|
Low-salt Diet
A low sodium diet is a diet that includes no more than 1,500 to 2,400 mg of sodium per day. The human minimum requirement for sodium in the diet is about 500 mg per day, which is typically less than one-sixth as much as many diets "seasoned to taste". For certain people with salt-sensitive blood pressure or diseases such as Ménière's disease, this extra intake may cause a negative effect on health. Health effects A low sodium diet has a useful effect to reduce blood pressure, both in people with hypertension and in people with normal blood pressure. Taken together, a low salt diet (median of approximately 4.4 g/day – approx 1800 mg sodium) in hypertensive people resulted in a decrease in systolic blood pressure by 4.2 mmHg, and in diastolic blood pressure by 2.1 mmHg. Advising people to eat a low salt diet, however, is of unclear effect in either hypertensive or normal tensive people. In 2012, the British Journal ''Heart'' published an article claiming that a l ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sodium
Sodium is a chemical element with the symbol Na (from Latin ''natrium'') and atomic number 11. It is a soft, silvery-white, highly reactive metal. Sodium is an alkali metal, being in group 1 of the periodic table. Its only stable isotope is 23Na. The free metal does not occur in nature, and must be prepared from compounds. Sodium is the sixth most abundant element in the Earth's crust and exists in numerous minerals such as feldspars, sodalite, and halite (NaCl). Many salts of sodium are highly water-soluble: sodium ions have been leached by the action of water from the Earth's minerals over eons, and thus sodium and chlorine are the most common dissolved elements by weight in the oceans. Sodium was first isolated by Humphry Davy in 1807 by the electrolysis of sodium hydroxide. Among many other useful sodium compounds, sodium hydroxide (lye) is used in soap manufacture, and sodium chloride (edible salt) is a de-icing agent and a nutrient for animals including h ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
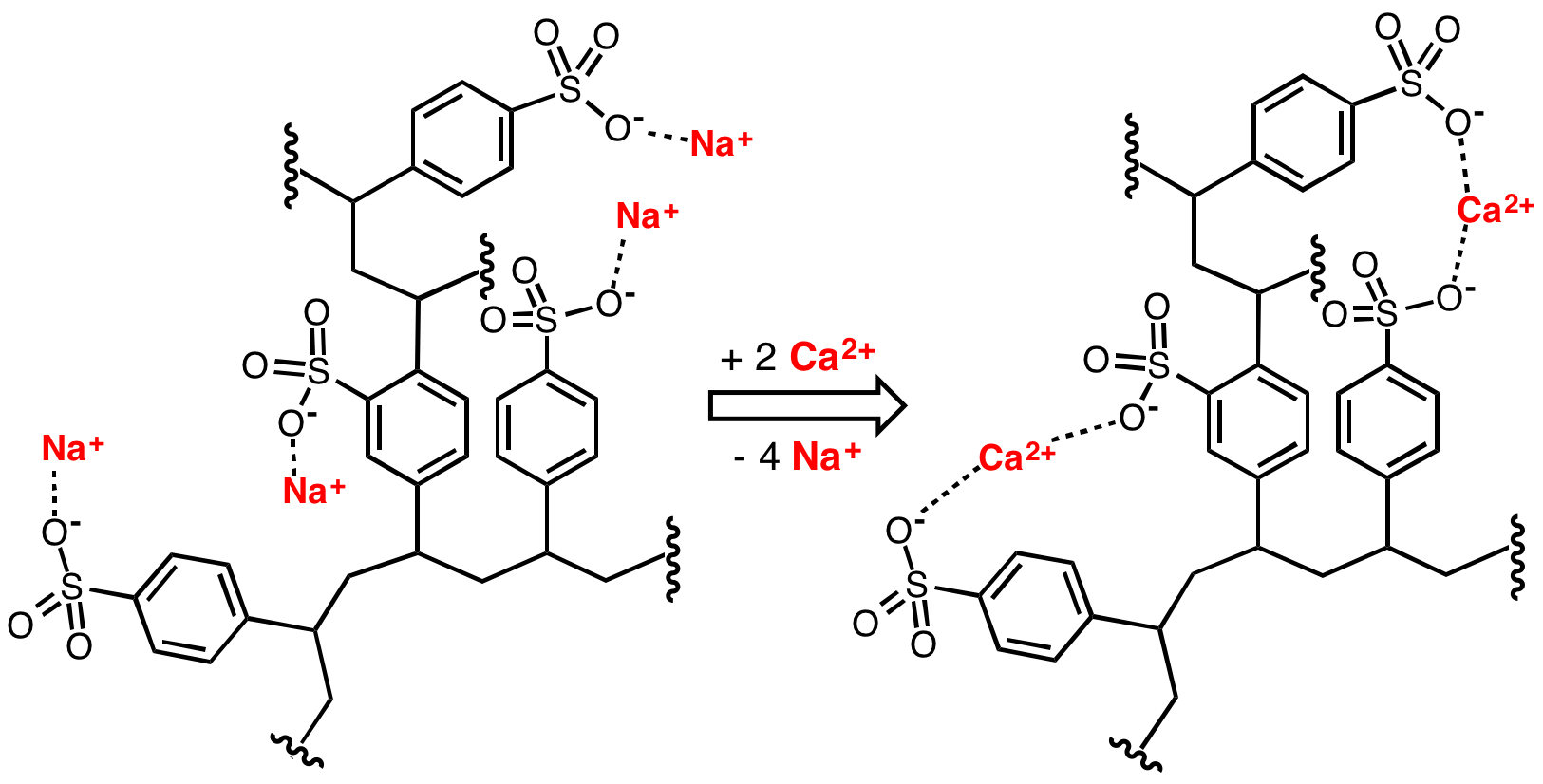
Water Softener
Water softening is the removal of calcium, magnesium, and certain other metal cations in hard water. The resulting soft water requires less soap for the same cleaning effort, as soap is not wasted bonding with calcium ions. Soft water also extends the lifetime of plumbing by reducing or eliminating scale build-up in pipes and fittings. Water softening is usually achieved using lime softening or ion-exchange resins but is increasingly being accomplished using nanofiltration or reverse osmosis membranes. Rationale The presence of certain metal ions like calcium and magnesium, principally as bicarbonates, chlorides, and sulfates, in water causes a variety of problems. Hard water leads to the buildup of limescale, which can foul plumbing, and promote galvanic corrosion. In industrial scale water softening plants, the effluent flow from the re-generation process can precipitate scale that can interfere with sewage systems. The slippery feeling associated with washing in soft water ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cured Meat
Curing is any of various food preservation and flavoring processes of foods such as meat, fish and vegetables, by the addition of salt, with the aim of drawing moisture out of the food by the process of osmosis. Because curing increases the solute concentration in the food and hence decreases its water potential, the food becomes inhospitable for the microbe growth that causes food spoilage. Curing can be traced back to antiquity, and was the primary method of preserving meat and fish until the late 19th century. Dehydration was the earliest form of food curing. Many curing processes also involve smoking, spicing, cooking, or the addition of combinations of sugar, nitrate, and nitrite."Historical Origins of Food Preservation." [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Frozen Dinner
A frozen meal (also called TV dinner (Canada and US), prepackaged meal, ready-made meal, ready meal (UK), frozen dinner, and microwave meal) is a packaged frozen meal that comes portioned for an individual. A frozen meal in the United States and Canada usually consists of a type of meat for the main course, and sometimes vegetables, potatoes, and/or a dessert. The main dish can also be pasta or fish. In European frozen meals, Indian and Chinese meals are common. Another form of convenience food, which is merely a refrigerated ready meal that requires less heating but expires sooner, is popular in the UK. The term ''TV dinner'', which has become common, was first used as part of a brand of packaged meals developed in 1953 by the company C.A. Swanson & Sons (the full name was ''TV Brand Frozen Dinner''). The original ''TV Dinner'' came in an aluminum tray and was heated in an oven. In the US and Canada, the term is synonymous with any packaged meal or dish ("dinner") purchas ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Potato Chip
A potato chip (North American English; often just chip) or crisp (British and Irish English) is a thin slice of potato that has been either deep fried, baked, or air fried until crunchy. They are commonly served as a snack, side dish, or appetizer. The basic chips are cooked and salted; additional varieties are manufactured using various flavorings and ingredients including herbs, spices, cheeses, other natural flavors, artificial flavors, and additives. Potato chips form a large part of the snack food and convenience food market in Western countries. The global potato chip market generated total revenue of US$16.49 billion in 2005. This accounted for 35.5% of the total savory snacks market in that year ($46.1 billion). History The earliest known recipe for something similar to today's potato chips is in William Kitchiner's book '' The Cook's Oracle'' published in 1817, which was a bestseller in the United Kingdom and the United States. The 1822 edition's recipe for "Pota ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fast Food
Fast food is a type of mass-produced food designed for commercial resale, with a strong priority placed on speed of service. It is a commercial term, limited to food sold in a restaurant or store with frozen, preheated or precooked ingredients and served in packaging for take-out/take-away. Fast food was created as a commercial strategy to accommodate large numbers of busy commuters, travelers and wage workers. In 2018, the fast food industry was worth an estimated $570 billion globally. The fastest form of "fast food" consists of pre-cooked meals which reduce waiting periods to mere seconds. Other fast food outlets, primarily hamburger outlets such as McDonald's, use mass-produced, pre-prepared ingredients (bagged buns and condiments, frozen beef patties, vegetables which are prewashed, pre-sliced, or both; etc.) and cook the meat and french fries fresh, before assembling "to order". Fast food restaurants are traditionally distinguished by the drive-through. Outlets may ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
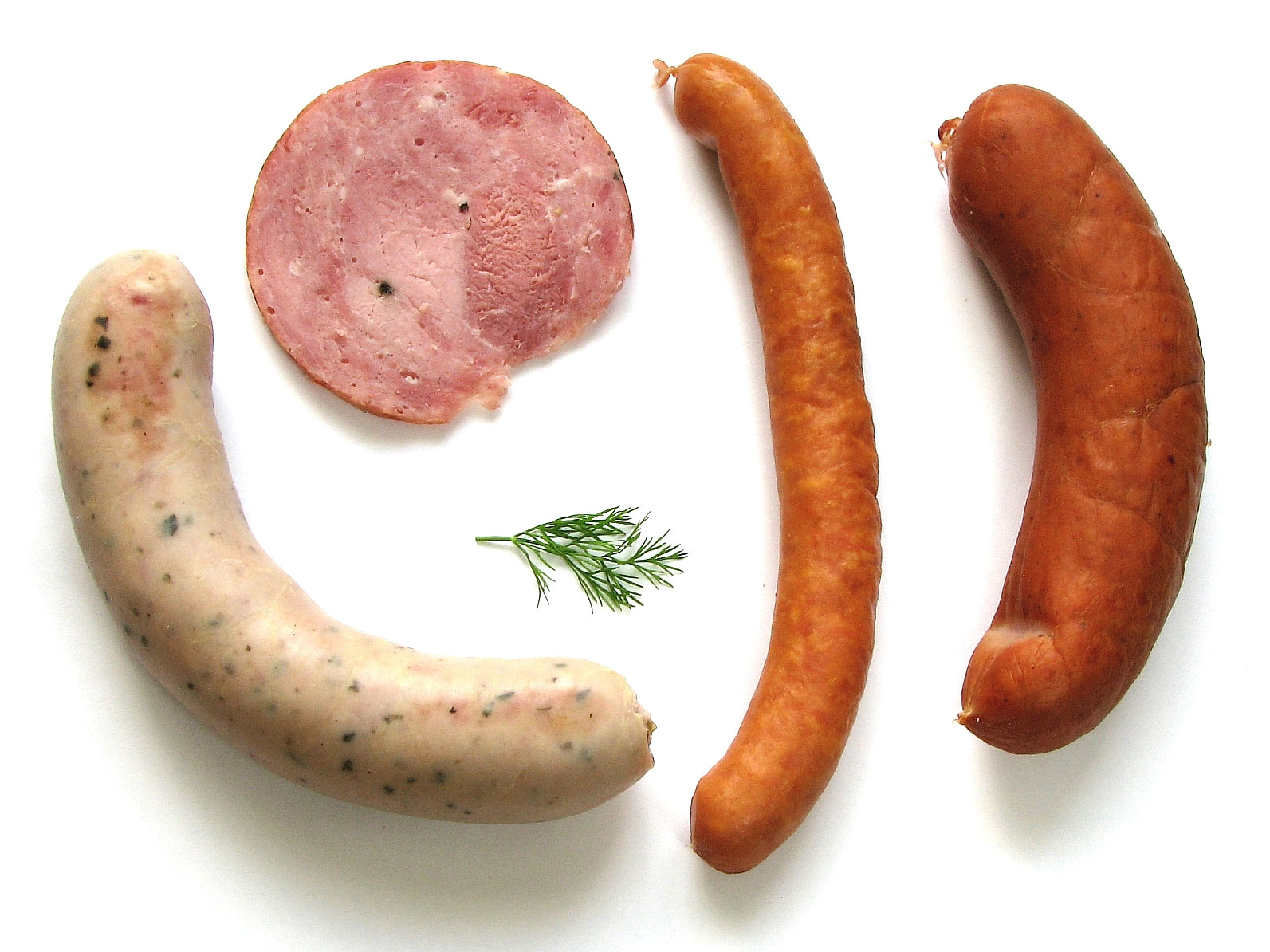
Sausage
A sausage is a type of meat product usually made from ground meat—often pork, beef, or poultry—along with salt, spices and other flavourings. Other ingredients, such as grains or breadcrumbs may be included as fillers or extenders. When used as an adjective, the word ''sausage'' can refer to the loose sausage meat, which can be formed into patties or stuffed into a skin. When referred to as "a sausage", the product is usually cylindrical and encased in a skin. Typically, a sausage is formed in a casing traditionally made from intestine, but sometimes from synthetic materials. Sausages that are sold raw are cooked in many ways, including pan-frying, broiling and barbecuing. Some sausages are cooked during processing, and the casing may then be removed. Sausage-making is a traditional food preservation technique. Sausages may be preserved by curing, drying (often in association with fermentation or culturing, which can contribute to preservation), smoking, or ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
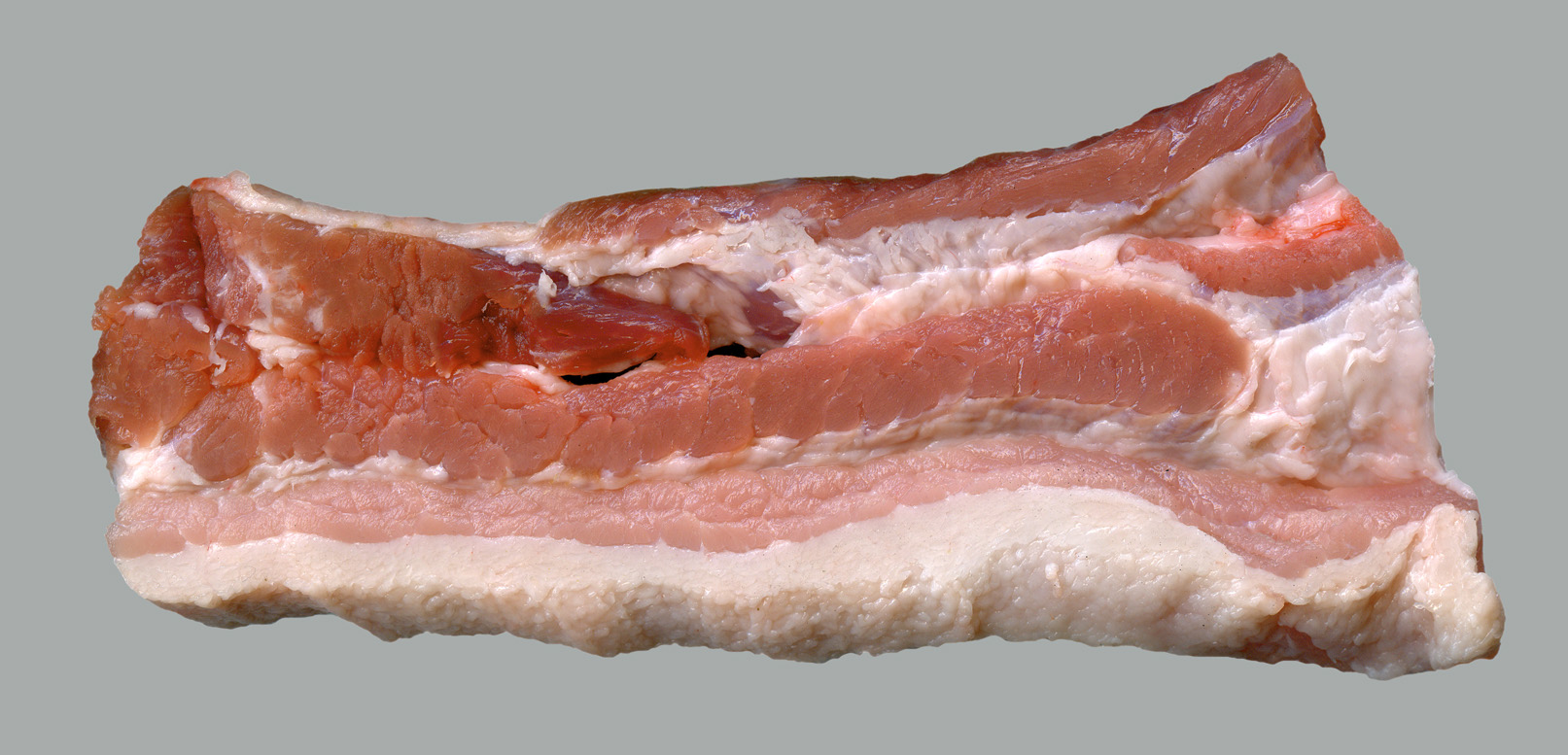
Bacon
Bacon is a type of salt-cured pork made from various cuts, typically the belly or less fatty parts of the back. It is eaten as a side dish (particularly in breakfasts), used as a central ingredient (e.g., the bacon, lettuce, and tomato sandwich (BLT)), or as a flavouring or accent (as in bacon bits in a salad). Bacon is also used for barding and larding roasts, especially game, including venison and pheasant, and may also be used to insulate or flavour roast joints by being layered onto the meat. The word is derived from the Proto-Germanic ''*bakkon'', meaning "back meat". Meat from other animals, such as beef, lamb, chicken, goat, or turkey, may also be cut, cured, or otherwise prepared to resemble bacon, and may even be referred to as, for example, "turkey bacon". Such use is common in areas with significant Jewish and Muslim populations as both religions prohibit the consumption of pork. Vegetarian bacons such as "soy bacon" also exist. Curing and smoking Before t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Processed Meat
Processed meat is considered to be any meat which has been modified in order to either improve its taste or to extend its shelf life. Methods of meat processing include salting, curing, fermentation, smoking, and/or the addition of chemical preservatives. Processed meat is usually composed of pork or beef, but also poultry, while it can also contain offal or meat by-products such as blood. Processed meat products include bacon, ham, sausages, salami, corned beef, jerky, hot dogs, lunch meat, canned meat, chicken nuggets, and meat-based sauces. Meat processing includes all the processes that change fresh meat with the exception of simple mechanical processes such as cutting, grinding or mixing.Introductio/ref> Meat processing began as soon as people realized that cooking and salting prolongs the life of fresh meat. It is not known when this took place; however, the process of salting and Drying (food), sun-drying was recorded in Ancient Egypt, while using ice and snow is credi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bouillon Cube
A bouillon cube (Canada and US), stock cube ( Australia, Ireland, New Zealand, South Africa and UK), or broth cube (Asia) is dehydrated broth or stock formed into a small cube about wide. It is typically made from dehydrated vegetables or meat stock, a small portion of fat, MSG, salt, and seasonings, shaped into a small cube. Vegetarian and vegan types are also made. Bouillon is also available in granular, powdered, liquid, and paste forms. History Dehydrated meat stock, in the form of tablets, was known in the 17th century to English food writer Anne Blencowe, who died in 1718,Joan Thirsk, ‘Blencowe , Anne, Lady Blencowe (1656–1718)’, Oxford Dictionary of National Biography, Oxford University Press, Oct 2005; online edn, Jan 200accessed 17 Nov 2016/ref> and elsewhere as early as 1735. Various French cooks in the early 19th century (Lefesse, Massué, and Martin) tried to patent bouillon cubes and tablets, but were turned down for lack of originality.Jennifer Davis, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
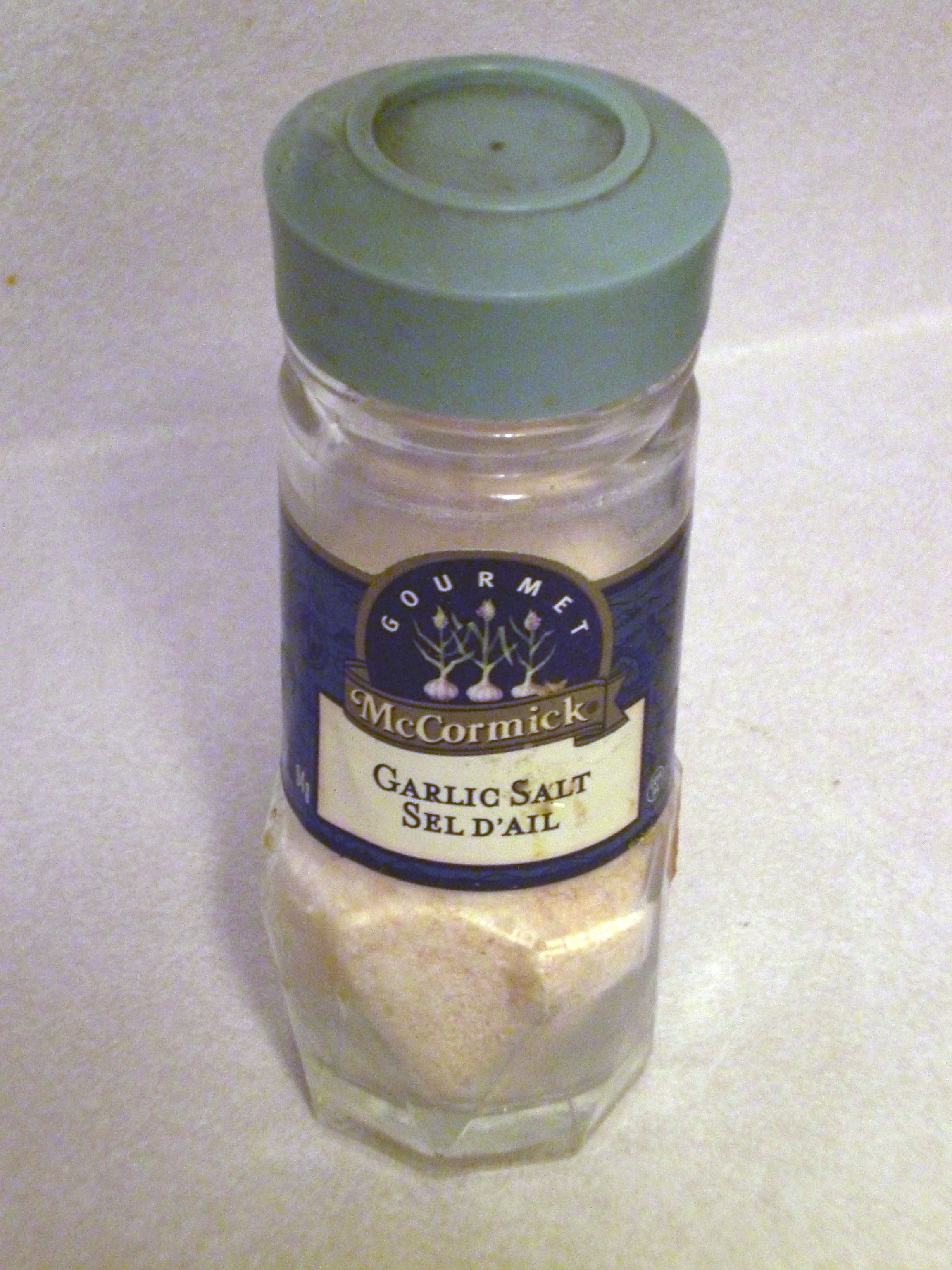
Garlic Salt
Garlic salt is a seasoned salt made of a mixture of dried, ground garlic and table salt with an anti-caking agent (e.g. calcium silicate). In its most basic form it is made by combining 3 parts salt and 1 part dried garlic powder Garlic powder is a spice that is derived from Dehydrated food, dehydrated garlic and used in cooking for flavour enhancement. The process of making garlic powder includes drying and dehydrating the vegetable, then powdering it through machinery o ... by volume, or 6 parts salt and 1 part garlic powder by weight. References Herb and spice mixtures Edible salt {{spice-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
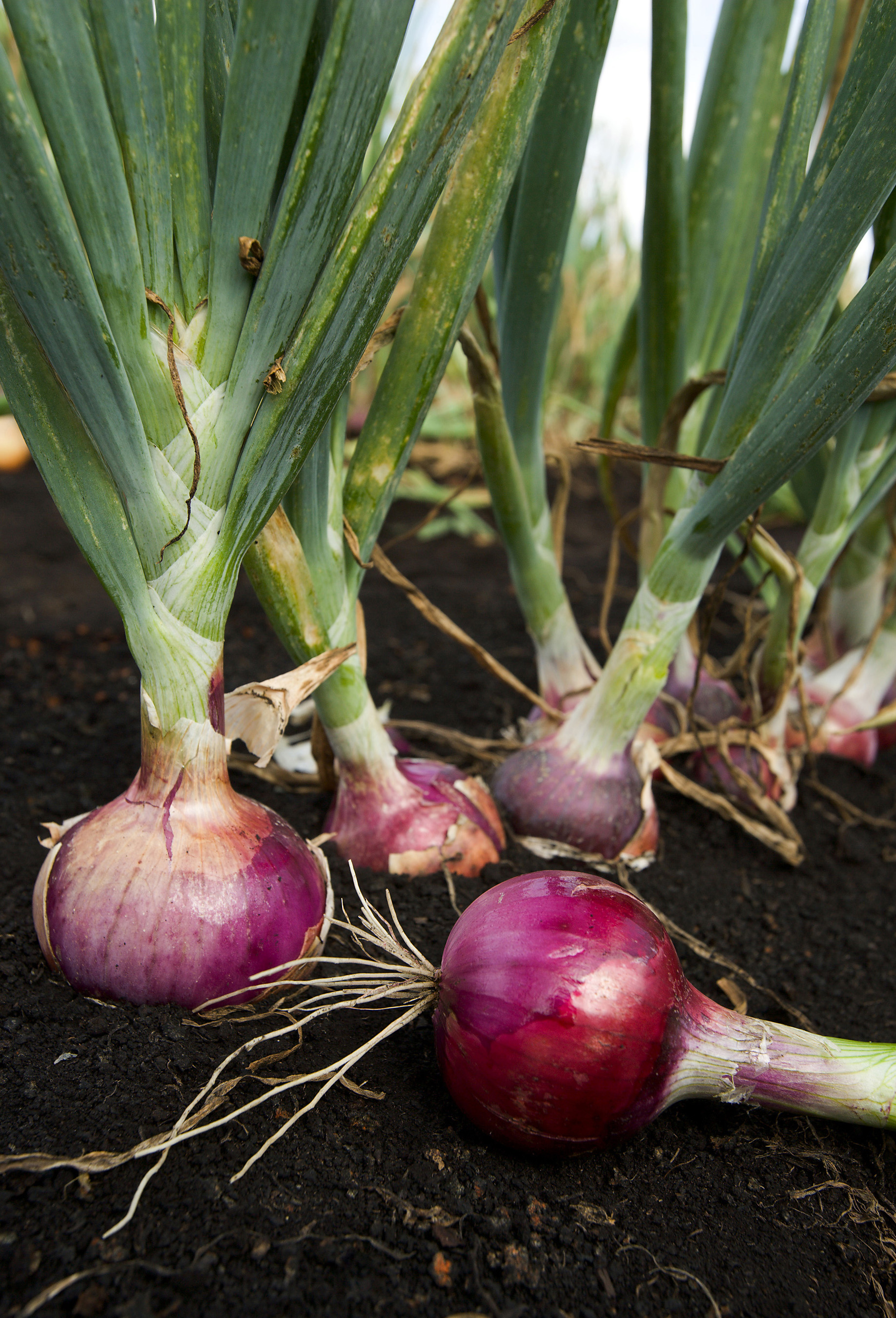
Onion Salt
An onion (''Allium cepa'' L., from Latin ''cepa'' meaning "onion"), also known as the bulb onion or common onion, is a vegetable that is the most widely cultivated species of the genus ''Allium''. The shallot is a variety (botany), botanical variety of the onion which was classified as a separate species until 2010. Its close relatives include garlic, scallion, leek, and chive. This genus also contains several other species variously referred to as onions and cultivated for food, such as the Allium fistulosum, Japanese bunching onion (''Allium fistulosum''), the tree onion, tree onion (''A.'' × ''proliferum''), and the Allium canadense, Canada onion (''Allium canadense''). The name ''wild onion (other), wild onion'' is applied to a number of ''Allium'' species, but ''A. cepa'' is exclusively known from cultivation. Its ancestral wild original form is not known, although escapes from cultivation have become established in some regions. The onion is most frequently a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |