|
Louis Augustin De Monteclerc
Louis Augustin de Monteclerc (La Rongère, Maine, 1727 – 25 March 1784) was a French Navy officer. He served in the War of American Independence. Biography Monteclerc joined the Navy as a Garde-Marine in 1743. Monteclerc was promoted to Lieutenant in 1757. He served on ''Éveillé'', in Conflans' squadron, during the Seven Years' War. Monteclerc was promoted to Captain in 1772. In 1777, he commanded the 64-gun ''Bizarre''. Navy Minister Sartine had chosen her to be one of the six ships held ready for immediate departure at all times. In 1779, he commanded a division comprising the 64-gun ''Solitaire'' and the frigates ''Inconstante'' and ''Surveillante'', and led an expedition to hunt down privateers. The division returned to Brest on 4 May 1779 with 400 prisoners. Later that year, ''Solitaire'' was attached to a squadron under Orvilliers. In late 1799, Monteclerc was appointed vice-Director of naval constructions in Brest, and he was promoted to Director on 1 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
War Of American Independence
The American Revolutionary War (April 19, 1775 – September 3, 1783), also known as the Revolutionary War or American War of Independence, was a major war of the American Revolution. Widely considered as the war that secured the independence of the United States, fighting began on April 19, 1775, followed by the Lee Resolution on July 2, 1776, and the United States Declaration of Independence, Declaration of Independence on July 4, 1776. The American Patriot (American Revolution), Patriots were supported by the Kingdom of France and, to a lesser extent, the Dutch Republic and the Spanish Empire, in a conflict taking place in North America, the Caribbean, and the Atlantic Ocean. Established by royal charter in the 17th and 18th centuries, the American colonies were largely autonomous in domestic affairs and commercially prosperous, trading with Britain and its British West Indies, Caribbean colonies, as well as other European powers via their Caribbean entrepôts. After British vic ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
French Ship Triton (1747)
''Triton'' was a 64-gun ship of the line of the French Navy designed by François Coulomb the Younger. She took part in the Seven Years' War and in the War of American Independence. Career On 30 July 1757, ''Triton'' rescued the crew of the 30-gun frigate French frigate Rose (1754), ''Rose'', and her captain, Hippolyte de Sade de Vaudronne, Sade de Vaudronne, had her beached and scuttled by fire to prevent her falling into British hands after a battle with the 32-gun HMS Thames (1758), HMS ''Thames''. In June 1758, under Captain du Lac de Montvert, ''Triton'' captured the frigate HMS Deal Castle (1756), HMS ''Deal Castle''.''Triton'' took part in the Battle of Lagos on 18–19 August 1759. In 1777, she was under François-Louis de Brach, Brach. Navy Minister Antoine de Sartine, Sartine chose her to be one of the six ships held ready for immediate departure at all times. In 1778, ''Triton'' was part of the squadron under Louis Guillouet, comte d'Orvilliers, Orvilliers, being ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Louis-Philippe De Rigaud, Marquis De Vaudreuil
Louis-Philippe de Rigaud, Marquis de Vaudreuil (18 April 1724 – 14 December 1802) was second in command of the French squadron off America during the American Revolutionary War. Biography Early life Louis-Philippe Rigaud de Vaudreuil was born into a family with a rich political and military tradition. His grandfather, Philippe de Rigaud de Vaudreuil, and his uncle Pierre de Rigaud de Vaudreuil de Cavagnal, were both governors of Canada; the latter was its last governor, surrendering Montreal to the British in 1760. Another uncle, Pierre-François de Rigaud, fought with Montcalm at the Battle of Oswego. His father, also named Louis-Philippe de Rigaud de Vaudreuil, was an admiral of the French Navy: he saved Desherbiers de l'Etenduère at the Second battle of Cape Finisterre while commanding the 74-gun ''Intrépide'' and was in charge of the Navy in North America in 1747. His younger brother, Louis de Rigaud de Vaudreuil, was also a Navy officer. They served together ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Battle Of The Saintes
The Battle of the Saintes (known to the French as the Bataille de la Dominique), also known as the Battle of Dominica, was an important naval battle in the Caribbean between the British and the French that took place 9–12 April 1782. The British victory was considered their greatest over the French during the American Revolutionary War. The British fleet under Admiral Sir George Rodney defeated a French fleet under the Comte de Grasse, forcing the French and Spanish to abandon a planned invasion of Jamaica. The battle is named after the Îles des Saintes, a group of small islands between Guadeloupe and Dominica in the West Indies. The French had blockaded the British Army at Chesapeake Bay the year before, during the Siege of Yorktown, and supported the eventual American victory in their revolution. This battle, however, halted their momentum and had a significant effect on peace negotiations to end the war. The French suffered heavy casualties at the Saintes and many were t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
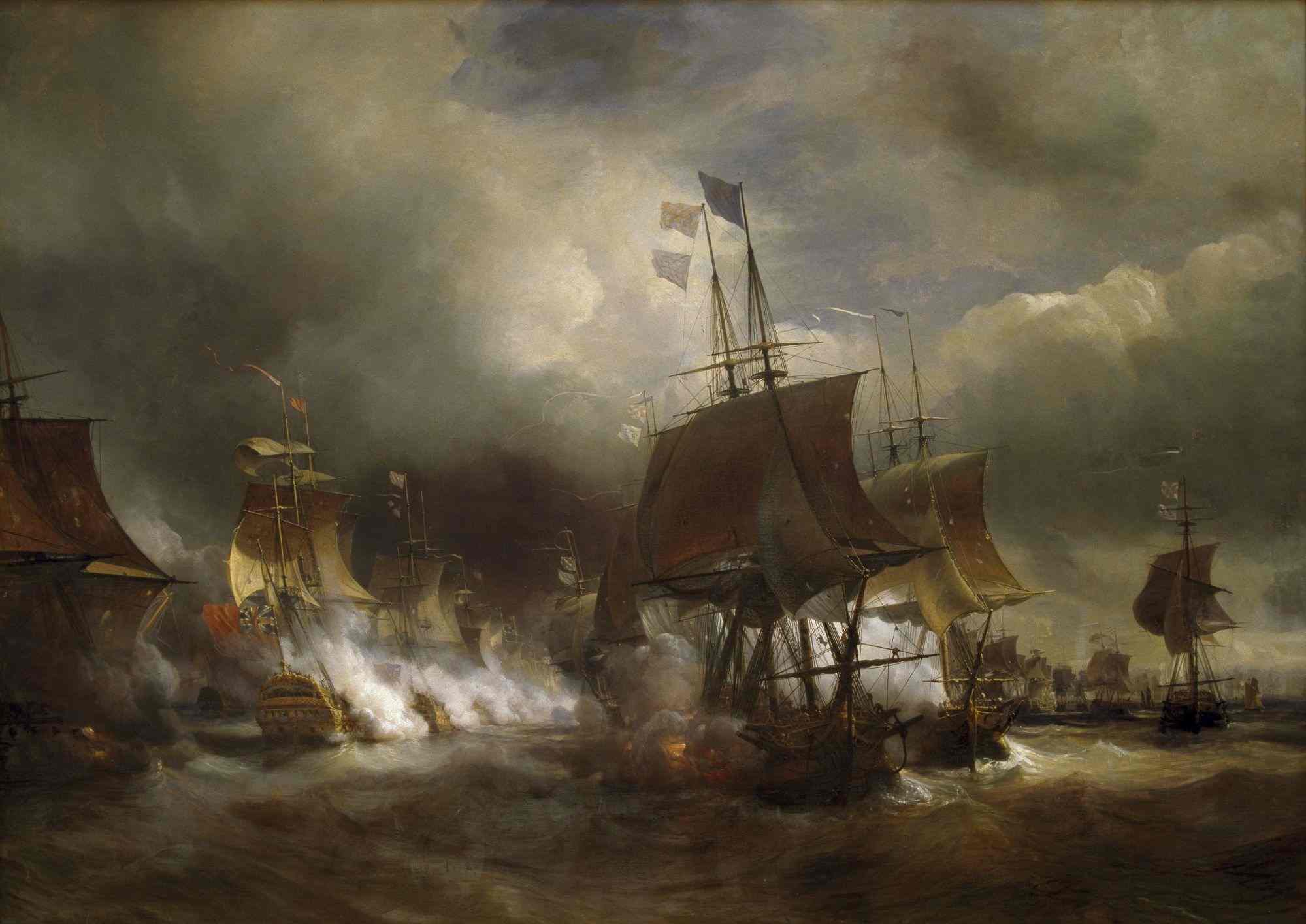
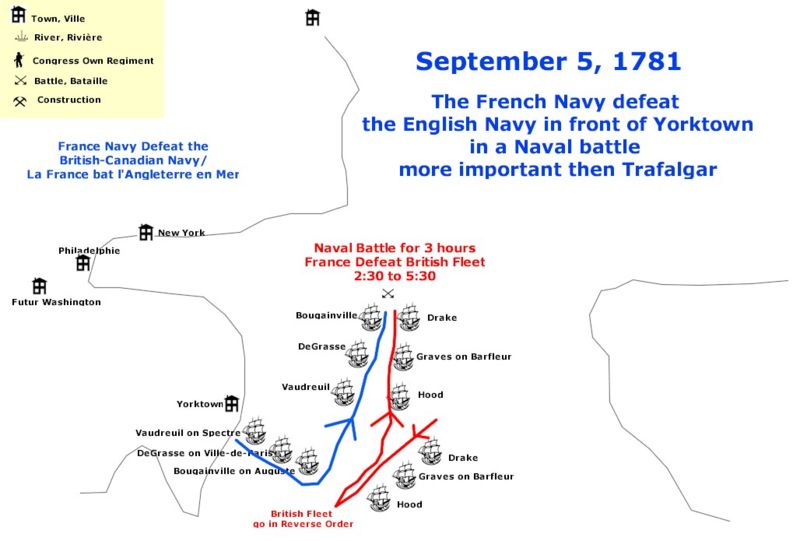
Battle Of The Chesapeake
The Battle of the Chesapeake, also known as the Battle of the Virginia Capes or simply the Battle of the Capes, was a crucial naval battle in the American Revolutionary War that took place near the mouth of the Chesapeake Bay on 5 September 1781. The combatants were a British fleet led by Rear Admiral Sir Thomas Graves and a French fleet led by Rear Admiral François Joseph Paul, the Comte de Grasse. The battle was strategically decisive, in that it prevented the Royal Navy from reinforcing or evacuating the besieged forces of Lieutenant General Lord Cornwallis at Yorktown, Virginia. The French were able to achieve control of the sea lanes against the British and provided the Franco-American army with siege artillery and French reinforcements. These proved decisive in the Siege of Yorktown, effectively securing independence for the Thirteen Colonies. Admiral de Grasse had the option to attack British forces in either New York or Virginia; he opted for Virginia, arriving at t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
François Joseph Paul De Grasse
François Joseph Paul, Comte de Grasse, Marquis of Grasse-Tilly SMOM (13 September 1722 – 11 January 1788) was a career French officer who achieved the rank of admiral. He is best known for his command of the French fleet at the Battle of the Chesapeake in 1781 in the last year of the American Revolutionary War. It led directly to the British surrender at Yorktown and helped gain the rebels' victory. After this action, de Grasse returned with his fleet to the Caribbean. In 1782 British Admiral Rodney decisively defeated and captured Grasse at the Battle of the Saintes. Grasse was widely criticised for his loss in that battle. On his return to France in 1784, he blamed his captains for the defeat. A court martial exonerated all of his captains, effectively ending his naval career. Early life François-Joseph de Grasse was born and raised at Bar-sur-Loup in south-eastern France, the last child of Francois de Grasse Rouville, Marquis de Grasse. He earned his title and supporte ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
French Ship Diadème (1756)
''Diadème'' was the lead ship of the 74-gun ship of the line of the French Navy. Career On 17 March 1757, along with the 64-gun , she captured , commanded by Captain Robert Roddam, off Saint-Domingue. In 1761, she was under Breugnon. In 1780, under Picot de Dampierre, she was part of La Motte-Piquet's division, along with , and . She took part in the naval operations in the American Revolutionary War under de Grasse, notably fighting at the Battle of the Chesapeake under Louis Augustin de Monteclerc. At the Battle of the Saintes on 12 April 1782 it was the gap between ''Diadème'' and the mastless which allowed to break the French line. She was severely damaged by ''Formidable'' and withdrew from the battle. on 25 April she was one of the ships ordered to rally at Cap Francois on San Domingo with de Vaudreuil's fleet. On 29 September 1792, she was renamed ''Brutus''. She was razéed down to a 42-gun frigate in May 1794, and cruised off Groix under Captain Baud ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
French Ship Hector (1755)
''Hector'' was a 74-gun ship of the line of the French Navy, lead ship of her class. ''Hector'' was launched in 1755 and fought in the American Revolutionary War during which she captured two ships of the British Royal Navy on 14 August 1778. In 1782, the ship was captured by the Royal Navy at the Battle of the Saintes in 1782. Taken into service by the Royal Navy, the vessel was renamed HMS ''Hector''. On 5 September 1782. HMS ''Hector'' fought two French frigates. Severely damaged during the battle, and by a hurricane that followed later in September, ''Hector'' sank on 4 October 1782. Career French service ''Hector'' was launched on 23 July 1755, and commissioned under Captain Vilarzel d'Hélie. In 1757, the vessel departed Toulon on 18 March, arriving in Louisbourg on 15 June. Returning to Brest on 23 November with 5,000 sick aboard, she spread typhus to the town; [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Louis Guillouet, Comte D'Orvilliers
Louis Guillouet, comte d'Orvilliers (26 March 1710 – 1792) was a French admiral. Life Louis Guillouet d'Orvilliers was born on 26 March 1710 in Moulins, Allier. His parents were Claude Guillouet d'Orvilliers (), seigneur d'Orvilliers, and Claude de Vict de Pongibaud (–1759). His older brother was Gilbert Guillouet d'Orvilliers, ( – 11 May 1764), governor of French Guiana from 1749 to 1763, D'Orvilliers spent most of his childhood in Cayenne, capital of the French colony French Guiana, where his father was governor. In 1723, aged fifteen, he joined the colony's infantry regiment and quickly rose to the rank of Lieutenant. In 1728, he transferred to the Navy and, by 1756, had become a captain, commanding one of the ships sent to Menorca under the direction of La Galissonière. He later took part in action near Santo Domingo and the Antilles and was rewarded with a promotion to rear admiral in 1764. Franco-American alliance In 1777, France began assisting the American coloni ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
French Frigate Surveillante (1778)
''Surveillante'' was an 32-gun frigate of the French Navy. She took part in the Naval operations in the American Revolutionary War, where she became famous for her battle with ; in 1783, she brought the news that the war was over to America. She later took part in the French Revolutionary Wars, and was eventually scuttled during the Expédition d'Irlande after sustaining severe damage in a storm. The wreck was found in 1979 and is now a memorial. Career Early career ''Surveillante'' was laid down in August 1777 in Lorient as the second frigate of the ''Iphigénie'' class, a series of 32-gun frigates carrying 12-pounder guns designed by Léon Guignace. She was launched on 26 March 1778, and commissioned in May. The very same month, she was refitted as to upgrade her hull with copper sheathing, which was being gradually introduced in the French Navy. In June 1778, ''Surveillante'' was part of a squadron of five French frigates that were seeking to retaliate against the British ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
French Frigate Inconstante (1766)
French (french: français(e), link=no) may refer to: * Something of, from, or related to France ** French language, which originated in France, and its various dialects and accents ** French people, a nation and ethnic group identified with France ** French cuisine, cooking traditions and practices Fortnite French places Arts and media * The French (band), a British rock band * "French" (episode), a live-action episode of ''The Super Mario Bros. Super Show!'' * ''Française'' (film), 2008 * French Stewart (born 1964), American actor Other uses * French (surname), a surname (including a list of people with the name) * French (tunic), a particular type of military jacket or tunic used in the Russian Empire and Soviet Union * French's, an American brand of mustard condiment * French catheter scale, a unit of measurement of diameter * French Defence, a chess opening * French kiss, a type of kiss involving the tongue See also * France (other) * Franch, a surname * Frenc ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
French Ship Solitaire (1774)
''Solitaire'' was a 64-gun ship of the line of the French Navy, built by Antoine Groignard and launched in 1774, lead ship of her class. She was captured by the Royal Navy on 6 December 1782, and commissioned as the third rate HMS ''Solitaire''. She was sold out of the Navy in 1790. Career In 1776, ''Solitaire'' was under Chef d'Escadre Chartres as flagship of one of the three division of the Escadre d'évolution that year. In June, she collided with ''Terpsichore'' and both ships had to repair in Cadiz. In 1778, ''Solitaire'' was part of the Third Division of the Blue squadron in the fleet of Orvilliers, and took part in the Battle of Ushant on 27 July 1778 under Captain Briqueville. In 1779, she was part of a division under Louis Augustin de Monteclerc, also comprising the frigates ''Inconstante'' and ''Surveillante'', and led an expedition to hunt down privateers. The division returned to Brest on 4 May 1779 with 400 prisoners. Later that year, ''Solitaire'' was a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |