок Любарта'', ''Zamok Liubarta'') or Upper Castle (, ''Верхній замок'', ''Verkhnii zamok''), began its life in the mid-14th century as the fortified seat of Gediminas' son Liubartas (Lubart), the last ruler of united Galicia-Volhynia. It is the most prominent landmark of Lutsk, Ukraine and as such appears on the 200 hryvnia bill. (Another city castle, called ''Lower Castle'', built by the Czartoryski family since the 14th century, is now a ruin). History The Kievan Rus' town of Luchesk had a wooden wall as early as 1075, when Boleslaus the Bold laid siege to it for six months. Yury Dolgoruky failed to take Lutsk after a six-weeks siege in 1149. In 1255, the walls of Lutsk were stormed by Khan Jochi's grandson Kuremsa. The current castle, towering over the Styr River, was built mostly in the 1340s, although some parts of the earlier walls were used. It repelled sieges by numerous poten ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lutsk
Lutsk (, ; see #Names and etymology, below for other names) is a city on the Styr River in northwestern Ukraine. It is the administrative center of Volyn Oblast and the administrative center of Lutsk Raion within the oblast. Lutsk has a population of A city with almost a thousand years of history, recorded in 1085, Lutsk historically served as an administrative, cultural and religious center in Volhynia. The city contains several landmarks in various styles, including Renaissance architecture, Renaissance, Baroque architecture, Baroque and Neoclassical architecture, Neoclassical, the most known being the medieval Lubart's Castle. Names and etymology Lutsk is an ancient Slavic peoples, Slavic town, mentioned in the Hypatian Chronicle as Luchesk in the records of 1085. The etymology of the name is unclear. There are three hypotheses: the name may have been derived from the Old Slavic word ''luka'' (an arc or bend in a river), or the name may have originated from ''Luka'' (the chi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
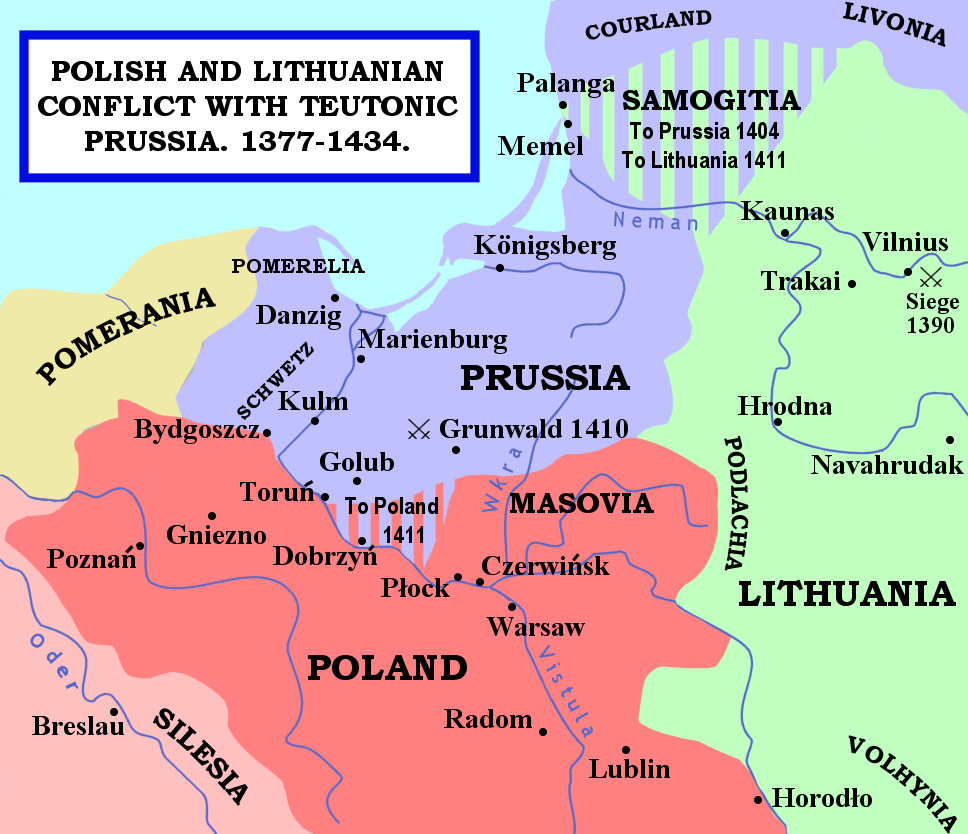
Władysław II Jagiełło
Jogaila (; 1 June 1434), later Władysław II Jagiełło (),Other names include (; ) (see also Names and titles of Władysław II Jagiełło) was Grand Duke of Lithuania beginning in 1377 and starting in 1386, becoming King of Poland as well. As Grand Duke, he ruled Lithuania from 1377 to 1381 and from 1382 to 1401, at which time he became the Supreme Duke of Lithuania in exchange for naming his cousin Vytautas as the new Grand Duke. Władysław II initially served as King of Poland alongside his wife Jadwiga of Poland, Jadwiga until her death in 1399, and then the sole ruler until his own death in 1434. Raised a Lithuanian polytheist, he converted to Catholicism in 1386 and baptized as Ladislaus () in Kraków, married the young Queen Jadwiga, and was crowned King of Poland as Władysław II Jagiełło. In 1387, he Christianization of Lithuania, converted Lithuania to Catholicism. His reign in Poland started in 1399, upon the death of Queen Jadwiga, lasted a further thirty-fiv ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Grand Duke Of Lithuania
This is a list of Lithuanian monarchs who ruled Lithuania from its inception until the fall of the Grand Duchy of Lithuania in 1795. The Lithuanian monarch bore the title of Grand duke, Grand Duke, with the exception of Mindaugas, who was crowned king in 1253. Other Lithuanian rulers, such as Vytautas the Great, also attempted to secure a royal coronation, but these efforts were unsuccessful.Nadveckė, Ineta (6 July 2019Trys Lietuvos karaliai: vienas tikras, vienas nelabai ir vienas beveik''Lithuanian National Radio and Television, LRT''. Until 1569, the Lithuanian monarchy was hereditary. In 1386, Grand Duke Jogaila was elected King of Poland. From that point onward, with some interruptions, the two states were united in a personal union, sharing a common ruler until 1569, when they were formally merged by the Union of Lublin to form the Polish–Lithuanian Commonwealth. The monarch of this new state was elected in a free election by the entire nobility. From the Christianizat ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Grand Duchy Of Lithuania
The Grand Duchy of Lithuania was a sovereign state in northeastern Europe that existed from the 13th century, succeeding the Kingdom of Lithuania, to the late 18th century, when the territory was suppressed during the 1795 Partitions of Poland, partitions of Poland–Lithuania. The state was founded by Lithuanians (tribe), Lithuanians, who were at the time a Lithuanian mythology, polytheistic nation of several united Baltic tribes from Aukštaitija. By 1440 the grand duchy had become the largest European state, controlling an area from the Baltic Sea in the north to the Black Sea in the south. The grand duchy expanded to include large portions of the former Kievan Rus' and other neighbouring states, including what is now Belarus, Lithuania, most of Ukraine as well as parts of Latvia, Moldova, Poland and Russia. At its greatest extent, in the 15th century, it was the largest state in Europe. It was a multinational state, multi-ethnic and multiconfessionalism, multiconfessional sta ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Švitrigaila
Švitrigaila (before 1370 – 10 February 1452; sometimes spelled Svidrigiello) was the Grand Duke of Lithuania from 1430 to 1432. He spent most of his life in largely unsuccessful dynastic struggles against his cousins Vytautas and Sigismund Kęstutaitis. Early life and Vitebsk rebellion Švitrigaila was born to Algirdas, Grand Duke of Lithuania, and his second wife Uliana of Tver. His date of birth is unknown, but it is believed that he was the youngest or second youngest son of Algirdas. He first appeared in politics in October 1382 when he witnessed the Treaty of Dubysa between his elder brother Jogaila and the Teutonic Knights. Historians believe that would indicate that at the time Švitrigaila was no younger than 12 which would put his date of birth sometime before 1370. In a complaint submitted to the Council of Florence, Švitrigaila claimed that he and Jogaila were favorite sons of Algirdas. Before his death in 1377, Algirdas transferred his throne to Jogaila but made h ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Moat
A moat is a deep, broad ditch dug around a castle, fortification, building, or town, historically to provide it with a preliminary line of defence. Moats can be dry or filled with water. In some places, moats evolved into more extensive water defences, including natural or artificial lakes, dams and sluices. In older fortifications, such as hillforts, they are usually referred to simply as ditches, although the function is similar. In later periods, moats or water defences may be largely ornamental. They could also act as a sewer. Historical use Ancient Some of the earliest evidence of moats has been uncovered around ancient Egyptian fortresses. One example is at Buhen, a settlement excavated in Nubia. Other evidence of ancient moats is found in the ruins of Babylon, and in reliefs from ancient Egypt, Assyria, and other cultures in the region. Evidence of early moats around settlements has been discovered in many archaeological sites throughout Southeast Asia, including ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bridge
A bridge is a structure built to Span (engineering), span a physical obstacle (such as a body of water, valley, road, or railway) without blocking the path underneath. It is constructed for the purpose of providing passage over the obstacle, which is usually something that is otherwise difficult or impossible to cross. There are many different designs of bridges, each serving a particular purpose and applicable to different situations. Designs of bridges vary depending on factors such as the function of the bridge, the nature of the terrain where the bridge is constructed and anchored, the material used to make it, and the funds available to build it. The earliest bridges were likely made with fallen trees and stepping stones. The Neolithic people built boardwalk bridges across marshland. The Arkadiko Bridge, dating from the 13th century BC, in the Peloponnese is one of the oldest arch bridges in existence and use. Etymology The ''Oxford English Dictionary'' traces the origin of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Artillery
Artillery consists of ranged weapons that launch Ammunition, munitions far beyond the range and power of infantry firearms. Early artillery development focused on the ability to breach defensive walls and fortifications during sieges, and led to heavy, fairly immobile siege engines. As technology improved, lighter, more mobile field artillery cannons were developed for battlefield use. This development continues today; modern self-propelled artillery vehicles are highly mobile weapons of great versatility generally providing the largest share of an army's total firepower. Originally, the word "artillery" referred to any group of soldiers primarily armed with some form of manufactured weapon or armour. Since the introduction of gunpowder and cannon, "artillery" has largely meant cannon, and in contemporary usage, usually refers to Shell (projectile), shell-firing Field gun, guns, howitzers, and Mortar (weapon), mortars (collectively called ''barrel artillery'', ''cannon artil ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dan II Of Wallachia
Dan II cel Viteaz According to a statue in Târgoviște. ''Cel Viteaz'' = ″courageous″ (? – 1 June 1432) was a voivode of the principality of Wallachia, ruling an extraordinary five times, and succeeded four times by Radu II Chelul, his rival for the throne. Of those five periods on the throne of Wallachia (1420–1421, 1421–1423, 1423–1424, 1426–1427, and 1427–1431), four were within a period of only seven years. Early life Dan was the son of Dan I of Wallachia. His father was the eldest son and successor of Radu I of Wallachia. After Dan I was murdered in 1386, his brother, Mircea, ascended the throne. Dan was loyal to his uncle during Mircea's reign. Mircea was the first ruler of Wallachia to be forced to pay an annual tribute to the Ottoman Empire. He made his only legitimate son, Michael I, his co-ruler.Dan appears first in the records leading a contingent sent by his uncle Mircea I to assist Musa Celebi in taking Adrianople during the Ottoman civil war i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
List Of Princes Of Wallachia
This is a list of princes of Wallachia, from the first mention of a medieval polity situated between the Southern Carpathians and the Danube until the union with Moldavia in 1859, which unification of Moldavia and Wallachia, led to the creation of Romania. Notes Dynastic rule is hard to ascribe, given the loose traditional definition of the ruling family. On principle, princes were chosen from any family branch, including a previous ruler's bastard sons, being defined as ''os de domn'', "of Voivode marrow", or as having ''heregie'', "heredity" (from the Latin ''hereditas''); the institutions charged with the Elective monarchy, election, dominated by the boyars, had fluctuating degrees of influence. The system itself was challenged by usurpers, and became obsolete with the Phanariotes, Phanariote epoch, when rulers were appointed by the Ottoman Empire, Ottoman Sultans; between 1821 and 1878 (the date of Romania's independence), various systems combining election and appointment were ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Vasily II Of Moscow
Vasily II Vasilyevich (; 10 March 141527 March 1462), nicknamed the Blind or the Dark (), was Grand Prince of Moscow from 1425 until his death in 1462. He succeeded his father, Vasily I, only to be challenged by his uncle Yuri of Zvenigorod. During this time, Moscow changed hands several times. At one point, Vasily was captured and blinded by his cousin Dmitry Shemyaka in 1446. The final victory went to Vasily, who was supported by most people. Due to his disability, he made his son Ivan III his co-ruler in his later years. Reign First ten years of struggle Vasily II was the youngest son of Vasily I of Moscow by Sophia of Lithuania, the only daughter of Vytautas the Great, and the only son to survive his father (his elder brother Ivan died in 1417 at the age of 22). On his father's death Vasily II was proclaimed Grand Duke at the age of 10. His mother acted as a regent. His uncle, Yuri of Zvenigorod (the prince of Galich-Mersky), and his two sons, Va ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Grand Prince Of Moscow
The Grand Prince of Moscow (), known as the Prince of Moscow until 1389, was the ruler of the Grand Principality of Moscow. The Moscow principality was initially established in the 13th century as an appanage within the Vladimir-Suzdal grand principality. By the late 14th century, the grand principality became a family possession of the princes of Moscow; the monarch bore the title of ''grand prince of Vladimir and Moscow'' and later the title of ''grand prince of Vladimir, Moscow and all Russia''. History The grand principality of Vladimir-Suzdal fell apart into feuding appanages over the course of the 13th century. The princes of Moscow were descendants of Daniel of Moscow, Daniel. As Daniel never became grand prince of Vladimir before he died in 1303, this meant that according to traditional succession practices, his descendants were ''izgoi'': his son and successor Yury of Moscow had no legitimate claim to the throne of Vladimir. This is why Tokhta Khan granted Mikhail of Tver ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |